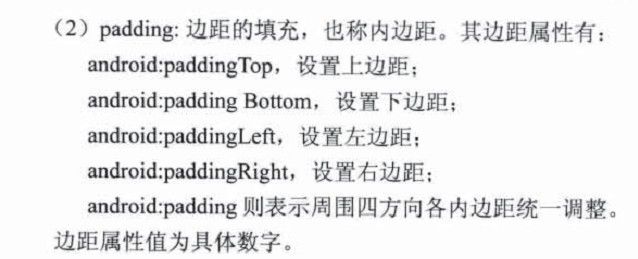
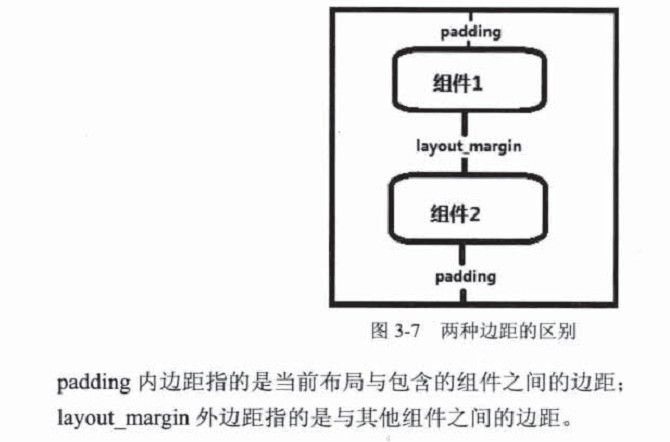
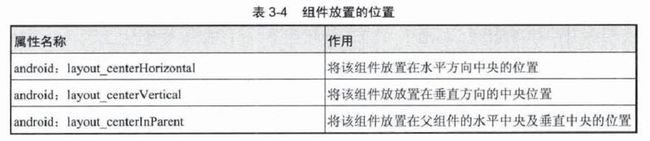
【读书笔记-《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】3.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(Button、Layout、ImageButton)
3.1 Button
Button这控件不用多说,就是一个按钮,主要是点击后进行相应事件的响应。
给组件添加ID属性:定义格式为 android:id="@+id/name",这里的name是自定义的,不是索引变量。“@+”表示新声明,"@"表示引用,例如:
"@+id/tv" 表示新声明一个id,是id名为tv的组件;
"@id/tv" 表示引用id名为tv的组件。
给按钮添加点击事件响应
想知道按钮是否被用户点击,就需要一个“点击监听器”来对其进行监听,然后通过监听器来获取点击的事件,就可以判断关注的按钮是否被用户所点击。
使用监听器有两种方式:
1.当前类使用点击监听器接口,修改后源码如下:
//使用点击监听器 public class ButtonProject extends Activity implements OnClickListener { private Button btn_submit,btn_cancel; private TextView tv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.button_project_layout); btn_submit = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_submit); btn_cancel = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_cancel); tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv); btn_submit.setOnClickListener(this); btn_cancel.setOnClickListener(this); } //使用点击监听器必须重写其抽象函数, //@Override 表示重写函数 @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(v == btn_submit) { tv.setText("确定按钮触发事件!"); }else if(v==btn_cancel) { tv.setText("取消按钮触发事件!"); } } }
先用当前类使用点击监听器接口(onClickListner),重写点击监听器的抽象函数(onClick);然后对需要监听的按钮进行按钮绑定监听器操作,这样监听器才能对绑定的按钮进行监听,以判断其是否被用户点击,一旦按钮被点击,就会自动响应onClick函数,并将点击的button(button也是 1个view)传入;最后就可以在onClick函数中书写点击会触发的事件(因为定义了多个按钮,所以在onClick函数中对系统传入的view进行按钮匹配的判断,让不同的按钮做不通的处理事件)。
2.使用内部类实现监听器进行监听,修改后源代码如下:
public class ButtonProject extends Activity { private Button btn_submit,btn_cancel; private TextView tv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.button_project_layout); btn_submit = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_submit); btn_cancel = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_cancel); tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv); //将btn_submit按钮绑定点击监听器 btn_submit.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub tv.setText("确定按钮触发事件!"); } }); btn_cancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub tv.setText("取消按钮触发事件!"); } }); } }
利用内部类的形式也需要重写监听器的抽象函数,然后在onClick里进行处理事件,这里不用判断view了,因为一个Button对应了一个监听器。
Button类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/Button.html
其中有说明,如果不用OnClickListener监听器的话,现在可以在XML布局按钮控件中使用android:onClick属性。然后在类中调用你设置的onClick方法。代码如下:
<Button android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:text="@string/self_destruct" android:onClick="selfDestruct" />
当用户单击按钮时,Android系统调用selfDestruct方法。该方法必须是公开并接受一个视图作为其唯一的参数。
public void selfDestruct(View view) { // 按钮响应事件 }
3.2 Layout
1.线性布局 LinearLayout
LinearLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/LinearLayout.html
2.相对布局 RelativeLayout
RelativeLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/RelativeLayout.html
3.表格布局 TableLayout
TableLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/TableLayout.html
4.绝对布局 AbsoluteLayout
AbsoluteLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/AbsoluteLayout.html
5.单帧布局 FrameLayout
FrameLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/FrameLayout.html
3.3 ImageButton
ImageButton类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/ImageButton.html
ImageButton与Button类似 ,区别在于ImageButton可以自定义一张图片作为一个按钮;也正因为使用图片代替了按钮,所以ImageButton按下与抬起的样式效果需要自定义。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <ImageButton android:id="@+id/btn_ImageButton" android:layout_marginLeft="100dp" android:layout_marginTop="100dp" android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="@drawable/dsfvsdf" /> </LinearLayout>
public class ImageButtonProject extends Activity { private ImageButton btn_ImageButton; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.imagebutton_layout); btn_ImageButton = (ImageButton)findViewById(R.id.btn_ImageButton); //为图片按钮添加触屏监听 btn_ImageButton.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() { @Override //第一个参数:表示触发触屏事件的事件源view //第二个参数:表示触屏事件的类型,如按下、抬起、移动等。 public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(event.getAction()==MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN)//按下事件 { //设置图片按钮背景 //getResources().getDrawable(int ID) 传入图片ID得到一个Drawable对象。 btn_ImageButton.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.dsfvsdf_bg)); }else if(event.getAction()==MotionEvent.ACTION_UP)//抬起事件 { btn_ImageButton.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.dsfvsdf)); } return false; } }); } }
显示不同的按钮状态官方文档中有提到可以在单独在xml文件中配置,然后布局文件中引用就可以了,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:state_pressed="true" android:drawable="@drawable/button_pressed" /> <!-- pressed 按下状态--> <item android:state_focused="true" android:drawable="@drawable/button_focused" /> <!-- focused 聚焦状态--> <item android:drawable="@drawable/button_normal" /> <!-- default 默认状态--> </selector>