Android常用控件之ExpandableList的使用
先来看下什么是ExpandableListView
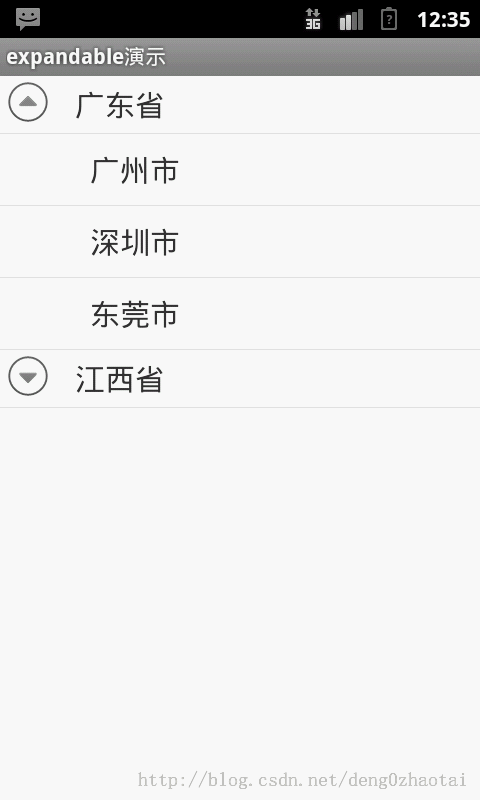
跟列表有点像,这种是可以折叠的列表,下面来看下是如何在代码中实现
一、在布局文件中声明一个ExpandableListView
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<ExpandableListView
android:id="@id/android:list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:drawSelectorOnTop="false" >
</ExpandableListView>
<TextView
android:id="@id/android:empty"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/no_data" />
</LinearLayout>
二、为每个Group和Child定义一个布局
group.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/groupTo"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:paddingLeft="50dp"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="@string/no_data"/>
</LinearLayout>
child.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/childTo"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:paddingLeft="60dp"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:paddingBottom="10dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="@string/no_data"/>
</LinearLayout>
以上两个文件只有缩进不一样,这样可以明显区分Group和Child
三、在代码中实现
package com.example.expandableList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.ExpandableListActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.ExpandableListView;
import android.widget.ExpandableListView.OnChildClickListener;
import android.widget.SimpleExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.example.widgetdemo.R;
public class expandableList extends ExpandableListActivity {
ExpandableListView expandableList = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.expandable);
expandableList = getExpandableListView();
// 写入当前组数
List<Map<String, String>> groups = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
Map<String, String> group1 = new HashMap<String, String>();
group1.put("group", "广东省");
Map<String, String> group2 = new HashMap<String, String>();
group2.put("group", "江西省");
groups.add(group1);
groups.add(group2);
// 写入第一组的数据
List<Map<String, String>> child1 = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
Map<String, String> childData1 = new HashMap<String, String>();
childData1.put("child", "广州市");
Map<String, String> childData2 = new HashMap<String, String>();
childData2.put("child", "深圳市");
Map<String, String> childData3 = new HashMap<String, String>();
childData3.put("child", "东莞市");
child1.add(childData1);
child1.add(childData2);
child1.add(childData3);
// 写入第二组的数据
List<Map<String, String>> child2 = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
Map<String, String> childData4 = new HashMap<String, String>();
childData4.put("child", "赣州市");
Map<String, String> childData5 = new HashMap<String, String>();
childData5.put("child", "南昌市");
Map<String, String> childData6 = new HashMap<String, String>();
childData6.put("child", "九江市");
Map<String, String> childData7 = new HashMap<String, String>();
childData7.put("child", "吉安市");
child2.add(childData4);
child2.add(childData5);
child2.add(childData6);
child2.add(childData7);
List<List<Map<String, String>>> childs = new ArrayList<List<Map<String, String>>>();
childs.add(child1);
childs.add(child2);
SimpleExpandableListAdapter sela = new SimpleExpandableListAdapter(
expandableList.this, groups, R.layout.group,
new String[] { "group" }, new int[] { R.id.groupTo }, childs,
R.layout.child, new String[] { "child" },
new int[] { R.id.childTo });
setListAdapter(sela);
expandableList.setOnChildClickListener(new expandableListListener());
}
//为ExpandableListView编写监听器
class expandableListListener implements OnChildClickListener {
@Override
public boolean onChildClick(ExpandableListView parent, View v,
int groupPosition, int childPosition, long id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("group = " + groupPosition + " child = "
+ childPosition + " id = " + id);
ExpandableListAdapter exAdapter = parent.getExpandableListAdapter();
// 获得选中项的HashMap对象
Map<String, String> childMap = (HashMap<String, String>) exAdapter
.getChild(groupPosition, childPosition);
String contentChild = childMap.get("child");
Map<String, String> groupMap = (HashMap<String, String>) exAdapter
.getGroup(groupPosition);
String contentGroup = groupMap.get("group");
Toast.makeText(
getApplicationContext(),
"你选择了第" + groupPosition + " 个Group, 第 " + childPosition
+ " 个Child的值是:" + contentChild + " Group的值是 " + contentGroup,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return false;
}
}
}
关于如何获取选中的值,我查看文档终于找到ExpandableListAdapter,在这个适配器有获取那个child和group的方法。
下面看下效果
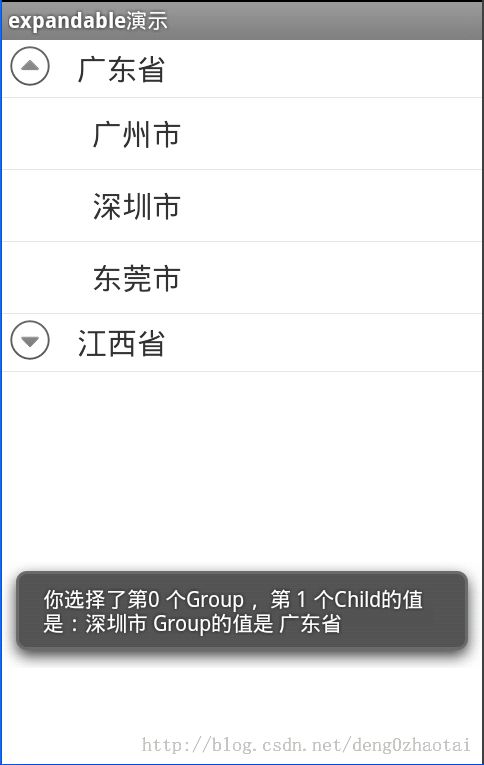
最后还是传上源码