Spark SQL Catalyst源代码分析之TreeNode Library
/** Spark SQL源代码分析系列文章*/
前几篇文章介绍了Spark SQL的Catalyst的核心执行流程、SqlParser,和Analyzer,本来打算直接写Optimizer的,可是发现忘记介绍TreeNode这个Catalyst的核心概念,介绍这个能够更好的理解Optimizer是怎样对Analyzed Logical Plan进行优化的生成Optimized Logical Plan,本文就将TreeNode基本架构进行解释。
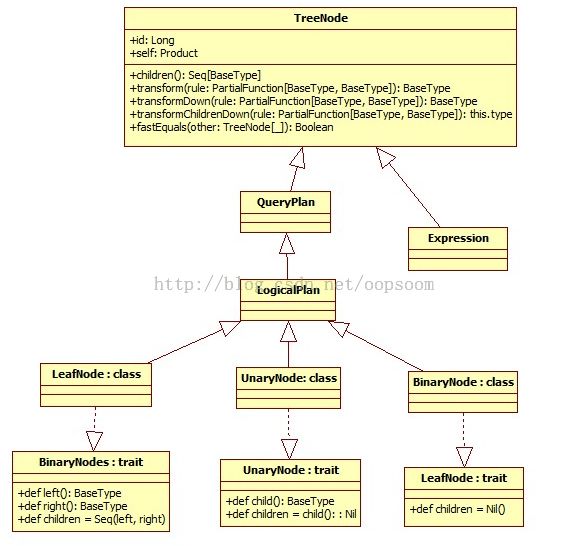
一、TreeNode类型
TreeNode Library是Catalyst的核心类库,语法树的构建都是由一个个TreeNode组成。TreeNode本身是一个BaseType <: TreeNode[BaseType] 的类型,而且实现了Product这个trait,这样能够存放异构的元素了。TreeNode有三种形态: BinaryNode、 UnaryNode、 Leaf Node.
在Catalyst里,这些Node都是继承自Logical Plan,能够说每个TreeNode节点就是一个Logical Plan(包括Expression)(直接继承自TreeNode)
主要继承关系类图例如以下:
1、BinaryNode
二元节点,即有左右孩子的二叉节点
[[TreeNode]] that has two children, [[left]] and [[right]].
trait BinaryNode[BaseType <: TreeNode[BaseType]] {
def left: BaseType
def right: BaseType
def children = Seq(left, right)
}
abstract class BinaryNode extends LogicalPlan with trees.BinaryNode[LogicalPlan] {
self: Product =>
} 节点定义比較简单,左孩子,右孩子都是BaseType。 children是一个Seq(left, right)
以下列出主要继承二元节点的类,能够当查询手冊用 :)
2、UnaryNode
一元节点,即仅仅有一个孩子节点
A [[TreeNode]] with a single [[child]].
trait UnaryNode[BaseType <: TreeNode[BaseType]] {
def child: BaseType
def children = child :: Nil
}
abstract class UnaryNode extends LogicalPlan with trees.UnaryNode[LogicalPlan] {
self: Product =>
}以下列出主要继承一元节点的类,能够当查询手冊用 :)
经常使用的二元节点有,Project,Subquery,Filter,Limit ...等

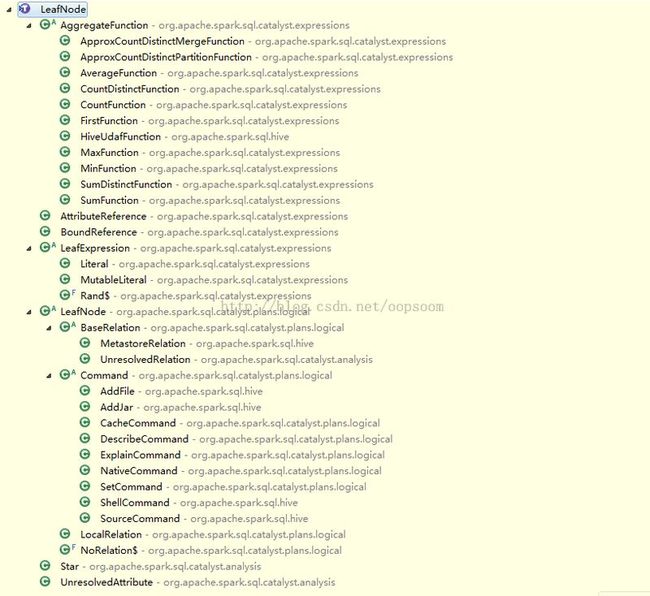
3、Leaf Node
叶子节点,没有孩子节点的节点。
A [[TreeNode]] with no children.
trait LeafNode[BaseType <: TreeNode[BaseType]] {
def children = Nil
}
abstract class LeafNode extends LogicalPlan with trees.LeafNode[LogicalPlan] {
self: Product =>
// Leaf nodes by definition cannot reference any input attributes.
override def references = Set.empty
}以下列出主要继承叶子节点的类,能够当查询手冊用 :)
提示经常使用的叶子节点: Command类系列,一些Funtion函数,以及Unresolved Relation...etc.
二、TreeNode 核心方法
简介一个TreeNode这个类的属性和方法
currentId
一颗树里的TreeNode有个唯一的id,类型是java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong原子类型。
private val currentId = new java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong protected def nextId() = currentId.getAndIncrement()sameInstance
推断2个实例是否是同一个的时候,仅仅须要推断TreeNode的id。
def sameInstance(other: TreeNode[_]): Boolean = {
this.id == other.id
}
fastEquals,更经常使用的一个快捷的判定方法,没有重写Object.Equals,这样防止scala编译器生成case class equals 方法
def fastEquals(other: TreeNode[_]): Boolean = {
sameInstance(other) || this == other
} map,flatMap,collect都是递归的对子节点进行应用PartialFunction,其他方法还有非常多,篇幅有限这里不一一描写叙述了。
2.1、核心方法 transform 方法
transform该方法接受一个PartialFunction,就是就是前一篇文章Analyzer里提到的Batch里面的Rule。是会将Rule迭代应用到该节点的全部子节点,最后返回这个节点的副本(一个和当前节点不同的节点,后面会介绍,事实上就是利用反射来返回一个改动后的节点)。
假设rule没有对一个节点进行PartialFunction的操作,就返回这个节点本身。
来看一个样例:
object GlobalAggregates extends Rule[LogicalPlan] {
def apply(plan: LogicalPlan): LogicalPlan = plan transform { //apply方法这里调用了logical plan(TreeNode) 的transform方法来应用一个PartialFunction。
case Project(projectList, child) if containsAggregates(projectList) =>
Aggregate(Nil, projectList, child)
}
def containsAggregates(exprs: Seq[Expression]): Boolean = {
exprs.foreach(_.foreach {
case agg: AggregateExpression => return true
case _ =>
})
false
}
} 这种方法真正的调用是transformChildrenDown,这里提到了用先序遍历来对子节点进行递归的Rule应用。
假设在对当前节点应用rule成功,改动后的节点afterRule,来对其children节点进行rule的应用。
transformDown方法:
/**
* Returns a copy of this node where `rule` has been recursively applied to it and all of its
* children (pre-order). When `rule` does not apply to a given node it is left unchanged.
* @param rule the function used to transform this nodes children
*/
def transformDown(rule: PartialFunction[BaseType, BaseType]): BaseType = {
val afterRule = rule.applyOrElse(this, identity[BaseType])
// Check if unchanged and then possibly return old copy to avoid gc churn.
if (this fastEquals afterRule) {
transformChildrenDown(rule) //改动前节点this.transformChildrenDown(rule)
} else {
afterRule.transformChildrenDown(rule) //改动后节点进行transformChildrenDown
}
} 最重要的方法transformChildrenDown:
对children节点进行递归的调用PartialFunction,利用终于返回的newArgs来生成一个新的节点,这里调用了makeCopy()来生成节点。
transformChildrenDown方法:
/**
* Returns a copy of this node where `rule` has been recursively applied to all the children of
* this node. When `rule` does not apply to a given node it is left unchanged.
* @param rule the function used to transform this nodes children
*/
def transformChildrenDown(rule: PartialFunction[BaseType, BaseType]): this.type = {
var changed = false
val newArgs = productIterator.map {
case arg: TreeNode[_] if children contains arg =>
val newChild = arg.asInstanceOf[BaseType].transformDown(rule) //递归子节点应用rule
if (!(newChild fastEquals arg)) {
changed = true
newChild
} else {
arg
}
case Some(arg: TreeNode[_]) if children contains arg =>
val newChild = arg.asInstanceOf[BaseType].transformDown(rule)
if (!(newChild fastEquals arg)) {
changed = true
Some(newChild)
} else {
Some(arg)
}
case m: Map[_,_] => m
case args: Traversable[_] => args.map {
case arg: TreeNode[_] if children contains arg =>
val newChild = arg.asInstanceOf[BaseType].transformDown(rule)
if (!(newChild fastEquals arg)) {
changed = true
newChild
} else {
arg
}
case other => other
}
case nonChild: AnyRef => nonChild
case null => null
}.toArray
if (changed) makeCopy(newArgs) else this //依据作用结果返回的newArgs数组,反射生成新的节点副本。
}
makeCopy方法,反射生成节点副本
/**
* Creates a copy of this type of tree node after a transformation.
* Must be overridden by child classes that have constructor arguments
* that are not present in the productIterator.
* @param newArgs the new product arguments.
*/
def makeCopy(newArgs: Array[AnyRef]): this.type = attachTree(this, "makeCopy") {
try {
val defaultCtor = getClass.getConstructors.head //反射获取默认构造函数的第一个
if (otherCopyArgs.isEmpty) {
defaultCtor.newInstance(newArgs: _*).asInstanceOf[this.type] //反射生成当前节点类型的节点
} else {
defaultCtor.newInstance((newArgs ++ otherCopyArgs).toArray: _*).asInstanceOf[this.type] //假设还有其他參数,++
}
} catch {
case e: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException =>
throw new TreeNodeException(
this, s"Failed to copy node. Is otherCopyArgs specified correctly for $nodeName? "
+ s"Exception message: ${e.getMessage}.")
}
}
三、TreeNode实例
如今准备从一段sql来出发,画一下这个spark sql的总体树的transformation。
SELECT * FROM (SELECT * FROM src) a join (select * from src)b on a.key=b.key
首先,我们先运行一下,在控制台里看一下生成的计划:
<span style="font-size:12px;">sbt/sbt hive/console
Using /usr/java/default as default JAVA_HOME.
Note, this will be overridden by -java-home if it is set.
[info] Loading project definition from /app/hadoop/shengli/spark/project/project
[info] Loading project definition from /app/hadoop/shengli/spark/project
[info] Set current project to root (in build file:/app/hadoop/shengli/spark/)
[info] Starting scala interpreter...
[info]
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.analysis._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.dsl._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.errors._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.plans.logical._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.rules._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.types._
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.util._
import org.apache.spark.sql.execution
import org.apache.spark.sql.hive._
import org.apache.spark.sql.hive.test.TestHive._
import org.apache.spark.sql.parquet.ParquetTestData
scala> val query = sql("SELECT * FROM (SELECT * FROM src) a join (select * from src)b on a.key=b.key")</span>
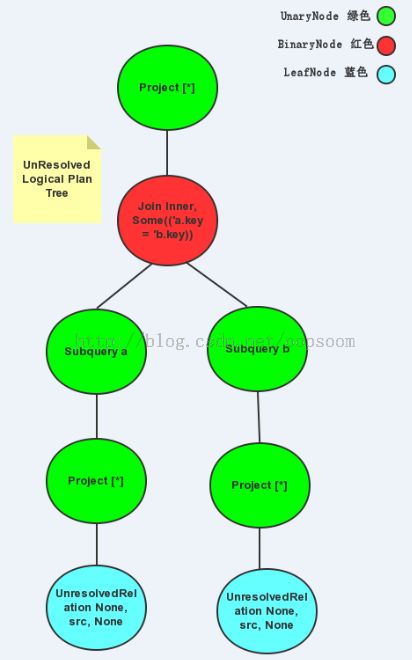
3.1、UnResolve Logical Plan
第一步生成UnResolve Logical Plan 例如以下:
scala> query.queryExecution.logical
res0: org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.plans.logical.LogicalPlan =
Project [*]
Join Inner, Some(('a.key = 'b.key))
Subquery a
Project [*]
UnresolvedRelation None, src, None
Subquery b
Project [*]
UnresolvedRelation None, src, None 假设画成树是这种,仅个人理解:
我将一開始介绍的三种Node分别用绿色UnaryNode,红色Binary Node 和 蓝色 LeafNode 来表示。
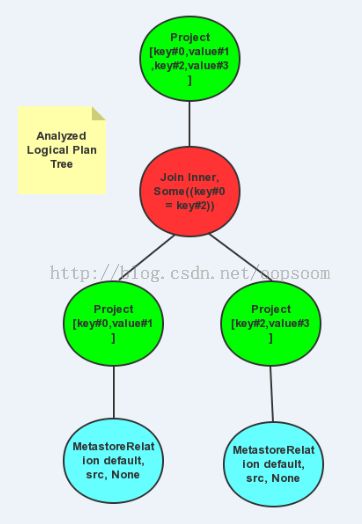
3.2、Analyzed Logical Plan
Analyzer会将允用Batch的Rules来对Unresolved Logical Plan Tree 进行rule应用,这里用来EliminateAnalysisOperators将Subquery给消除掉,Batch("Resolution将Atrribute和Relation给Resolve了,Analyzed Logical Plan Tree例如以下图:
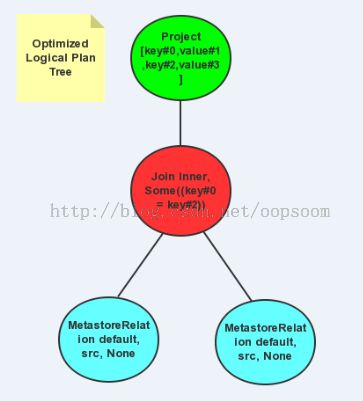
3.3、Optimized Plan
我把Catalyst里的Optimizer戏称为Spark SQL的优化大师,由于整个Spark SQL的优化都是在这里进行的,后面会有文章来解说Optimizer。
在这里,优化的不明显,由于SQL本身不复杂
scala> query.queryExecution.optimizedPlan res3: org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.plans.logical.LogicalPlan = Project [key#0,value#1,key#2,value#3] Join Inner, Some((key#0 = key#2)) MetastoreRelation default, src, None MetastoreRelation default, src, None
生成的树例如以下图:
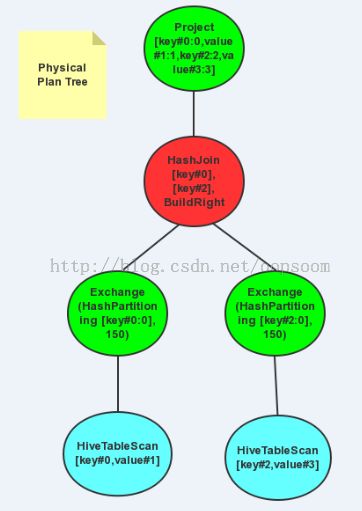
3.4、executedPlan
最后一步是终于生成的物理运行计划,里面涉及到了Hive的TableScan,涉及到了HashJoin操作,还涉及到了Exchange,Exchange涉及到了Shuffle和Partition操作。
scala> query.queryExecution.executedPlan res4: org.apache.spark.sql.execution.SparkPlan = Project [key#0:0,value#1:1,key#2:2,value#3:3] HashJoin [key#0], [key#2], BuildRight Exchange (HashPartitioning [key#0:0], 150) HiveTableScan [key#0,value#1], (MetastoreRelation default, src, None), None Exchange (HashPartitioning [key#2:0], 150) HiveTableScan [key#2,value#3], (MetastoreRelation default, src, None), None生成的物理运行树如图:
四、总结:
本文介绍了Spark SQL的Catalyst框架核心TreeNode类库,绘制了TreeNode继承关系的类图,了解了TreeNode这个类在Catalyst所起到的作用。语法树中的Logical Plan均派生自TreeNode,而且Logical Plan派生出TreeNode的三种形态,即Binary Node, Unary Node, Leaft Node。 正式这几种节点,组成了Spark SQl的Catalyst的语法树。
TreeNode的transform方法是核心的方法,它接受一个rule,会对当前节点的孩子节点进行递归的调用rule,最后会返回一个TreeNode的copy,这样的操作就是transformation,贯穿了Spark SQL运行的几个核心阶段,如Analyze,Optimize阶段。
最后用一个实际的样例,展示出来Spark SQL的运行树生成流程。
我眼下的理解就是这些,假设分析不到位的地方,请大家多多指正。
TreeNode的transform方法是核心的方法,它接受一个rule,会对当前节点的孩子节点进行递归的调用rule,最后会返回一个TreeNode的copy,这样的操作就是transformation,贯穿了Spark SQL运行的几个核心阶段,如Analyze,Optimize阶段。
最后用一个实际的样例,展示出来Spark SQL的运行树生成流程。
我眼下的理解就是这些,假设分析不到位的地方,请大家多多指正。
——EOF——