go - 内置基础类型
Go 语言中包括以下内置基础类型:
布尔型:bool
整型:int int64 int32 int16 int8 uint8(byte) uint16 uint32 uint64 uint
浮点型:float32 float64
复数型:complex64 complex128
字符串:string
字符型:rune
错误型:error
1. bool类型
关键字: bool
可定义为: true 或者 false 或者 逻辑表达式
var bool1 bool = true var bool2 bool = (2 == 2)
注:不能接受其他类型的赋值,包括(0, 1),也不支持自动或强制类型转换
2. 整型
分为有符号与无符号两种
值范围,如: int8 2^8 -128~127, uint8 0~255, 其他以此类推
int/uint 其值范围与平台有关,所以 int32 != int
支持强制类型转换,注意精度问题
变量2 = 类型(变量1)
3. 浮点型
即含小数点的数据
有两种: float32 float64(默认)
可相互转换,
注:比较大小时最好先确定比较精度, 再比较大小
4. 字符串
声明方式: var str string
值用 "" 或者 `` 包括, `` 可包含多行字符串
字符串的操作与数组相同
与如php等其他语言不同的是,字符串的内容在初始化后,不能被修改,但可重新完全赋值
s := "123" s[1] = "3" //compile error
$s = "123"; $s[1] = "3"; echo $s; //133
5. 字符型
两种字符类型:
byte 对应 utf-8
rune 对应 unicode
6. 错误型
在 go 语言中,负责错误信息处理的是 error 接口,也可以使用 errors 包
var e error = errors.New("...")
在 go 语言中,函数支持多个返回值
可用下面的方式来处理错误
res, err := funName(param)
if err != nil {
//处理错误
} else {
//无错误
}
func funName(param) (res type, err error) {
if ... {
err = errors.New(...)
return
}
...
return res, nil
}
7. 复数
在此省略,有需要可再了解
note_type_1.go code list
package main
import "fmt"
import "errors" //引入 errors 包
//声明 bool 型全局变量
var (
enable = true
disable = false
)
func main() {
//预定义常量 iota
const (
c0 = iota //0
c1 = iota //0+1
c2 //会自动赋上一个定义常量的值或者表达式
)
const (
c3 = iota //0
c4
)
fmt.Println("c0, c1, c2 = ", c0, c1, c2)
fmt.Println("c3, c4 = ", c3, c4)
/*
//这种写法编译时会报错,需要 if condition { 在同一行代码中
//missing condition in if statement
//enable == true not used
if enable == true
{
fmt.Println("error")
}
*/
if enable == true {
fmt.Println("enabled = ", enable)
} else {
fmt.Println("enabled = ", disable)
}
/*
//编译时会出现以下错误:
// cannot use 1 (type int) as type bool in assignment
enable = 1;
// cannot convert 1 to type bool
// cannot convert 1 (type int) to type bool
// cannot use 1 (type int) as type bool in assignment
enable = bool(1)
*/
var (
a int8 = 1
b int = 2
)
//invalid operation: a + b (mismatched types int8 and int)
//c := a + b
//需要做类型转换
c := int(a) + b
fmt.Println("c = a + b = ", c)
//int32 与 int 是两种不同的类型,但是可用强制类型转换
var d int32
//d = b // cannot use b (type int) as type int32 in assignment
d = int32(b)
fmt.Println("d = ", d)
var f1 float32 = 1.23456
fmt.Printf("f1 = %.3f \n", f1) //1.235
f2 := 1.111
//compile error: invalid operation: f1 + f2 (mismatched types float32 and float64
//f3 := f1 + f2
b1 := (float64(f1) == f2)//该比较方式不严谨
if b1 {
fmt.Println("float64(f1) == f2")
} else {
fmt.Println("float64(f1) != f2")
}
//用 "" 括起来表示字符串
//字符串的操作与数组一样
var str string = "hello"
fmt.Println("str = ", str)
fmt.Println("str[1] = ", str[1])
fmt.Printf("%c \n", str[1]) // s[i]取第i+1个字符
//str = "hi" //compile ok
//str[0] = 'c' //compile error: cannot assign to str[0]
//多行字符串,用 `` 包含
str2 := `
SELECT username, pwd
FROM tb_user
WHERE id = 123456
`
fmt.Println(str2)
str3 := " world!"
fmt.Println("str + str3 = ", str + str3) // s1 + s2, 连接字符串
//len(s)返回字符串的长度
fmt.Printf("length of str2 = %d \n", len(str2))
//s[m:n] 返回从m位开始到n结束之间的字符串,m, n可以省略, 此时m为0, n为len(s)
s := "hello"
s = "c" + s[1:]
fmt.Println(s) //cello
fmt.Println(s[:3]) //cel
fmt.Println(s[1:3]) //el
fmt.Println(s[:]) //cello
//byte 用 '' 包括字符
//var ch byte = "1" //compile error: cannot use "1" (type string) as type byte in assignment
var ch1 byte = 'a'
fmt.Printf("ch1 = %c \n", ch1) //ch1 = a
fmt.Println(ch1) //97
//rune
var ch2 rune = 'b'
fmt.Printf("ch2 = %c \n", ch2) //ch2 = b
fmt.Println(ch2) //98
//error
err := errors.New("error1")
if err != nil {
//错误处理...
fmt.Println(err)
}
var e1 error
if e1 == nil {
fmt.Println("no problem")
}
res, e := div(5, 0)
//res, e := div(5, 1)
if e != nil {
//错误处理
fmt.Println(e) //如果div(5, 0), 会输出: error: division by zero
} else {
//正确
fmt.Println("res = ", res) //如果div(5, 1),会输出: res = 5
}
}
//定义函数
func div(a, b int) (res int, e error) {
if b == 0 {
e = errors.New("error: division by zero")
return
}
return a /b , nil
}
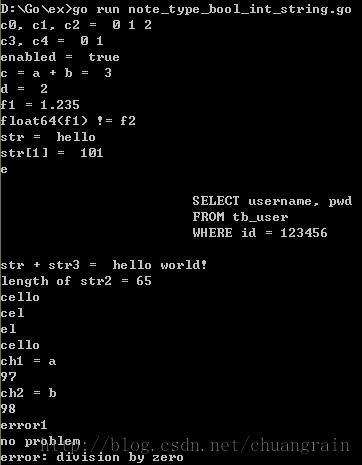
运行结果: