Windows Phone本地数据库的使用框架和技巧
在Wp7.1中加入了数据库,使保存、查找、插入数据成为可能。
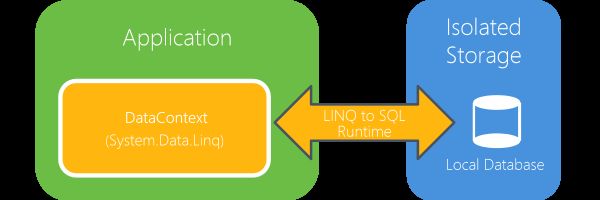
1. 架构
这个本地数据库,不能直接支持Transact-SQL,需要通过LINQ to SQL 对象模型作为Proxy来操作数据库,为此引入了一个新的类System.Data.Linq.DataContext。这与windows mobile上的SQL CE有了很大的差别。
2. LINQ to SQL
在Windows phone中,LINQ to SQL既不能直接支持执行Data Definition Language(DDL)也不支持Data Modeling Language(DML),另外也不能直接访问ADO.NET。只能支持Microsoft SQL Server Compact Edition (SQL CE)的数据类型。并且需要通过DataContext方式来操来数据库。
3. 支持的数据类型
| 数据类型 |
描述 |
| bigint |
Integer (whole number) data from –2^63 (–9,223,372,036,854,775,808) through 2^63–1 (9,223,372,036,854,775,807). Storage size is 8 bytes. |
| integer |
Integer (whole number) data from –2^31 (–2,147,483,648) through 2^31–1 (2,147,483,647). Storage size is 4 bytes. |
| smallint |
Integer data from –32,768 to 32,767. Storage size is 2 bytes. |
| tinyint |
Integer data from 0 to 255. Storage size is 1 byte. |
| bit |
Integer data with a value of either 1 or 0. Storage size is 1 bit. |
| numeric (p, s) Synonyms: decimal(p,s) and dec (p,s) |
Fixed-precision and scale-numeric data from –10^38+1 through 10^38–1. The p variable specifies precision and can vary between 1 and 38. The s variable specifies scale and can vary between 0 and p. Storage size is 19 bytes. |
| money |
Monetary data values from (–2^63/10000) (–922,337,203,685,477.5808) through 2^63–1 (922,337,203,685,477.5807), with accuracy to a ten-thousandth of a monetary unit. Storage size is 8 bytes. |
| float |
Floating point number data from –1.79E +308 through 1.79E+308 Storage size is 8 bytes. |
| real |
Floating precision number data from –3.40E+38 through 3.40E+38. Storage size is 4 bytes. |
| datetime |
Date and time data from January 1, 1753, to December 31, 9999, with an accuracy of one three-hundredth second, or 3.33 milliseconds. Values are rounded to increments of .000, .003, or .007 milliseconds. Stored as two 4-byte integers. The first 4 bytes store the number of days before or after the base date, January 1, 1900. The base date is the system's reference date. Values for datetime earlier than January 1, 1753, are not permitted. The other 4 bytes store the time of day represented as the number of milliseconds after midnight. Seconds have a valid range of 0–59. Format Example yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss 1947/08/15 03:33:20 mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss 04/15/1947 03:33:20 dd mmm yyyy hh:mm:ss 15 Jan 1947 03:33:20 dd mmmm yyyy h:mm:ss 15 January 1947 03:33:20 |
| national character(n) Synonym:nchar(n) |
Fixed-length Unicode data with a maximum length of 4000 characters. Default length = 1. Storage size, in bytes, is two times the number of characters entered. |
| national character varying(n) Synonym:nvarchar(n) |
Variable-length Unicode data with a length of 1 to 4000 characters. Default length = 1. Storage size, in bytes, is two times the number of characters entered. |
| ntext¹ |
Variable-length Unicode data with a maximum length of (2^30–2)/2 (536,870,911) characters. Storage size, in bytes, is two times the number of characters entered. Note ntext is no longer supported in string functions. |
| nchar |
Fixed-length Unicode character data of n characters. n must be a value from 1 through 4,000. The storage size is two times n bytes. |
| binary(n) |
Fixed-length binary data with a maximum length of 8000 bytes. Default length = 1. Storage size is fixed, which is the length in bytes declared in the type. |
| varbinary(n) |
Variable-length binary data with a maximum length of 8000 bytes. Default length = 1. Storage size varies. It is the length of the value in bytes. |
| image¹ |
Variable-length binary data with a maximum length of 2^30–1 (1,073,741,823) bytes. Storage is the length of the value in bytes. |
| uniqueidentifier |
A globally unique identifier (GUID). Storage size is 16 bytes. |
| IDENTITY [(s, i)] |
This is a property of a data column, not a distinct data type. Only data columns of the integer data types can be used for identity columns. A table can have only one identity column. A seed and increment can be specified and the column cannot be updated. s (seed) = starting value i(increment) = increment value |
| ROWGUIDCOL |
This is a property of a data column, not a distinct data type. It is a column in a table that is defined by using the uniqueidentifier data type. A table can have only one ROWGUIDCOL column. |
| Timestamp/rowversion |
This is an automatically generated unique binary number. Storage size is 8 bytes. |
¹在SQL Server Compact 4.0中,当Ntext 和 image 数据超过256 bytes 时将会保存到一个新的数据页。这会影响到数据库的密度,因为SQL Server Compact 4.0 数据库是按页方式面不是按字节方式来压缩的。
4. 创建工程
新建一个Windows Phone工程,最好是MVVM工程,也就是选择新建工程中的Windows Phone Databound Application 模板直接生成或者手工创建MVVM工程。创建好后,将System.Data.Linq命名空间引入到工程。这个命名空间所在位置\Program Files\Reference Assemblies\Microsoft\Framework\Silverlight\v4.0\Profile\WindowsPhone71中。
5. 创建数据库
新建一个类继承System.Data.Linq.DataContext类,这样就可以用这个类来控制数据库了。
public class MyDataContext : DataContext
{
public const string ConnectionStr = "Data Source=isostore:/MyDB.sdf";
public Table<MyTable> Rows;
public MyDataContext()
: base(ConnectionStr)
{
}
}
在这个类中同时创建数据库表类。
[Table]
public class MyTable : INotifyPropertyChanged, INotifyPropertyChanging
{
private int _index;
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, CanBeNull = false, IsDbGenerated = true, DbType = "INT NOT NULL Identity", AutoSync=AutoSync.OnInsert)]
public int Index
{
get
{
return _index;
}
set
{
if (_index != value)
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Index");
_index = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Index");
}
}
}
private string _name;
[Column]
public string Name
{
get
{
return _name;
}
set
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Name");
_name = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Name");
}
}
private String _gen;
[Column]
public String Gen
{
get
{
return _gen;
}
set
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Gen");
_gen = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Gen");
}
}
private int _age;
[Column]
public int Age
{
get
{
return _age;
}
set
{
NotifyPropertyChanging("Age");
_age = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Age");
}
}
#region INotifyPropertyChanged Members
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void NotifyPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
if (PropertyChanged != null)
{
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
#region INotifyPropertyChanging Members
public event PropertyChangingEventHandler PropertyChanging;
private void NotifyPropertyChanging(string propertyName)
{
if (PropertyChanging != null)
{
PropertyChanging(this, new PropertyChangingEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
}
6. 操作数据库
新建一个ViewModel类,在这个类中实现数据库的操作。在这个类中实现了对数据的选择、保存、更新和删除。在对数据库的操作因为不能直接使用Transact_SQL,所以操作都是通过LINQ来完成的。
MyDataContext _DB;
public void SelectData()
{
if (IsAddedToDB)
{
if (_DB.DatabaseExists())
{
IEnumerator<MyTable> enumerator = _DB.Rows.GetEnumerator();
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
this.Items.Add(enumerator.Current);
}
IsAddedToDB = false;
}
}
}
public bool SaveData(MyTable table)
{
try
{
this.Items.Add(table);
_DB.Rows.InsertOnSubmit(table);
_DB.SubmitChanges();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
public bool DeleteData(MyTable table)
{
try
{
if (_DB.DatabaseExists())
{
_DB.Rows.DeleteOnSubmit(table);
_DB.SubmitChanges();
this.Items.Remove(table);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
public bool UpdateData(MyTable source, MyTable dest)
{
try
{
var tables = from item in this.Items where (int)item.Index == source.Index select item;
foreach (MyTable mt in tables)
{
mt.Name = dest.Name;
mt.Age = dest.Age;
mt.Gen = dest.Gen;
break;
}
MyTable table = _DB.Rows.GetOriginalEntityState(source);
table.Name = dest.Name;
table.Age = dest.Age;
table.Gen = dest.Gen;
_DB.SubmitChanges();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
以下是运行效果: