一个天气App案例(一)
原文:raywenderlich ios-7-best-practices-part-1
翻译:http://www.cocoachina.com/industry/20140224/7868.html
在这个两部分的系列教程中,您将探索如何使用以下工具和技术来创建自己的App:
1 Cocoapods
2 Manual layout in code(纯代码布局)
3 ReactiveCocoa
4 OpenWeatherMap
开始
打开Xcode新建Single View Application,将项目命名为SimpleWeather。下一步将要集成第三方工具,首先关闭Xcode,确保不会影响下一步。
1.Cocoapods
你将要下载Cocoapods的代码,在Xcode项目中添加文件来使用,并配置项目需要的设置。
2.Mantle
Mantle由于Github团队开发,目的是去除Objective-C把JSON数据转为NSObject子类的所有样板代码。Mantle也能做数据转换,通过一种神奇的方式把JSON原始数据(strings, ints, floats)转换为复杂数据,比如NSDate、NSURL甚至是自定义类。
3.LBBlurredImage
LBBlurredImage是一个继承自UIImageView,轻而易举使图像模糊的项目。你将仅仅用一行代码来创建一个神奇的模糊效果。
4.TSMessages
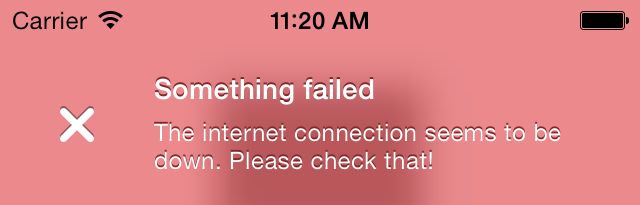
TSMessages是另一个非常简单的库,用来显示浮层警告和通知。当出现错误信息而不直接影响用户的时候,最好使用浮层来代替模态窗口(例如UIAlertView),这样你将尽可能减少对用户的影响。在网络失去连接或API错误的时候,你将看到类似这样的一个浮层:
5.ReactiveCocoa
ReactiveCocoa也是来自于GitHub团队。ReactiveCocoa给Objective-C带来了函数编程,类似与.NET的Reactive Extensions。你将在第二部分花费大部分时间去实现ReactiveCocoa。
设置你的Cocoapods
先要确保你已经安装了Cocoapods。为此,打开命令行程序,并输入:
which pod
你将会看到类似这样的输出:
/usr/bin/pod
这决定于你如何管理Ruby gems,例如你使用rbenv或RVM,路径可能有所不同。如果命令行简单的返回提示,或显示pod not found,表示Cocoapods未安装在你的机器上。可以查看Cocoapods教程作为安装说明。这也是一个很好的资源,如果你想更多得了解Cocoapods的话。
设置你的podfile
podfile用来告诉Cocoapods哪些开源项目需要导入。
要创建你的第一个Cocoapod,首先在命令行中用cd命令导航到你的XCode项目所在的文件夹,在命令行中输入vim podfile启动编辑器,输入i进入编辑模式并输入:
source 'https://github.com/CocoaPods/Specs.git' platform :ios, ‘8.1’ target 'SimpleWeather' do pod 'Mantle' pod 'LBBlurredImage' pod 'TSMessages' pod 'ReactiveCocoa' end
按esc退出编辑模式,并输入:wq退出编辑器。podfile文件做了两件事情:
1.告诉Cocoapods你的目标平台与版本,这里的你目标是iOS 8.1。
2.列给Cocoapods一个项目所有需要引入和安装的三方库清单。
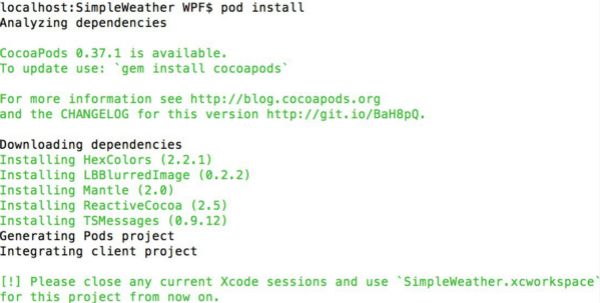
在命令行中输入pod install进行安装。
这可能需要花一到两分钟的时间去安装各种包。你的命令行应该输出如下所示:
若你之前安装过Cocoapods的话,这里安装报错的话,可以看看http://blog.cocoapods.org/Repairing-Our-Broken-Specs-Repository/ 修复问题
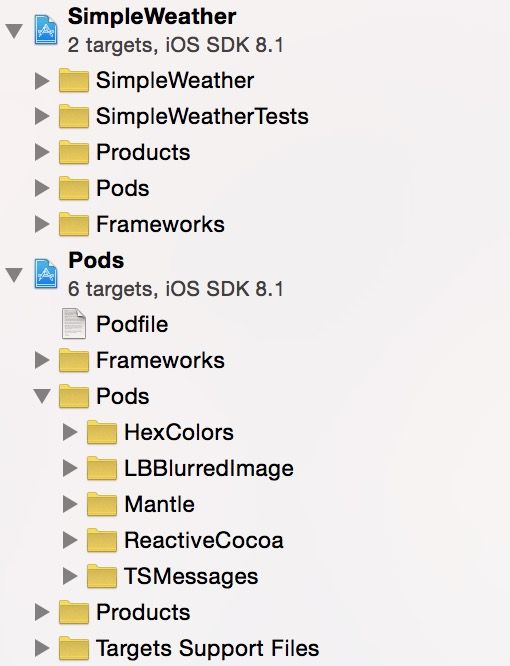
用Xcode打开SimpleWeather.xcworkspace。看看你的项目设置,现在有一个Pods项目在你的项目工作区,以及在Pods文件夹放着每一个你引入的库,如下所示:
确保你已经选择SimpleWeather项目,如图所示: Select SimpleWeather Project,构建并运行App,以确保一切工作正常:
创建你的主视图控制器
虽然这个App看起来复杂,但它还会通过一个单一的View Controller完成。现在,你将添加它。
选中SimpleWeather项目,新建Cocoa Class,命名为WXController,并设置为UIViewController的子类。
确保Targeted for iPad和With XIB for user interface都没有选中,如下图所示: Create WXController
打开WXController.m然后用如下所示替换-viewDidLoad方法:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Remove this later
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
}
现在打开AppDelegate.m,并且引入如下两个class:
#import "WXController.h" #import <TSMessage.h>
眼尖的读者会注意到WXController使用引号引入,TSMessage使用单括号引入。回头看下当你创建Podfile的时候,你使用Cocoapods引入TSMessage。Cocoapods创建TSMessage项目,并把它加入到工作空间。既然你从工作区的其他项目导入,可以使用尖括号代替引号
代替-application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions的内容:
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds]];
// 1
self.window.rootViewController = [[WXController alloc] init];
self.window.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
// 2
[TSMessage setDefaultViewController: self.window.rootViewController];
return YES;
}
1 初始化并设置WXController实例作为App的根视图控制器。通常这个控制器是一个的UINavigationController或UITabBarController,但在当前情况下,你使用WXController的单个实例。
2 设置默认的视图控制器来显示你的TSMessages。这样做,你将不再需要手动指定要使用的控制器来显示警告
构建并运行,tableView显示的背景颜色为红色。
在红色背景下,黑色状态栏显示不太清晰。幸运的是,有一个简单的方法,使状态栏更清晰。
UIViewController有一个新的API用来控制状态栏的外观。打开WXController,直接添加下面的代码到-viewDidLoad:方法下:
- (UIStatusBarStyle)preferredStatusBarStyle {
return UIStatusBarStyleLightContent;
}
再次运行,黑色状态栏变为白色高亮显示。
设置你的App视图
现在是时候让你的App接近现实生活。下载这个项目的图片,并解压缩到一个合适的位置。这个压缩包的背景图片出自Flickr用户idleformat之手,天气图片出自Dribbble用户heeyeun之手。
切换回Xcode,单击File\Add Files to “SimpleWeather”….定位到你刚刚解压缩的图片文件夹并选择它。选择Copy items into destination group’s folder (if needed),然后单击Add。
打开WXController.h, 添加如下委托协议:
<UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate, UIScrollViewDelegate>
现在打开WXController.m。 小提示:你可以使用Control-Command-Up的快捷键来实现.h和.m文件之间的快速切换。
添加如下代码到WXController.m顶部:
#import <LBBlurredImage/UIImageView+LBBlurredImage.h>
LBBlurredImage.h包含在Cocoapods引入的LBBlurredImage项目,你会使用这个库来模糊背景图片
应该有一个空的私有接口样板在WXController imports的下方。它具有以下属性:
@interface WXController : UIViewController<UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate, UIScrollViewDelegate> @property (nonatomic, strong) UIImageView *backgroundImageView; @property (nonatomic, strong) UIImageView *blurredImageView; @property (nonatomic, strong) UITableView *tableView; @property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat screenHeight; @end
现在,是时候在项目中创建并设置视图。下面是你App的分解图,记住,table view将是透明的:
为了实现动态模糊效果,在你的App中,你会根据App的滚动来改变模糊图像的alpha值。
打开WXController.m,使用如下代码来,替换掉-viewDidLoad中设置背景色的代码:
// 1 self.screenHeight = [UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.height; UIImage *background = [UIImage imageNamed:@"bg@2x"]; // 2 self.backgroundImageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:background]; self.backgroundImageView.contentMode = UIViewContentModeScaleAspectFill; [self.view addSubview:self.backgroundImageView]; // 3 self.blurredImageView = [[UIImageView alloc] init]; self.blurredImageView.contentMode = UIViewContentModeScaleAspectFill; self.blurredImageView.alpha = 0; [self.blurredImageView setImageToBlur:background blurRadius:10 completionBlock:nil]; [self.view addSubview:self.blurredImageView]; // 4 self.tableView = [[UITableView alloc] init]; self.tableView.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; self.tableView.delegate = self; self.tableView.dataSource = self; self.tableView.separatorColor = [UIColor colorWithWhite:1 alpha:0.2]; self.tableView.pagingEnabled = YES; [self.view addSubview:self.tableView];
1.获取并存储屏幕高度。之后,你将在用分页的方式来显示所有天气数据时使用它
2.创建一个静态的背景图,并添加到视图上
3.使用LBBlurredImage来创建一个模糊的背景图像,并设置alpha为0,使得开始backgroundImageView是可见的
4.创建tableview来处理所有的数据呈现;设置WXController为delegate和dataSource以及滚动视图的delegate;设置pagingEnabled为YES
添加如下UITableView的delegate和dataSource的代码到WXController.m的@implementation块中:
#pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return 2;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
// TODO: Return count of forecast
return 0;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
static NSString *CellIdentifier = @"CellIdentifier";
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
if (! cell) {
cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleValue1 reuseIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
}
cell.selectionStyle = UITableViewCellSelectionStyleNone;
cell.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithWhite:0 alpha:0.2];
cell.textLabel.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
cell.detailTextLabel.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
// TODO: Setup the cell
return cell;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
// TODO: Determine cell height based on screen
return 44;
}
你的table view有两个部分,一个是每小时的天气预报,另一个用于每日播报。table view的section数目,设置为2
最后,添加如下代码到WXController.m:
- (void)viewWillLayoutSubviews {
[super viewWillLayoutSubviews];
CGRect bounds = self.view.bounds;
self.backgroundImageView.frame = bounds;
self.blurredImageView.frame = bounds;
self.tableView.frame = bounds;
}
在WXController.m中,你的视图控制器调用该方法来编排其子视图
构建并运行你的App:
仔细看,你会看到所有空的table cell的cell分隔线
仍然在-viewDidLoad中,添加下面的代码来设置你的布局框架和边距:
// 5 CGRect headerFrame = [UIScreen mainScreen].bounds; // 6 CGFloat inset = 20; // 7 CGFloat temperatureHeight = 110; CGFloat hiloHeight = 40; CGFloat iconHeight = 30; // 8 CGRect hiloFrame = CGRectMake(inset, headerFrame.size.height - hiloHeight, headerFrame.size.width - (2 * inset), hiloHeight); CGRect temperatureFrame = CGRectMake(inset, headerFrame.size.height - (temperatureHeight + hiloHeight), headerFrame.size.width - (2 * inset), temperatureHeight); CGRect iconFrame = CGRectMake(inset, temperatureFrame.origin.y - iconHeight, iconHeight, iconHeight); // 9 CGRect conditionsFrame = iconFrame; conditionsFrame.size.width = self.view.bounds.size.width - (((2 * inset) + iconHeight) + 10); conditionsFrame.origin.x = iconFrame.origin.x + (iconHeight + 10);
5 设置table的header大小与屏幕相同。你将利用的UITableView的分页来分隔页面页头和每日每时的天气预报部分
6 创建inset(或padding)变量,以便您的所有标签均匀分布并居中
7 创建并初始化为各种视图创建的高度变量。设置这些值作为常量,使得可以很容易地在需要的时候,配置和更改您的视图设置
8 使用常量和inset变量,为label和view创建框架
9 复制图标框,调整它,使文本具有一定的扩展空间,并将其移动到该图标的右侧。当我们把标签添加到视图,你会看到布局的效果
继续添加如下代码到-viewDidLoad:
// 10 UIView *header = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:headerFrame]; header.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; self.tableView.tableHeaderView = header; // 11 // bottom left UILabel *temperatureLabel = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:temperatureFrame]; temperatureLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; temperatureLabel.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; temperatureLabel.text = @"0°"; temperatureLabel.font = [UIFont fontWithName:@"HelveticaNeue-UltraLight" size:120]; [header addSubview:temperatureLabel]; // bottom left UILabel *hiloLabel = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:hiloFrame]; hiloLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; hiloLabel.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; hiloLabel.text = @"0° / 0°"; hiloLabel.font = [UIFont fontWithName:@"HelveticaNeue-Light" size:28]; [header addSubview:hiloLabel]; // top UILabel *cityLabel = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 20, self.view.bounds.size.width, 30)]; cityLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; cityLabel.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; cityLabel.text = @"Loading..."; cityLabel.font = [UIFont fontWithName:@"HelveticaNeue-Light" size:18]; cityLabel.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter; [header addSubview:cityLabel]; // bottom left UILabel *conditionsLabel = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:conditionsFrame]; conditionsLabel.text = @"Clear"; conditionsLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; conditionsLabel.font = [UIFont fontWithName:@"HelveticaNeue-Light" size:18]; conditionsLabel.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; [header addSubview:conditionsLabel]; // 12 // bottom left UIImageView *iconView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithFrame:iconFrame]; iconView.contentMode = UIViewContentModeScaleAspectFit; iconView.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; iconView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"weather-clear@2x"]; [header addSubview:iconView];
10 设置当前view为你的table header
11 构建每一个显示气象数据的标签
12 添加一个天气图标的图像视图
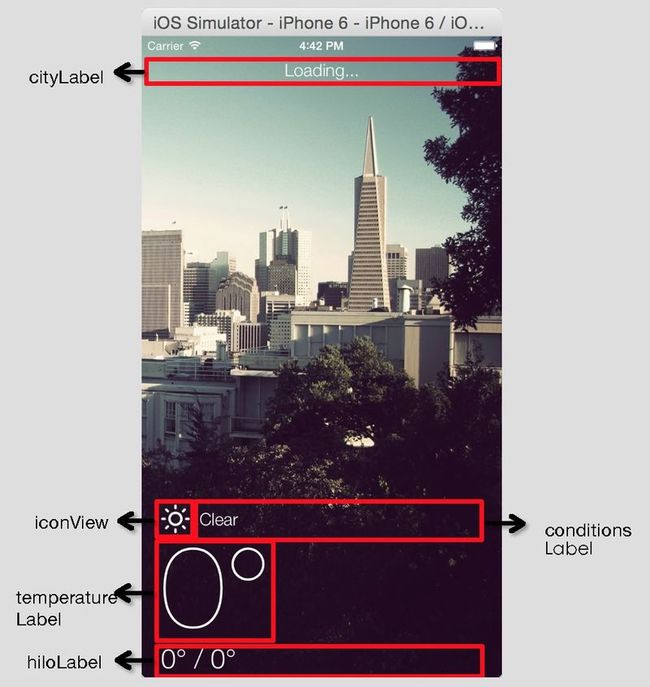
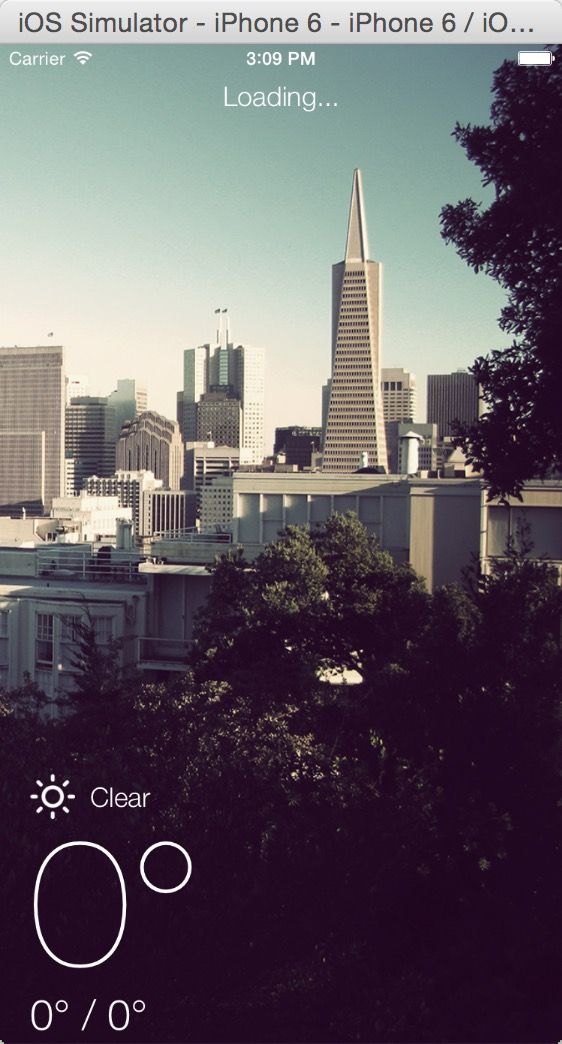
构建并运行你的App,你应该可以看到你之前布局的所有所有view。下面的屏幕截图显示了使用手工布局的、所有标签框在视觉上的显示:
获取气象数据
你会注意到,App显示“Loading…”,但它不是真正地在工作。是时候获取一些真正的天气数据。
你会从OpenWeatherMap的API拉取数据,OpenWeatherMap是一个非常棒的服务,旨在提供实时、准确、免费的天气数据给任何人。虽然当前有很多天气API,但它们大都使用较旧的数据格式(如XML),或是有偿服务(有时相当昂贵)。
遵循以下基本步骤,获取设备位置的气象数据:
1.找到设备的位置
2.从API端下载JSON数据
3.映射JSON到WXConditions和WXDailyForecasts
4.告诉UI有新数据了
开始创建天气模型和数据管理类,新建Cocoa Class并命名为WXClient,子类选择NSObject。
重复再做三次创建以下类:
1.WXManager作为NSObject的子类
2.WXCondition作为MTLModel的子类
3.WXDailyForecast作为WXCondition的子类
接下去将实现映射和转换天气数据。
创建天气模型
模型将使用Mantle,这使得数据映射和转型非常简单。
打开WXCondition.h如下列代码,修改接口:
@interface WXCondition : MTLModel <MTLJSONSerializing> @property (nonatomic, strong) NSDate *date; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *humidity; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *temperature; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *tempHigh; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *tempLow; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *locationName; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSDate *sunrise; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSDate *sunset; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *conditionDescription; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *condition; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *windBearing; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *windSpeed; @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *icon; - (NSString *) imageName; @end
MTLJSONSerializing协议告诉Mantle序列化该对象如何从JSON映射到Objective-C的属性。这些都是你的天气数据的属性。你将会使用这些属性的get set方法,当你要扩展App的时候,这是一种很好的访问数据的方法。这是一个简单的辅助方法,从天气状况映射到图像文件。
构建并运行App。失败了……原因是你没有从你的Cocoapods项目中引入Mantle。解决方法是,在WXCondition.h中,你需要把MTLModel.h替换为#import <Mantle.h>。现在构建并运行App。成功了。你会看到一些新的警告,但你可以忽略他们。
首先,你需要处理未实现的-imageName方法。
打开WXCondition.m,添加如下方法:
+ (NSDictionary *)imageMap {
// 1
static NSDictionary *_imageMap = nil;
if (! _imageMap) {
// 2
_imageMap = @{
@"01d" : @"weather-clear",
@"02d" : @"weather-few",
@"03d" : @"weather-few",
@"04d" : @"weather-broken",
@"09d" : @"weather-shower",
@"10d" : @"weather-rain",
@"11d" : @"weather-tstorm",
@"13d" : @"weather-snow",
@"50d" : @"weather-mist",
@"01n" : @"weather-moon",
@"02n" : @"weather-few-night",
@"03n" : @"weather-few-night",
@"04n" : @"weather-broken",
@"09n" : @"weather-shower",
@"10n" : @"weather-rain-night",
@"11n" : @"weather-tstorm",
@"13n" : @"weather-snow",
@"50n" : @"weather-mist"
};
}
return _imageMap;
}
// 3
- (NSString *) imageName {
return [WXCondition imageMap][self.icon];
}
1 创建一个静态的NSDictionary,因为WXCondition的每个实例都将使用相同的数据映射
2 天气状况与图像文件的关系(例如“01d”代表“weather-clear.png”)
3 声明获取图像文件名的公有方法
看一看从OpenWeatherMap返回的JSON响应数据:
{
"dt": 1384279857,
"id": 5391959,
"main": {
"humidity": 69,
"pressure": 1025,
"temp": 62.29,
"temp_max": 69.01,
"temp_min": 57.2
},
"name": "San Francisco",
"weather": [
{
"description": "haze",
"icon": "50d",
"id": 721,
"main": "Haze"
}
]
}
你需要把嵌套的JSON值映射到Objective-C的属性,嵌套的JSON值是元素(如温度),即上面看到的main节点。要做到这一点,你将利用的Objective-C的Key-Value Coding和Mantle的MTLJSONAdapter。
在WXCondition.m,添加+JSONKeyPathsByPropertyKey方法实现“JSON到模型属性”的映射,该方法是MTLJSONSerializing协议的require方法。
+ (NSDictionary *)JSONKeyPathsByPropertyKey {
return @{
@"date": @"dt",
@"humidity": @"main.humidity",
@"temperature": @"main.temp",
@"tempHigh": @"main.temp_max",
@"tempLow": @"main.temp_min",
@"locationName": @"name",
@"sunrise": @"sys.sunrise",
@"sunset": @"sys.sunset",
@"conditionDescription": @"weather.description",
@"condition": @"weather.main",
@"windBearing": @"wind.deg",
@"windSpeed": @"wind.speed",
@"icon": @"weather.icon"
};
}
dictionary的key是WXCondition的属性名称,而dictionary的value是JSON的路径
你可能已经注意到,这里有一个从JSON数据映射到Objective-C属性的问题。属性date是NSDate类型的,但JSON有一个Unix时间类型(sjpsega注:即从1970年1月1日0时0分0秒起至现在的总秒数)的NSInteger值。你需要完成两者之间的转换。
Mantle正好有一个功能来为你解决这个问题:MTLValueTransformer。这个类允许你声明一个block,详细说明值的相互转换。
Mantle的转换器语法有点怪。要创建一个特定属性的转换器,你可以添加一个以属性名开头和JSONTransformer结尾的类方法。可能看实际代码比试图解释它更容易理解,所以在WXCondition.m中添加以下为NSDate属性设置的转换器。
// 1
+ (NSValueTransformer *)dateJSONTransformer {
return [MTLValueTransformer transformerUsingForwardBlock:^(NSString *str, BOOL *success, NSError **error){
return [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSince1970:str.floatValue];
} reverseBlock:^(NSDate *date, BOOL *success, NSError **error){
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%f", [date timeIntervalSince1970]];
}];
}
// 2
+ (NSValueTransformer *)sunriseJSONTransformer {
return [self dateJSONTransformer];
}
+ (NSValueTransformer *)sunsetJSONTransformer {
return [self dateJSONTransformer];
}
1 使用blocks做属性的转换的工作,并返回一个MTLValueTransformer返回值
2 只需要详细说明Unix时间和NSDate之间进行转换一次,就可以重用-dateJSONTransformer方法为sunrise和sunset属性做转换
下一个值转型有点讨厌,但它只是使用OpenWeatherMap的API,并自己的格式化JSON响应方式的结果。weather键对应的值是一个JSON数组,但你只关注单一的天气状况。
在WXCondition.m中,使用dateJSONTransformer相同的结构,可以创建一个NSArray和NSString的之间的转换。该解决方案提供如下:
+ (NSValueTransformer *)conditionDescriptionJSONTransformer {
return [MTLValueTransformer transformerUsingForwardBlock:^(NSArray *values, BOOL *success, NSError **error){
return [values firstObject];
} reverseBlock:^(NSString *str, BOOL *success, NSError **error){
return @[str];
}];}
+ (NSValueTransformer *)conditionJSONTransformer {
return [self conditionDescriptionJSONTransformer];
}
+ (NSValueTransformer *)iconJSONTransformer {
return [self conditionDescriptionJSONTransformer];
}
OpenWeatherAPI使用每秒/米的风速。由于您的App使用英制系统,你需要将其转换为每小时/英里。在WXCondition.m的实现中添加以下转换器的方法和宏定义:
#define MPS_TO_MPH 2.23694f
+ (NSValueTransformer *)windSpeedJSONTransformer {
return [MTLValueTransformer transformerUsingForwardBlock:^(NSNumber *num, BOOL *success, NSError **error) {
return @(num.floatValue*MPS_TO_MPH);
} reverseBlock:^(NSNumber *speed, BOOL *success, NSError **error) {
return @(speed.floatValue/MPS_TO_MPH);
}];
}
在OpenWeatherMap的API中有一个小的差异,你必须处理。看一看在位于当前状况的响应和每日预测反应之间的温度:
// current
"main": {
"grnd_level": 1021.87,
"humidity": 64,
"pressure": 1021.87,
"sea_level": 1030.6,
"temp": 58.09,
"temp_max": 58.09,
"temp_min": 58.09
}
// daily forecast
"temp": {
"day": 58.14,
"eve": 58.14,
"max": 58.14,
"min": 57.18,
"morn": 58.14,
"night": 57.18
}
current的第一个key是main,最高温度存储在key temp_max中,而daily forecast的第一个key是temp,最高温度存储在key max中
key Temperature的差异放在一边,其他都一样。所以,你真正需要做的是修改daily forecasts的键映射。
打开WXDailyForecast.m重写+JSONKeyPathsByPropertyKey方法:
+ (NSDictionary *)JSONKeyPathsByPropertyKey {
// 1
NSMutableDictionary *paths = [[super JSONKeyPathsByPropertyKey] mutableCopy];
// 2
paths[@"tempHigh"] = @"temp.max";
paths[@"tempLow"] = @"temp.min";
// 3
return paths;
}
1 获取WXCondition的映射,并创建它的可变副本
2 daily forecast改变max和min键映射
3 返回新的映射
构建并运行您的App,看起来和上次运行没什么改变,但好的一点是,App编译和运行没有任何错误。
何去何从?
你可以从这里这里完整程序。
在这部分教程中,您使用Cocoapods设置项目,增加视图到控制器,编排视图,并建立模型来反映你抓取的气象数据。该App还没有充分发挥作用,但是你成功用纯代码创建视图,并学习了如何使用Mantle映射和转换JSON数据。
接下来看看教程的第二部分,你将充实你的App,从weather API获取数据,并在UI上显示。您将使用新的iOS8 NSURLSession去下载数据,以及使用ReactiveCocoa把位置查找,天气数据抓取和UI更新事件绑在一起。