java collection 集合源码分析(一)
collection 为java集合的接口,collection的接口继承Iterable
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
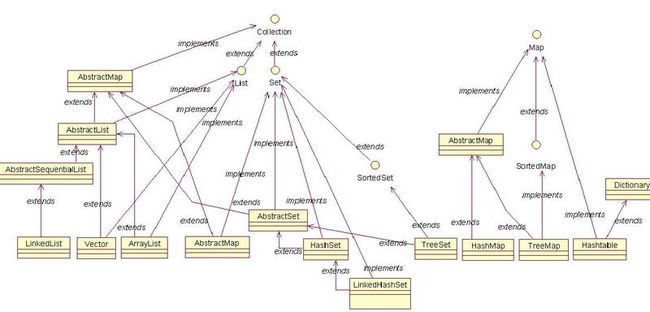
没有自己在画类图了 找到网上有大哥画的关系图如下
上图中有个位置可能错了,AbstrctList应该继承自
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E>
一、List(接口)
1、ArrayList
内部持有一个Object[] 数组
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //默认大小
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //对象数组
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA will be expanded to
* DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
private transient Object[] elementData;
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size; //数组大小
所有的操作基于这个数组进行组织,一般不轻易对这个数组进行遍历,一般多用system.arraycopy的方式进行操作,删除的动作有时候依赖与gc来回收,如下删除方法:
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved); //通过副本的形式完成操作
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
2、LinkedList
LinkedList,内部持有一系列的Node ,node结构如下
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
从上可以看出 node中 保存了前一个和后一个的节点信息,和数据,分为三部分
对节点的管理如下:
transient int size = 0; //有多少节点 /** * Pointer to first node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */ transient Node<E> first; //头节点 /** * Pointer to last node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */ transient Node<E> last; //尾节点
所有的操作围绕对节点的增删来操作,看一个添加所有的操作
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
} //构造
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in
* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is
* this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index); //返回索引处的特征节点,这个方法会优化从头部还是从尾部查找的过程具体参看源码
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
} //添加过程
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
3、Vector
arrayList类似,源码多处增加了synchronized 关键字,线程安全
二、Set(接口)
1、HashSet
HashSet内部实际持有的是一个hashmap对象,所有的操作都是通过操作map实现,这个map是无值,只有key,
内部的一个hashmap对象
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16)); //开辟一个比原有集合4/3大小的集合。默认16
addAll(c);
}
看一个获取迭代器的方法
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this set. The elements
* are returned in no particular order.
*
* @return an Iterator over the elements in this set
* @see ConcurrentModificationException
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
2、TreeSet
TreeSet也是通过map来实现
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m; //这里使用的是NavigableMap,这个继承自SortedMap接口 since1.6之后
其他的方法都是调用map的实现,在map中在看
Map 单立一章来写把
ps:以上的源码来自openjdk7u75-b13版本