android核心基础(4)_android框架简介
Android是什么
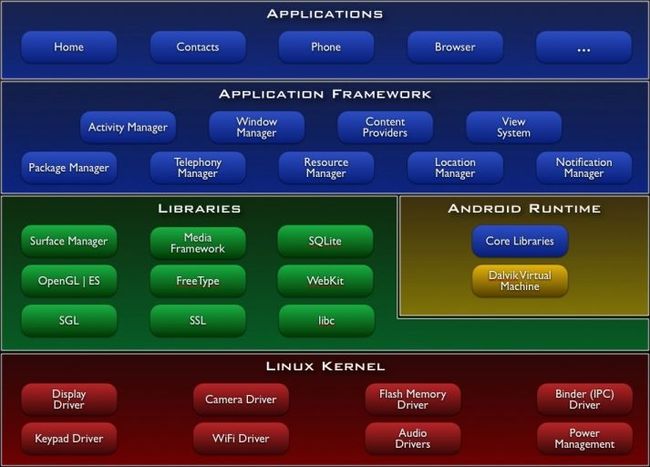
手机设备的软件栈,包括1. 一个完整的操作系统。2.中间件 3. 关键的应用程序。
底层是linux内核:安全管理、内存管理、进程管理、电源管理、硬件驱动。
Android系统是基于Linux内核2.6进行的开发。其中库函数中有:Surface Manager(与显示相关)、Media Framework(与多媒体播放相关)、Sqlite(嵌入式数据库)、OpenGL|ES(3D的图形渲染引擎)、FreeType(与字体相关)、WebKit(浏览器内核)、SSL(安全相关)、libc(标准的库)等。
android运行环境:包括核心库和android下的java虚拟机。
应用程序框架:界面,窗体,拨打电话等。通过调用此层的API运行。
应用:桌面,联系人,拨号等,是android系统的标准应用。
What is Android?
Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications. The Android SDK provides the tools and APIs necessary to begin developing applications on the Android platform using the Java programming language.
Features
- Application framework enabling reuse and replacement of components
- Dalvik virtual machine optimized for mobile devices
- Integrated browser based on the open source WebKit engine
- Optimized graphics powered by a custom 2D graphics library; 3D graphics based on the OpenGL ES 1.0 specification (hardware acceleration optional)
- SQLite for structured data storage
- Media support for common audio, video, and still image formats (MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, PNG, GIF)
- GSM Telephony (hardware dependent)
- Bluetooth, EDGE, 3G, and WiFi (hardware dependent)
- Camera, GPS, compass, and accelerometer (hardware dependent)
- Rich development environment including a device emulator, tools for debugging, memory and performance profiling, and a plugin for the Eclipse IDE
Android Architecture
The following diagram shows the major components of the Android operating system. Each section is described in more detail below.
Applications
Android will ship with a set of core applications including an email client, SMS program, calendar, maps, browser, contacts, and others. All applications are written using the Java programming language.
Application Framework
By providing an open development platform, Android offers developers the ability to build extremely rich and innovative applications. Developers are free to take advantage of the device hardware, access location information, run background services, set alarms, add notifications to the status bar, and much, much more.
Developers have full access to the same framework APIs used by the core applications. The application architecture is designed to simplify the reuse of components; any application can publish its capabilities and any other application may then make use of those capabilities (subject to security constraints enforced by the framework). This same mechanism allows components to be replaced by the user.
Underlying all applications is a set of services and systems, including:
- A rich and extensible set of Views that can be used to build an application, including lists, grids, text boxes, buttons, and even an embeddable web browser
- Content Providers that enable applications to access data from other applications (such as Contacts), or to share their own data
- A Resource Manager, providing access to non-code resources such as localized strings, graphics, and layout files
- ANotification Managerthat enables all applications to display custom alerts in the status bar
- AnActivity Managerthat manages the lifecycle of applications and provides a common navigation backstack
For more details and a walkthrough of an application, see the Notepad Tutorial.
Libraries
Android includes a set of C/C++ libraries used by various components of the Android system. These capabilities are exposed to developers through the Android application framework. Some of the core libraries are listed below:
- System C library - a BSD-derived implementation of the standard C system library (libc), tuned for embedded Linux-based devices
- Media Libraries - based on PacketVideo's OpenCORE; the libraries support playback and recording of many popular audio and video formats, as well as static image files, including MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, and PNG
- Surface Manager - manages access to the display subsystem and seamlessly composites 2D and 3D graphic layers from multiple applications
- LibWebCore - a modern web browser engine which powers both the Android browser and an embeddable web view
- SGL - the underlying 2D graphics engine
- 3D libraries - an implementation based on OpenGL ES 1.0 APIs; the libraries use either hardware 3D acceleration (where available) or the included, highly optimized 3D software rasterizer
- FreeType - bitmap and vector font rendering
- SQLite - a powerful and lightweight relational database engine available to all applications
Android Runtime
Android includes a set of core libraries that provides most of the functionality available in the core libraries of the Java programming language.
Every Android application runs in its own process, with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine. Dalvik has been written so that a device can run multiple VMs efficiently. The Dalvik VM executes files in the Dalvik Executable (.dex) format which is optimized for minimal memory footprint. The VM is register-based, and runs classes compiled by a Java language compiler that have been transformed into the .dex format by the included "dx" tool.
The Dalvik VM relies on the Linux kernel for underlying functionality such as threading and low-level memory management.
Linux Kernel
Android relies on Linux version 2.6 for core system services such as security, memory management, process management, network stack, and driver model. The kernel also acts as an abstraction layer between the hardware and the rest of the software stack.