Trie树详解
Trie原理
Trie的核心思想是空间换时间。利用字符串的公共前缀来降低查询时间的开销以达到提高效率的目的。
Trie性质
好多人说trie的根节点不包含任何字符信息,我所习惯的trie根节点却是包含信息的,而且认为这样也方便,下面说一下它的性质 (基于本文所讨论的简单trie树)
1. 字符的种数决定每个节点的出度,即branch数组(空间换时间思想)
2. branch数组的下标代表字符相对于a的相对位置
3. 采用标记的方法确定是否为字符串。
4. 插入、查找的复杂度均为O(len),len为字符串长度
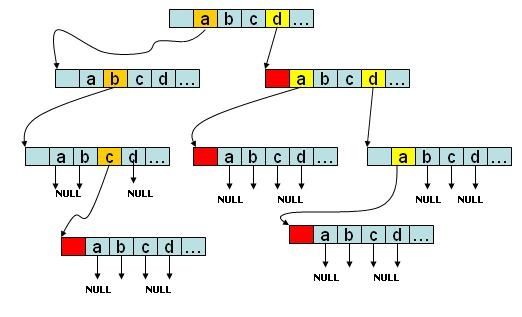
Trie的示意图
如图所示,该trie树存有abc、d、da、dda四个字符串,如果是字符串会在节点的尾部进行标记。没有后续字符的branch分支指向NULL
TrieTrie的优点举例
已知n个由小写字母构成的平均长度为10的单词,判断其中是否存在某个串为另一个串的前缀子串。下面对比3种方法:
1. 最容易想到的:即从字符串集中从头往后搜,看每个字符串是否为字符串集中某个字符串的前缀,复杂度为O(n^2)。
2. 使用hash:我们用hash存下所有字符串的所有的前缀子串。建立存有子串hash的复杂度为O(n*len)。查询的复杂度为O(n)* O(1)= O(n)。
3. 使用trie:因为当查询如字符串abc是否为某个字符串的前缀时,显然以b,c,d....等不是以a开头的字符串就不用查找了。所以建立trie的复杂度为O(n*len),而建立+查询在trie中是可以同时执行的,建立的过程也就可以成为查询的过程,hash就不能实现这个功能。所以总的复杂度为O(n*len),实际查询的复杂度只是O(len)。
Trie的简单实现(插入、查询)
C++语言:
高亮代码由发芽网提供
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int branchNum = 26; //声明常量
int i;
struct Trie_node
{
bool isStr; //记录此处是否构成一个串。
Trie_node * next [ branchNum ]; //指向各个子树的指针,下标0-25代表26字符
Trie_node()
{
isStr = false;
memset( next , NULL , sizeof( next));
}
};
class Trie
{
public :
Trie();
void insert( const char * word);
bool search( char * word);
void deleteTrie( Trie_node * root);
private :
Trie_node * root;
};
Trie :: Trie()
{
root = new Trie_node();
}
void Trie :: insert( const char * word)
{
Trie_node * location = root;
while( * word)
{
if( location -> next [ * word - 'a' ] == NULL) //不存在则建立
{
Trie_node * tmp = new Trie_node();
location -> next [ * word - 'a' ] = tmp;
}
location = location -> next [ * word - 'a' ]; //每插入一步,相当于有一个新串经过,指针要向下移动
word ++;
}
location -> isStr = true; //到达尾部,标记一个串
}
bool Trie :: search( char * word)
{
Trie_node * location = root;
while( * word && location)
{
location = location -> next [ * word - 'a' ];
word ++;
}
return( location != NULL && location -> isStr);
}
void Trie :: deleteTrie( Trie_node * root)
{
for( i = 0; i < branchNum; i ++)
{
if( root -> next [ i ] != NULL)
{
deleteTrie( root -> next [ i ]);
}
}
delete root;
}
int main() //简单测试
{
Trie t;
t . insert( "a");
t . insert( "abandon");
char * c = "abandoned";
t . insert( c);
t . insert( "abashed");
if( t . search( "abashed"))
printf( "true \n ");
}
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int branchNum = 26; //声明常量
int i;
struct Trie_node
{
bool isStr; //记录此处是否构成一个串。
Trie_node * next [ branchNum ]; //指向各个子树的指针,下标0-25代表26字符
Trie_node()
{
isStr = false;
memset( next , NULL , sizeof( next));
}
};
class Trie
{
public :
Trie();
void insert( const char * word);
bool search( char * word);
void deleteTrie( Trie_node * root);
private :
Trie_node * root;
};
Trie :: Trie()
{
root = new Trie_node();
}
void Trie :: insert( const char * word)
{
Trie_node * location = root;
while( * word)
{
if( location -> next [ * word - 'a' ] == NULL) //不存在则建立
{
Trie_node * tmp = new Trie_node();
location -> next [ * word - 'a' ] = tmp;
}
location = location -> next [ * word - 'a' ]; //每插入一步,相当于有一个新串经过,指针要向下移动
word ++;
}
location -> isStr = true; //到达尾部,标记一个串
}
bool Trie :: search( char * word)
{
Trie_node * location = root;
while( * word && location)
{
location = location -> next [ * word - 'a' ];
word ++;
}
return( location != NULL && location -> isStr);
}
void Trie :: deleteTrie( Trie_node * root)
{
for( i = 0; i < branchNum; i ++)
{
if( root -> next [ i ] != NULL)
{
deleteTrie( root -> next [ i ]);
}
}
delete root;
}
int main() //简单测试
{
Trie t;
t . insert( "a");
t . insert( "abandon");
char * c = "abandoned";
t . insert( c);
t . insert( "abashed");
if( t . search( "abashed"))
printf( "true \n ");
}