《易道客》源码剖析之五:权限管理
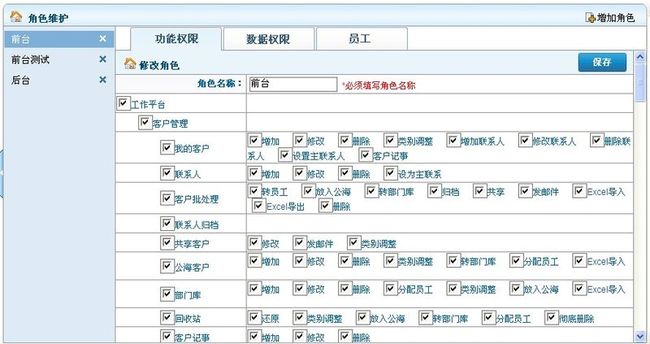
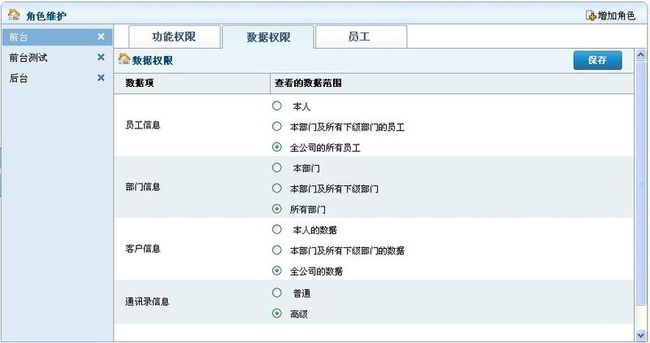
一、在本系统中,权限管理分为两种,功能权限和数据权限。
1、功能权限。即用户是否对某一功能是否有操作权限的控制。
(1)菜单控制:当用户不具备某一菜单操作权限时,看不到相应的菜单。
(2)操作控制:可以控制是否可看到某个按钮。例如当一个用户对只有查看权限,没有增加、修改、删除的权限,则进入菜单后,看不到增加、修改、删除的按钮。
(3)链接控制:如果你不具备某操作的访问权限,但你知道这个操作的链接地址,直接在地址栏中输入地址访问时,也会被拦截。
2、数据权限。即可以访问哪些数据,是针对特定功能的。如对于客户数据,可控制能看到本人的、本部门的、还是全公司的数据。
二、功能权限定义。
1、在struts.xml中,定义了两个过滤器,分别用于是否登录验证和权限验证。其中权限验证中包含有是否登陆的验证。如果一个action访问只需要验证用户是否已登陆,则用前者验证。如果一个action还需要验证用户是否有访问该action的权限,则用后者验证。
<interceptors>
<interceptor name="loginInterceptor" class="com.abc.domain.common.util.LoginInterceptor"></interceptor>
<interceptor name="accessInterceptor" class="com.abc.domain.common.util.AccessInterceptor"></interceptor>
<!-- 是否登录控制 -->
<interceptor-stack name="isLogin">
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
<interceptor-ref name="loginInterceptor"/>
</interceptor-stack>
<!-- 是否有操作权限,包含有是否登录的功能 -->
<interceptor-stack name="canAccess">
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
<interceptor-ref name="accessInterceptor"/>
</interceptor-stack>
</interceptors>
2、LoginInterceptor.java中的登录验证
UserInfoLogin userInfo = (UserInfoLogin) ActionContext.getContext().getSession().get("userInfo_login");
if (userInfo != null)
{//正确登录,验证是否重复提交
//......(略)
}
else
{//未正确登录
ActionContext.getContext().getSession().put("errorInfo","登录信息丢失,请重新登录!");
return "gotoLogin";
}
3、AccessInterceptor.java中的权限验证
List<CandoDto> CandoList = userInfo.getCandoList(); // 所有可以访问的功能点
String methodName = invocation.getProxy().getMethod(); //所访问方法的名称
Class cls=invocation.getAction().getClass();//所访问的action类
Method m=cls.getMethod(methodName); //所访问的方法
//重复提交验证
Token token = m.getAnnotation(Token.class);
if (token != null)
{
return super.doIntercept(invocation);
}
//是否需要权限限制,只有有Access注释标签 的方法才会进行验证
Access annotation = m.getAnnotation(Access.class); //找到方法的权限代码
if(annotation==null) //如果为null,没有权限注释,无需控制
{
return invocation.invoke();
}
//方法访问权限验证
String accName=cls.getName()+"."+methodName;//所访问的类全名+方法名
boolean canAcc=false;//是否通过验证
if(CandoList!=null && CandoList.size()>0)
{
for(CandoDto candoDto:CandoList)
{
String classMethod=candoDto.getClassMethod();
if(classMethod!=null && classMethod.indexOf(accName)!=-1)
{//找到匹配项,说明有该方法权限
canAcc=true;
break;
}
}
}
if(!canAcc)
{
ActionContext.getContext().put("errorInfo", "你没有访问权限,请与管理员联系!");
return "noAccess";
}
return invocation.invoke();
4、Access.java
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Access
{
}
5、ModuleFere类中定义了对按钮的权限过滤方法。
public static Button[] getCanShowButton(Button[] buttons,String moduleId)
{
Module module=moduleMap.get(moduleId);
List<Operation> operations=module.getOperations();
//当前模块未定义动作的,不进行控制
if(operations==null || operations.size()==0)
{
return buttons;
}
//开发人员和系统管理员 不作权限控制
UserInfoLogin userInfo = (UserInfoLogin) ActionContext.getContext().getSession().get("userInfo_login");
if(userInfo.isAdmin() || userInfo.isDev())
{
return buttons;
}
List<Button> ls=new ArrayList<Button>();//存放可使用的按钮
Map<String,String> myOpeMap=userInfo.getMyOpeMap();
for(Button button:buttons)
{
String type=button.getType();
if(type==null || "".equals(type.trim()))
{//按钮无类型时,不需要控制
ls.add(button);
continue;
}
for(Operation ope:operations)
{//当前模块定义的操作
if(ope.getType().equals(button.getType()))
{//操作类型与按钮类型相匹配时,表示同一动作
if(myOpeMap.get(ope.getId())!=null)
{//如果当前用户的所有操作中有该操作权限,则可使用此按钮。
ls.add(button);
}
break;
}
}
}
Collections.sort(ls);
return ls.toArray(new Button[ls.size()]);
}
三、模块中对功能权限的使用。
1、在需要使用登录验证的action类之前,加入isLogin过滤器,需要进行权限验证的action类之前,加入canAccess验证。
@InterceptorRef("isLogin ")
public class MyClientAction
{}
或者
@InterceptorRef("canAccess")
public class MyClientAction
{}
2、在action类的方法中,有需要进行权限验证的方法前,加入access注释。这个注释只有在加有canAccess过滤器的类中才有效。
@Access
public String add() throws Exception
3、action方法中,需要对按钮进行权限验证过滤。
queryFere.setTopButtons(ModuleFere.getCanShowButton(buttonArr,ModuleFactory_myClient.moduleId));
4、在模块定义中的按钮定义。
如:ModuleFactory_myClient.java中在按钮的定义中,有该按钮功能所需要访问的action的方法,该参数会在AccessInterceptor.java过滤器中使用,以验证用户是否有访问的权限。
ops.add(new Operation(moduleId+"_01", "增加", "add", "com.abc.domain.kh.main.inside.action.MyClientAction.add,com.abc.domain.kh.main.inside.action.MyClientAction.addDone"));
ops.add(new Operation(moduleId+"_02", "修改", "update", "com.abc.domain.kh.main.inside.action.MyClientAction.update,com.abc.domain.kh.main.inside.action.MyClientAction.updateDone"));
四、角色维护中对权限的管理。
1、相关的类
(1)Module和Operation,模块类和操作类,分别对应模块的定义和模块下面操作(按钮)的定义。
(2)Menu,菜单类,里面记录有一个菜单使用的是哪个模块。
(3)Role,Cando,DataAccess分别是角色类,角色可操作的功能权限,角色可操作的数据权限。
(4)DataAccessFere,数据权限管理辅助类。
2、源码查看
(1)Role.java
public class Role implements Comparable<Role>
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuidGenerator")
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuidGenerator", strategy = "uuid")
@Column(length = 32)
private String id;
@Column(length = 20)
private String name;//名称
@OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "role")
private List<Cando> candoes; //可以进行的操作
@OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "role")
private List<DataAccess> dataAccesss; //数据权限
}
(2)Cando.java
public class Cando implements Comparable<Cando>
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuidGenerator")
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuidGenerator", strategy = "uuid")
@Column(length = 32)
private String id;//标识
@Column(length = 10)
private String menuCode;//对应的菜单编码
@Column(length = 32)
private String moduleId;//模块ID
@Column(length = 32)
private String operationId;//对应的操作ID
@Column
private int moduleVer = 1; //模块版本
@Column(length = 500)
private String classMethod; //由Operation冗余来,多处使用
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "role", insertable = true, updatable = true)
private Role role; //对应的角色
}
(3)DataAccess.java
public class DataAccess
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuidGenerator")
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuidGenerator", strategy = "uuid")
@Column(length = 32)
private String id;//标识
@Column(length = 20)
private String type;//类型(控制的那个数据项)
@Column
private int value;//值
@Column(length = 50)
private String des;//描述
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "role", insertable = true, updatable = true)
private Role role; //对应的角色
}
(4)DataAccessFere.java,需要增加一个新数据权限管理时,只需要在该类中加入如下一段代码即可。
{//客户数据权限
String name=kh;
String des="客户信息";
List<DataAccessDto> ls = new LinkedList<DataAccessDto>();
ls.add(new DataAccessDto(1, "本人的数据", true));
ls.add(new DataAccessDto(2, "本部门及所有下级部门的数据", false));
ls.add(new DataAccessDto(3, "全公司的数据", false));
accMap.put(name, ls);
nameMap.put(name, des);
}
五、UserInfoLogin.java中对权限的支持的。
该类是用户登录信息保存类,在一个用户登录时,就会创新一个这样的类,放在用户session中,里面存放的是当前用户的一系列相关信息。和权限有关的属性有:
private List<CandoDto> CandoList;//用户所有可操作的Cando private Map<String, Integer> dataAccessMap; //数据权限 private Map<String, String> myOpeMap;//我的操作map(操作ID,操作ID)