pg启动过程中的那些事三:加载GUC参数
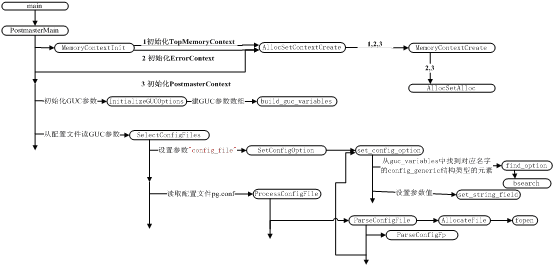
1 先上个图,看一下函数调用过程梗概,中间细节有略
GUC 参数初始化分两步,第一步先读取 buildin/ compiled-in 的 GUC 参数默认值,这里包括全部的 GUC 参数,建立 GUC 参数相关结构变量,第二步读取 postgresql.conf 配置文件中的参数设置之。从上图中能看出来,这个读取并设置 postgresql.conf 中参数的过程还是挺复杂的。
2 初始化 GUC 相关数据结构并取 hardcode/buildin 的参数值。
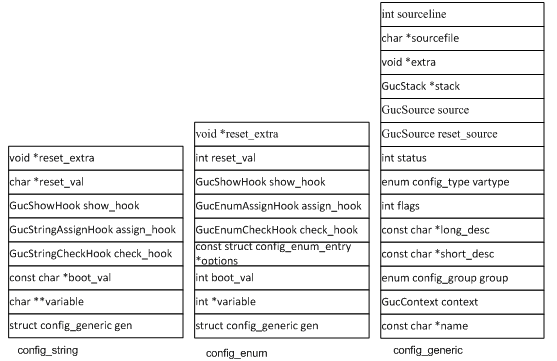
pg 里的GUC 参数按设置的值分五种类型,分别是bool 、int 、real 、string 、enum ,根据这五种类型,定义了五种结构类型,再根据这五种结构,每个类型建一个对应的静态数组,用于存储这些相应类型的GUC 参数。这五种类型是config_bool 、config_int 、config_real 、config_string 、config_enum ,对应的静态数组是ConfigureNamesBool 、ConfigureNamesInt 、ConfigureNamesReal 、ConfigureNamesString 、ConfigureNamesEnum 。具体结构和数组定义见下面。
五个结构定义:
struct config_bool
{
struct config_generic gen;
/* these fields must be set correctly in initial value: */
/* (all but reset_val are constants) */
bool *variable;
bool boot_val;
GucIntCheckHook check_hook;
GucBoolAssignHook assign_hook;
GucShowHook show_hook;
/* variable fields, initialized at runtime: */
bool reset_val;
void * reset_extra
};
struct config_int
{
struct config_generic gen;
/* constant fields, must be set correctly in initial value: */
int *variable;
int boot_val;
int min;
int max;
GucIntCheckHook check_hook;
GucIntAssignHook assign_hook;
GucShowHook show_hook;
/* variable fields, initialized at runtime: */
int reset_val;
void * reset_extra
};
struct config_real
{
struct config_generic gen;
/* constant fields, must be set correctly in initial value: */
double *variable;
double boot_val;
double min;
double max;
GucIntCheckHook check_hook;
GucRealAssignHook assign_hook;
GucShowHook show_hook;
/* variable fields, initialized at runtime: */
double reset_val;
void * reset_extra
};
struct config_string
{
struct config_generic gen;
/* constant fields, must be set correctly in initial value: */
char **variable;
const char *boot_val;
GucIntCheckHook check_hook;
GucStringAssignHook assign_hook;
GucShowHook show_hook;
/* variable fields, initialized at runtime: */
char *reset_val;
void * reset_extra
};
struct config_enum
{
struct config_generic gen;
/* constant fields, must be set correctly in initial value: */
int *variable;
int boot_val;
GucIntCheckHook check_hook;
GucStringAssignHook assign_hook;
GucShowHook show_hook;
/* variable fields, initialized at runtime: */
int reset_val;
void * reset_extra
};
和结构类型对应的五个静态数组:
static struct config_bool ConfigureNamesBool[] =
{
{
{"enable_seqscan", PGC_USERSET, QUERY_TUNING_METHOD,
gettext_noop("Enables the planner's use of sequential-scan plans."),
NULL
},
&enable_seqscan,
true,
NULL, NULL, NULL
},
……
/* End-of-list marker */
{
{NULL, 0, 0, NULL, NULL}, NULL, false, NULL, NULL, NULL
}
};
static struct config_int ConfigureNamesInt[] =
{
{
{"archive_timeout", PGC_SIGHUP, WAL_ARCHIVING,
gettext_noop("Forces a switch to the next xlog file if a "
"new file has not been started within N seconds."),
NULL,
GUC_UNIT_S
},
&XLogArchiveTimeout,
0, 0, INT_MAX,
NULL, NULL, NULL
},
……
/* End-of-list marker */
{
{NULL, 0, 0, NULL, NULL}, NULL, 0, 0, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL
}
};
static struct config_real ConfigureNamesReal[] =
{
{
{"seq_page_cost", PGC_USERSET, QUERY_TUNING_COST,
gettext_noop("Sets the planner's estimate of the cost of a "
"sequentially fetched disk page."),
NULL
},
&seq_page_cost,
DEFAULT_SEQ_PAGE_COST, 0, DBL_MAX,
NULL, NULL, NULL
},
/* End-of-list marker */
{
{NULL, 0, 0, NULL, NULL}, NULL, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, NULL, NULL, NULL
}
};
static struct config_string ConfigureNamesString[] =
{
{
{"archive_command", PGC_SIGHUP, WAL_ARCHIVING,
gettext_noop("Sets the shell command that will be called to archive a WAL file."),
NULL
},
&XLogArchiveCommand,
"",
NULL, NULL, show_archive_command
},
……
/* End-of-list marker */
{
{NULL, 0, 0, NULL, NULL}, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL
}
};
static struct config_enum ConfigureNamesEnum[] =
{
{
{"backslash_quote", PGC_USERSET, COMPAT_OPTIONS_PREVIOUS,
gettext_noop("Sets whether \"\\'\" is allowed in string literals."),
NULL
},
&backslash_quote,
BACKSLASH_QUOTE_SAFE_ENCODING, backslash_quote_options,
NULL, NULL, NULL
},
……
/* End-of-list marker */
{
{NULL, 0, 0, NULL, NULL}, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL
}
};
上面五个结构定义中,每个结构的第一个成员变量都是一个 config_generic 结构的 gen 成员,下面是 config_generic 的结构定义:
struct config_generic
{
/* constant fields, must be set correctly in initial value: */
const char *name; /* name of variable - MUST BE FIRST */
GucContext context; /* context required to set the variable */
enum config_group group; /* to help organize variables by function */
const char *short_desc; /* short desc. of this variable's purpose */
const char *long_desc; /* long desc. of this variable's purpose */
int flags; /* flag bits, see below */
/* variable fields, initialized at runtime: */
enum config_type vartype; /* type of variable (set only at startup) */
int status; /* status bits, see below */
GucSource reset_source; /* source of the reset_value */
GucSource source; /* source of the current actual value */
GucStack *stack; /* stacked outside-of-transaction states */
void *extra; /* "extra" pointer for current actual value */
char *sourcefile; /* file current setting is from (NULL if not
* file) */
int sourceline; /* line in source file */
};
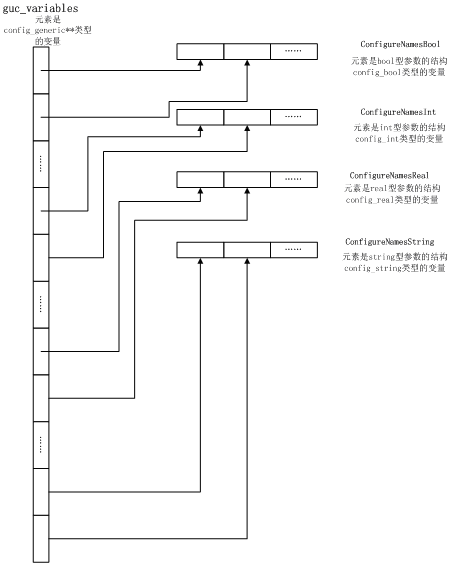
然后,定义一个 config_generic ** 类型的 静态变量数组 guc_variables , 再计算参数总数,所有参数以 config_generic * 类型计算所需内存空间,冗余 25% 内存后 malloc 分配内存空间。 把guc_variables 每一个元素指向ConfigureNamesBool 、ConfigureNamesInt 、ConfigureNamesReal 、ConfigureNamesString 、ConfigureNamesEnum 这五个数组的config_generic 类型成员gen 的地址,然后按照参数名称把所有元素做了快速排序。这个过程中还设置了一些GUC 参数的默认值。
static struct config_generic **guc_variables;
后面查询GUC 参数都是在guc_variables 这个已排序的数组里找。这样GUC 参数的数据结构就搭建完成了,下面看看GUC 参数相关的数据结构图吧。
先把涉及到的结构的图分别列出,再画个这些结构的组织关系示意图。
3 加载 postgresql.conf 参数配置文件里的参数设置
从 main->PostmasterMain->SelectConfigFiles->ProcessConfigFile 开始处理参数配置文件 postgresql.conf , 读取 postgresql.conf 配置文件的调用过程是 ProcessConfigFile -> ParseConfigFile -> AllocateFile->fopen ,最后用fopen 打开文件,其中ProcessConfigFile 、ParseConfigFile 在文件src\backend\utils\misc\guc-file.l 中,AllocateFile 在文件src\backend\storage\file\fd.c 中。
pg 使用 flex 去处理 conf 文件 。 在 ParseConfig File 中把配置文件中的配置项组织成一个链表,调用 set_config_option 检查这些值是否有效,若可以设置就调用 set_config_option 设置这些值。
这里以 "max_connections" 做例子 ,从配置文件读取 "max_connections" ,然后 从 guc_variables 数组 中找元素 " max_connections " , 比较参数结构的 GucContext (枚举类参数能被设置的时机。定义见下面)枚举类型成员 context 和当前时间,看是否可以此刻修改。接着比较参数结构的 GucSource (枚举了当前 GUC 参数设置的来源。除非参数新值的来源等级不小于原参数的来源等级时,新设置才能生效。例如,修改配置文件不能覆盖 postmaster command line 的设置。定义见下面)枚举类型成员 source 和新参数值的来源,看是否可以修改。如果可以, 把 config_generic 结构类型的元素 " max_connections " 类型转换为 config_int 类型,修改variable 成员为新值,修改该参数的来源source 为当前来源PGC_S_FILE ,如果 元素 " max_connections " 的 reset_source <= source ,修改reset_val 成员为新值,修改该参数的reset_source 为当前来源PGC_S_FILE 。
typedef enum
{
PGC_INTERNAL,
PGC_POSTMASTER,
PGC_SIGHUP,
PGC_BACKEND,
PGC_SUSET,
PGC_USERSET
} GucContext;
typedef enum
{
PGC_S_DEFAULT, /* wired-in default */
PGC_S_ENV_VAR, /* postmaster environment variable */
PGC_S_FILE, /* postgresql.conf */
PGC_S_ARGV, /* postmaster command line */
PGC_S_DATABASE, /* per-database setting */
PGC_S_USER, /* per-user setting */
PGC_S_CLIENT, /* from client connection request */
PGC_S_OVERRIDE, /* special case to forcibly set default */
PGC_S_INTERACTIVE, /* dividing line for error reporting */
PGC_S_TEST, /* test per-database or per-user setting */
PGC_S_SESSION /* SET command */
} GucSource