集成 IBM 元数据存储库,第 2 部分: 在 WebSphere Service Registry and Repository 中治理元数据生命周期
通过将您的应用程序与 IBM® Rational® Asset Manager 集成,学习如何支持基于资产的开发。在第 2 部分,您将了解到如何使用 WebSphere® Service Registry and Repository 定义和治理元数据生命周期治理。
本文将以 WebSphere Service Registry and Repository(此后简称为 Service Registry)治理概要文件为例描述生命周期定义和治理策略,以及它们在服务治理中的应用。本文还介绍了一种称为 Service Registry Advanced Lifecycle Edition (Service Registry ALE) 的集成元数据解决方案,它将遍历设计时和运行时生命周期。
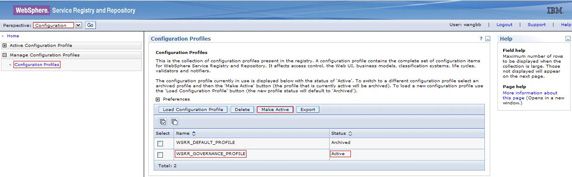
Service Registry V6.0.2 引入了配置概要文件的概念,该文件包含一组完整的 Service Registry 配置文件。它的功能在随后的版本中逐渐扩展,并且在 Service Registry V6.2 中,您可以定制一组配置文件,包括访问控制、业务模型系统、分类系统、生命周期、Web 用户接口、用户定义的验证符(validator)、修饰符(modifier)和通知符(notifier)。Service Registry V6.2 提供了一个默认概要文件,以及用于真实应用程序环境的治理概要文件。这两种文件均在安装时装载。要查看配置概要文件及其状态,如 图 1 所示,切换到 Service Registry Web 控制台的 Configuration 透视图,然后选择 Manage Configuration Profiles => Configuration Profiles 。您可以将任意数量的概要文件装载到 Service Registry,但是在给定的时间,只有一个概要文件可以处于 Active 状态。所有其他文件将处于 Archived 状态。要使一个不同的概要文件变为活动状态,选择该概要文件并单击 Make Active 。在导航树中,展开 Active Configuration Profile ,您可以看到活动概要文件中定义的所有项,如图 1 所示。
(查看图 1 的放大图 。)
Service Registry V6.2 治理概要文件是一组 Service Registry 配置工件,包括业务对象、分类系统、生命周期以及支持基本 SOA 治理的治理策略。这个概要文件的目的是作为 Service Registry SOA 治理的起始点。您可以修改业务模型、生命周期和策略来满足自己的需求。
本节将介绍治理概要文件的生命周期和治理策略,作为一项重要的治理功能,该文件在服务的整个生命周期中实现了服务的提升。下一小节将详细解释如何使用它们。
对于被治理的元数据,生命周期模型使用一个业务状态机来描述生命周期状态和它们之间的转换。使用 WebSphere Integration Developer (Integration Developer) 中的可视编辑器。
在默认概要文件中,只有一个 SOA 生命周期受到支持。然而,在真实的应用程序中,Service Registry 中的所有类型的元数据不可能都遵循这一种生命周期。因此,治理概要文件提供了一个符合状态机,其中,各种类型的元数据可以遵循不同的子状态机。
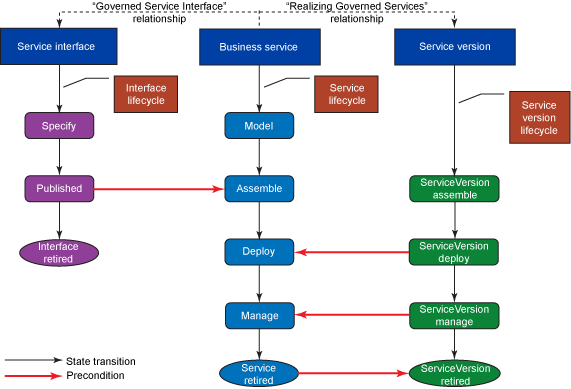
使用 Life Cycle Configuration 视图,如 图 2 所示,您可以查看和更新生命周期的内容,并将文件导入到 Integration Developer 以在图形视图中查看它,如 图 3 所示。最初始的状态为 Create ,终止状态为 Completed 。有 4 种复合状态:InterfaceLifecycle 、PolicyLifecycle 、ServiceVersionLifecycle 和 ServiceLifecycle 。每个复合状态都包括一个子状态机。
图 2. 治理概要文件中的生命周期定义 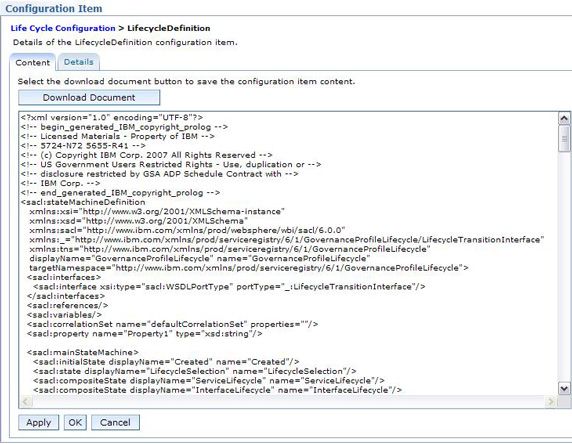
图 3. Integration Developer 图形视图中的生命周期定义 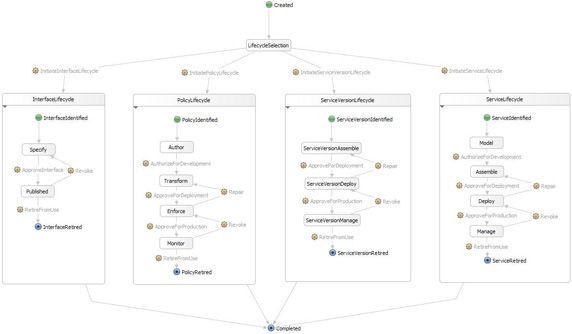
(查看图 3 的放大图 )。
查看以上的业务状态机后,您可能会产生两个疑问:
- 某个子状态机适合哪种或哪些类型的实体?
- 在两个状态之间执行转换时,元数据是否需要满足一些必要的条件?
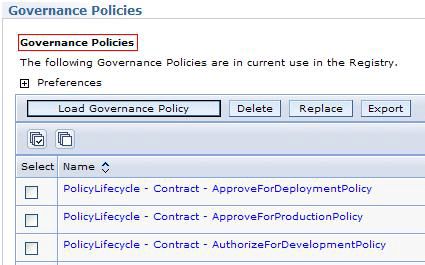
这两个问题的答案都可以从治理策略中定义。您可以从 Service Registry Web 控制台 Configuration 透视图查看和定制这些设置,只需要选择 Active Configuration Profile => Plug-ins => Governance Policies ,如 图 4 所示。
每个复合状态必须有一个策略可以定义该状态所适合的类型。例如,ServiceInterfaceLifecycle - InitiatePolicy 治理策略描述了适用于 ServiceInterfaceLifecycle 的必需条件。清单 1 展示了 ServiceInterfaceLifecycle - InitiatePolicy 治理策略的部分内容。
清单 1. ServiceInterfaceLifecycle - InitiatePolicy 治理策略的部分内容
1 <wsp:Policy xmlns:wsp="http://www.w3.org/ns/ws-policy" … > 2 <wsrrgp:ValidatorPolicy wsrrgp:name="ServiceInterfaceLifecycle 3 - Initiate Policy 4 … 5 <wsrrgp:WSRROperationFilter> 6 7 <wsrrgp:WSRROperation>MAKE_GOVERNABLE</wsrrgp:WSRROperation> 8 <wsrrgp:WSRROperation>TRANSITION</wsrrgp:WSRROperation> 9 </wsrrgp:WSRROperationFilter> 10 <wsrrgp:TransitionOperationFilter> 11 <wsrrgp:TransitionOperation> 12 http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry/6/1/GovernanceProfileLifecycle 13 #InitiateInterfaceLifecycle 14 </wsrrgp:TransitionOperation> 15 </wsrrgp:TransitionOperationFilter> 16 <wsrrgp:EntityAssertionPolicy> 17 <wsp:Policy wsrr:policyClass="EntityAssertionClass" 18 wsrr:policyClassDomain="http://www.ibm.com.policy/GovernancePolicyDomain"> 19 <wsrrgp:AnyOfAssertion 20 wsrrgp:name="GovernanceProfileLifecycleInitializationPolicy. 21 ServiceInterfaceLifecycleEntityAssertion"> 22 <wsrrgp:EntityAssertion 23 wsrrgp:name="GovernanceProfileLifecycleInitializationPolicy. 24 ServiceInterfaceLifecycleEntityAssertion" 25 wsrrgp:entityType="XSDDocument" /> 26 <wsrrgp:EntityAssertion 27 wsrrgp:name="GovernanceProfileLifecycleInitializationPolicy. 28 ServiceInterfaceLifecycleEntityAssertion" 29 wsrrgp:primaryType="http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry 30 /6/1/TechnicalModel#ServiceInterface" /> 31 <wsrrgp:EntityAssertion 32 wsrrgp:name="GovernanceProfileLifecycleInitializationPolicy. 33 ServiceInterfaceLifecycleEntityAssertion" 34 wsrrgp:primaryType="http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry 35 /6/1/TechnicalModel#ServiceBinding" /> 36 <wsrrgp:EntityAssertion 37 wsrrgp:name="GovernanceProfileLifecycleInitializationPolicy. 38 ServiceInterfaceLifecycleEntityAssertion" 39 wsrrgp:primaryType="http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry 40 /6/1/TechnicalModel#MessageSchema" /> 41 </wsrrgp:AnyOfAssertion> 42 </wsp:Policy> 43 </wsrrgp:EntityAssertionPolicy> 44 … 45 </wsrrgp:ValidatorPolicy> 46 </wsp:Policy> |
- 行 5-9 定义
WSRROperationFilter并指定只有MAKE_GOVERNABLE和TRANSITION操作适合该策略。MAKE_GOVERNABLE使未治理的元数据得到治理,而TRANSITION转换被治理的元数据的状态。 - 行 10-14 表示策略适合
InitiateInterfaceLifecycle转换,后者进入InterfaceLifecycle子状态机(参见 图 2 )。http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry/6/1/GovernanceProfileLifecycle#InitiateInterfaceLifecycle指定相应的转换分类 URL。 - 行 16-43 描述
ServiceInterfaceLifecycle限制为以下四种类型的元数据:XSDDocument、ServiceInterface、ServiceBinding和MessageSchema。
对于与复合状态兼容的每一种元数据类型,子状态机中的每一个转换都有一个限制策略。例如,ServiceInterfaceLifecycle - ServiceInterface - ApproveInterfacePolicy 治理策略描述了对 Service Interface 类型的元数据执行 ApproveInterface 转换时的必需条件。清单 2 展示了 ServiceInterfaceLifecycle - ServiceInterface - ApproveInterfacePolicy 治理策略的部分内容。
清单 2. ServiceInterfaceLifecycle - ServiceInterface - ApproveInterfacePolicy 治理策略的部分内容
1 <wsp:Policy xmlns:wsp="http://www.w3.org/ns/ws-policy" ... > 2 <wsrrgp:ValidatorPolicy wsrrgp:name="ServiceInterface Lifecycle 3 - ServiceInterface - ApproveInterface Policy"> 4 <wsp:Policy … wsp:Name="urn:ServiceInterfaceLifecycle_ServiceInterface_ 5 ApproveInterfacePolicy"> 6 … 7 <wsrrgp:TransitionOperationFilter> 8 <wsrrgp:TransitionOperation> 9 http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry/6/1/GovernanceProfileLifecycle 10 #ApproveInterface 11 </wsrrgp:TransitionOperation> 12 </wsrrgp:TransitionOperationFilter> 13 <wsrrgp:EntityAssertionPolicy> 14 <wsp:Policy …> 15 <wsrrgp:RelationshipAssertion 16 wsrrgp:relationshipName="wsrrtm_authoritativeWSDLs" 17 wsrrgp:minCardinality="1" wsrrgp:maxCardinality="1" 18 wsrrgp:name="ServiceInterfaceLifecyclePolicy. 19 ExactlyOneAuthoritativeInterfaceWSDLAssertion"> 20 <wsrrgp:EntityAssertion wsrrgp:entityType="WSDLDocument" 21 wsrrgp:name="ServiceInterfaceLifecyclePolicy. 22 ExactlyOneAuthoritativeInterfaceWSDLAssertion" /> 23 </wsrrgp:RelationshipAssertion> 24 </wsp:Policy> 25 </wsrrgp:EntityAssertionPolicy> 26 </wsp:Policy> 27 </wsrrgp:ValidatorPolicy> 28 </wsp:Policy> |
行 15-23 定义了 Service Interface 类型的元数据必须满足的条件,否则转换将会失败。此外,元数据应当对一个(且仅有一个)WSDL 文档有一个 wsrrtm_authoritativeWSDLs 关系。
Service Registry 可用于跨 SOA 生命周期的所有阶段使用。让我们查看一个场景,它演示了如何使用一个复合状态机和治理策略实现元数据治理。该场景涉及治理概要文件中指定的多种生命周期类型,包括 InterfaceLifecycle 、ServiceVersionLifecycle 和 ServiceLifecycle 。
治理概要文件可以进行轻松地定制以满足用户需求,比如修改生命周期或修改治理策略。在本例中,我们将修改 ServiceLifecycle - BusinessService - ApproveForDeploymentPolicy 治理策略,如 清单 3 所示。添加了粗体显示的部分,用来放宽限制,具有 wsrrgp:ClassificationAssertion 下两个类别的 Business Service 的条件可以放宽为两者中的任意一个。
有关定制治理概要文件的更多信息,请参考 Customize the WebSphere Service Registry and Repository 治理概要文件 。
清单 3. 定制 ServiceLifecycle – BusinessService - ApproveForDeploymentPolicy
<wsrrgp:RelationshipAssertion wsrrgp:relationshipName="wsrrgp_realizingServices"
wsrrgp:minCardinality="1"
wsrrgp:name="ServiceLifecyclePolicy.DeployedServiceVersionAvailableAssertion">
<wsrrgp:EntityAssertion wsrrgp:entityType="GenericObject"
wsrrgp:name="ServiceLifecyclePolicy.DeployedServiceVersionAvailableAssertion">
<wsrrgp:ClassificationAssertion wsrrgp:combinationCode="Any"
>
<wsrrgp:Classification>
http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry/6/1/GovernanceProfileLifecycle
#ServiceVersionDeploy
</wsrrgp:Classification>
<wsrrgp:Classification>
http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/serviceregistry/6/1/GovernanceProfileLifecycle
#ServiceVersionManage
</wsrrgp:Classification>
</wsrrgp:ClassificationAssertion>
</wsrrgp:EntityAssertion>
</wsrrgp:RelationshipAssertion>
|
服务描述实体是 Service Registry 提供的信息模型中的一个元数据类别,其中包括物理文档、逻辑派生和一般对象。要查看这些内容,切换到 Service Registry Web 控制台中的 GP Administrator 透视图。
- 物理文档:描述设备的实际文档,比如 WSDL 文档。要查看物理文档的类型,在导航树中展开 Service Documents 。
- 逻辑派生:Service Registry 自动解析物理文档来生成派生的对象,以表示文档内的结构,比如派生自 WSDL 的
portType定义。要查看逻辑派生类型,在导航树中展开 Service Metadata 。 - 一般对象:一般对象表示信息模型中任何在 Service Registry 中没有物理文档的内容。要查看一般对象,选择 Business Metadata => Concepts 。
在我们的场景中,使用了三种类型的一般对象:Business Service、Service Interface 和 Service Version。图 5 概述了三者之间的关系及其各自的生命周期。
下面的场景描述步骤中将介绍更详细的内容。我们将以 math 服务为例。该服务是一个简单的数学计算服务,提供了加法和减法操作。
完成以下步骤来建模服务。参考 Service Registry 配置概要文件 在 Service Registry Web 控制台中激活 WSRR_GOVERNANCE_PROFILE 。
- 选择 Business Metadata => Business Service View => Organizations 并创建一个名为
Sample的组织。在 Governance 对话中单击 Sample ,然后单击 Govern 来使其变得可治理。 - 要创建表示 math 服务的名为
MathService的一般对象,切换到 GP Administrator 透视图,并选择 Business Metadata => Business Service View => Business Services 。创建一个名为MathService的业务服务。在 Details 对话框中,单击 Edit Relationships ,将 Sample 添加到MathService的 Owning Organization 关系中,然后单击 Finish 。 - 单击 Edit Classification 并选择 Governance Profile Taxonomy => Business Domain => Finance ,然后将其添加到 MathService.wsdl,表示 math 服务应用于金融行业。
- 接下来,需要开发 math 服务端口 MathInterface.wsdl。MathInterface.wsdl 定义了 WSDL
portType(参见 SampleWSDLs.zip )。两个操作add_X_to_Y和subtract_X_from_Y代表数学中的加法和减法。 - 通过选择 Sevice Documents => WSDL Documents 发布 MathInterface.wsdl,以装载 MathInterface.wsdl。作为逻辑派生(
PortType)的 Math(此后称为Math(PT))和作为一般对象(Service Interface)的 Math(此后称为Math(SI))将自动生成;Math(SI) 与 MathInterface.wsdl 有一个Authoritative WSDLS关系,与 Math(PT) 有一个Interface Declarations关系。选择 Business Metadata => Governance Service View => Service Interfaces ,并单击 Math(SI) 在元数据的 Details 视图中查看依赖关系。
- 现在您需要将
Service Interface变得可治理并设置状态以建模阶段。切换到 Math(SI) 的 Governance 选项卡,然后从 Initial state transitions 列表中选择Initiate Interface Life Cycle,然后单击 Govern 。Math(SI) 的治理状态切换为Specify状态。根据 清单 1 中的治理策略中的分析,我们了解到 Math(SI) 的生命周期被授权为遵循InterfaceLifecycle子状态机。根据 清单 2 中的治理策略,Math(SI) 满足ApproveInterface转换的先决条件,因此您可以单击 Transition 来将治理状态转换为Published,如 图 6 所示。MathInterface.wsdl 的治理状态也是Published,因为它位于和 Math(SI) 相同的治理组中。
图 6. 将服务接口的状态设置为 Published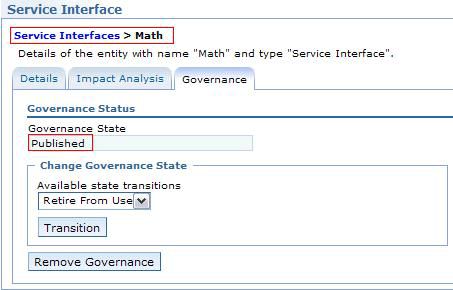
完成下面的步骤来组装服务:
- 开发 math 服务的绑定 MathBinding.wsdl。MathBinding.wsdl 定义了 WSDL 绑定,后者将导入 MathInterface.wsdl(参见 SampleWSDLs.zip )。
- 按照上面的步骤 5,将 MathBinding.wsdl 发布到 Service Registry。由于 MathInterface.wsdl 已经存在于 Service Registry 中了,满足导入关系,因此 MathBinding.wsdl 发布将会成功。
MathSoapBinding(此后称为MathSoapBinding(B))是逻辑派生的绑定,而MathSoapBinding(此后称为MathSoapBinding(SB))是一般对象的 Service Binding,两者均自动生成;MathSoapBinding(SB)与 MathBinding.wsdl 有一个Authoritative WSDLS关系,与MathSoapBinding(B)有一个Binding Declarations关系,与Math(SI)有一个Associated Interface关系。选择 Business Metadata => Governance Service View => Service Bindings ,并单击 MathSoapBinding(SB) 在元数据的 Details 视图中查看依赖关系。
-
Service Binding的生命周期被授权执行InterfaceLifecycle子状态机。将MathSoapBinding(SB)变为可治理并将治理状态转换为Published,如步骤 6 所示。 - 将
Math(SI)添加到MathService的Governed Service Interface关系。Business Service的生命周期被授权以遵循ServiceLifecycle子状态机,您可以在治理策略中查看。(参考 Service Registry 治理概要文件概述 中的样例)。将MathService变为可治理并将治理状态转换为 Assemble ,如 图 7 所示,表示该服务已经完全组装好了。
图 7. 将业务服务的状态设置为 assemble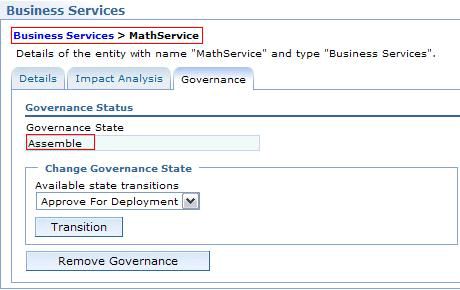
执行下面的步骤来部署服务:
- 开发 math 服务的端点。MathService.wsdl 定义了 WSDL 端点,这是用于访问 math 服务的 SOAP 地址。MathService.wsdl 导入了 MathBinding.wsdl(参见 SampleWSDLs.zip )。您可以使用 下载 提供的样例 WSDL,或参考 Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 2.0 Part 1: Core Language 获得有关编写 WSDL 的更多信息。
- 发布并对 MathService.wsdl 进行分类。向之前一样将 MathService.wsdl 发布到 Service Registry。作为逻辑派生(Service)的
MathService和作为一般对象(Service Version)的MathService(此后称为MathService(SV))都被自动创建。将一个 Test 分类添加到MathService.wsdl,如 图 8 所示,表示 math 服务被部署到一个测试环境应用服务器中。
图 8. 向 WSDL 添加一个 Test 分类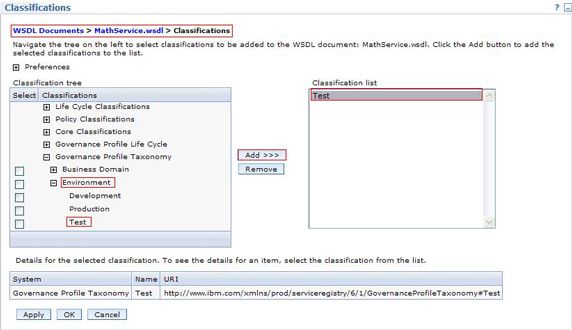
- 根据治理策略,Service Version 的生命周期被授权以遵循
ServiceVersionLifecycle子状态机。将MathService(SV)变为可治理(参见 图 9 )并将治理状态转换到 Service Version Deploy (参见 图 10 ),以表示 math 服务已得到部署。
图 9. Service Version 遵循 ServiceVersionLifecycle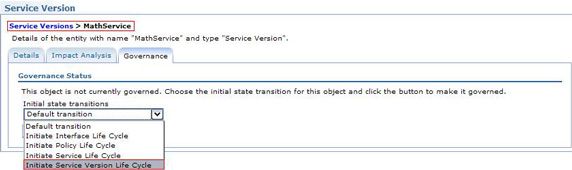
图 10. 将 service version 的状态设置为 Service Version Deploy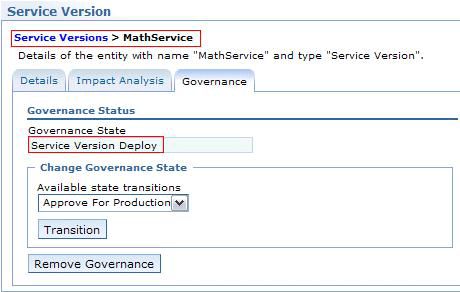
如果 MathService.wsdl 没有被分类为 Test ,那么在将
MathService(SV)的治理状态从Service Version Assemble转换到Service Version Deploy时,您将看到 图 11 所示的错误。因为MathService(SV)至少应该具有一个类别为 Test 的相关端点 WSDL。您可以从ServiceVersionLifecycle - ServiceVersion - ApproveForDeploymentPolicy治理策略获得这个相关端点。
图 11. 状态转换错误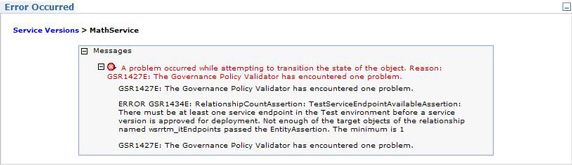
- 将
MathService(SV)添加到MathService的Realizing Governed Services关系。随后,将MathService的治理状态转换为Deploy。
执行下面的步骤,对服务进行管理:
- 对 MathService.wsdl 进行分类。当 math 服务在测试环境中正常运行后,可以将其部署到生产环境中,以真正使用它。移除
Test分类并为 MathService.wsdl 添加Production分类。 - 治理 Service Version 和 Business Service。将
MathService(SV)的治理状态转换为Service Version Manage,并将MathService转换为Manage,这表示 math 服务已经投入使用且进入了管理阶段。 - 卸载 math 服务之后,将
MathService的治理状态转换为Service Retired,并将MathService(SV)转换为Service Version Retired。注意,必须首先执行MathService的转换。如果顺序颠倒的话,那么在执行MathService(SV)转换时会得到一个错误(如 图 12 所示)。治理策略有一个限制,意味着只有在与MathService(SV)相关的Business ServiceMathService位于Service Retired治理状态时,MathService(SV)的转换才能得到执行。
图 12. 状态转换错误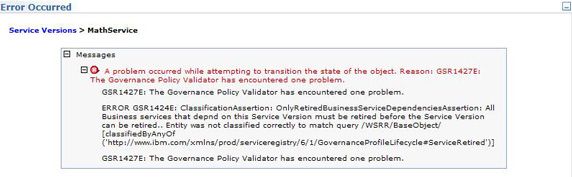
使用 Service Registry ALE 进行生命周期治理
Service Registry 可以与其他一些 IBM 产品集成以在整个生命周期(从设计时到运行时)中对元数据进行治理。Service Registry ALE V6.2 包含 Service Registry V6.2 和 IBM Rational® Asset Manager V7.1,它们两者共同合作,对从创建到使用的服务生命周期进行治理。在本节中,我们将描述如何使用 Service Registry ALE,特别是如何配置同步和 Service Registry 与 Rational Asset Manager 之间的集成,从而实现整个生命周期期间的元数据治理。
同步配置是在 Rational Asset Manager 中完成的。选择一个 Community , 比如 WSRR ALE ,然后创建一个到 Service Registry 服务器的新连接,如 图 13 所示。使用以下信息创建该连接:
- URL :Service Registry 服务器 URL。
- Login 和 Password :用于 Service Registry 安全性。
- Type :Publish 允许从 RAM 到 Service Registry 的同步;Synchronize 是反向的同步方向(从 Service Registry 到 RAM);Publish and Synchronize 同时支持两种方向。
完成配置后,单击 Test Connection 以确保修改生效。
图 13. 在 Rational Asset Manager 中新建与 Service Registry 服务器的连接 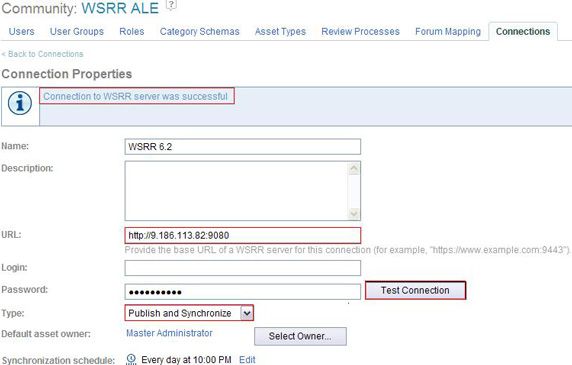
Rational Asset Manager 管理可重用资产的信息,特别是在设计时。完成下面的步骤,在设计时实现 ALE 解决方案。
- 举例而言,开发一个
AddressBook服务,该服务用于存储和查找地址。在 Rational Asset Manager Web 控制台中,使用名为 AddressBook.wsdl 的工件服务 WSDL 提交资产AddressBook(参见 SampleWSDLs.zip )。有关资产和工件概念的更多信息,请参考本系列的 第 1 部分 。资产包含了有关AddressBook服务的所有相关细节,表示该服务已经完成了全部部署。 - 对资产
AddressBook单击 Publish to service registry ,以将资产从 Rational Asset Manager 同步到 Service Registry,如 图 14 所示。注意,WSRR ALE community 中只有经过同步配置的资产可以被发布到 Service Registry。而且,同步将针对一个资产手动执行,而不是自动执行或是同时对多个资产执行。由于 Service Registry 是一个运行时元数据存储库,对元数据应当进行严格仔细的管理。
图 14. 将资产从 RAM 同步到 Service Registry
(参见图 14 的放大图 )。
- 选择要发布的工件,选中目的地,然后在 Categorize 页面中添加分类,在 Associate 页面中,在 Service Registry 中搜索和选择元数据,然后发布 AddressBook.wsdl。当第一次从 Service Registry 执行同步后,Rational Asset Manager 具有分类系统的本地副本,因此您现在可以添加分类。治理概要文件生命周期是 Service Registry 中的一个分类系统。选择并添加 State/Interface Life Cycle/Published ,如 图 15 所示。
图 15. 在将资产从 Rational Asset Manager 发布到 Service Registry 时添加分类
- 在成功执行同步后,打开 Service Registry Web 控制台以查看创建的新元数据:一个一般对象
AddressBook,表现为RationalAssetManagerAsset(此后称为 AddressBook(RAMA)),表示 Rational Asset Manager 中的AddressBook资产;一个 WSDL 文档 AddressBook.wsdl,与 Rational Asset Manager 中选择的工件 AddressBook.wsdl 对应;其他一般对象,比如AddressBook、AddressBookBinding、AddressBookPort和AddressBookService,将在发布 WSDL 文档时自动生成。图 16 展示了AddressBook(RAMA)的细节。
图 16.AddressBook(RAMA) 细节
下面介绍了一些在设计时从 Rational Asset Manager 到 Service Registry 之间执行同步的一般技巧:
- 在资产同步期间使用 Service Registry V6.2 分类系统。
- 提供在 Service Registry 中搜索元数据并向资产添加关系的功能。
- 在执行同步后,资产将与一般对象对应,而工件将与文档对应,并且资产和工件的关系将映射到一般对象中添加的关系。
Service Registry 管理元数据信息(特别是在运行时),比如服务动态查询或服务治理。在运行时,服务将经过测试、生产直至最后的退休阶段。在 Service Registry 中,Service Version 将继续通过 Service Version Deploy 、Service Version Manage 和 Service Version Retired 阶段得到治理。
从 Service Registry 到 Rational Asset Manager 的同步可以手动实现,也可以在指定的时间自动实现。要手动实现同步,打开 Rational Asset Manager Web 控制台并对一个已配置的 Service Registry 服务器单击 Synchronize 。您将看到如 图 17 所示的同步结果。
图 17. 从 Service Registry 到 RAM 的同步 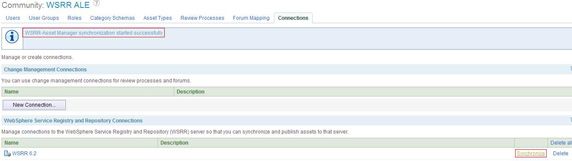
(查看图 17 的放大图 )
要在指定的时间自动实现同步,您需要在配置阶段使用 Synchronization schedule 设定时间(参见 图 13 )。
完成从 Service Registry 到 Rational Asset Manager 的同步后,将在 Rational Asset Manager 的 WSRR ALE community 中创建其他 AddressBook 资产。在 General Details 页面,如 图 18 所示,BsrURI 表示 Service Registry 中的惟一 ID;Link 指向 Service Registry Web 控制台中的相应元数据 AddressBook(RAMA) ;而 Publish by 与设计时提交的 AddressBook 资产相关。通过使用这种方法,您不仅集成了 Rational Asset Manager 和 Service Registry 中的元数据,还在设计时和运行时将它们关联了起来。
图 18. 从 Service Registry 到 Rational Asset Manager 的 AddressBook 细节 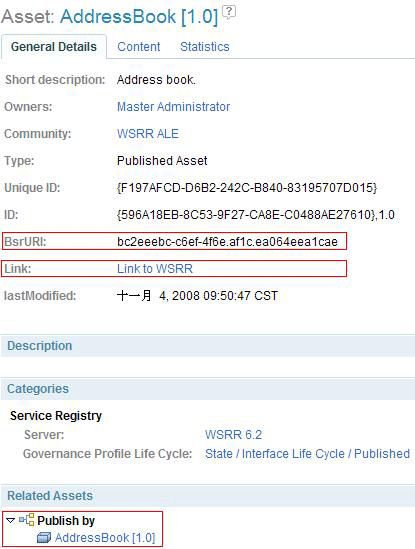
此外,其他不在 Rational Asset Manager 中的元数据可以在此时同步。例如,Service Registry 中的 MathInterface.wsdl、MathBinding.wsdl 和 MathService.wsdl 被作为三个资产发布到 Rational Asset Manager。在资产的 General Details 页面(比如 图 19 所示的 MathBinding.wsdl 资产),显示了 BsrURI 、Governance State 、Governance Profile Life Cycle 和关系,以及一个连接到 Service Registry Web 控制台中的原始元数据的链接。通过这种方式,Service Registry 中托管的元数据就可以在 Rational Asset Manager 设计时存储库中重用。
图 19. 从 Service Registry 到 Rational Asset Manager 的 MathBinding.wsdl 细节 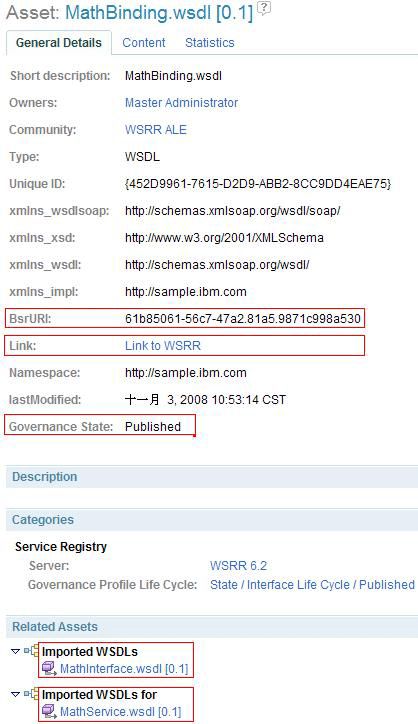
最后,在运行时从 Service Registry 到 Rational Asset Manager 的同步包括以下内容:
- Service Registry 中的一个 WSDL 文档与 Rational Asset Manager 中的资产相对应;
- 此前从 Rational Asset Manager 同步到 Service Registry 的资产被重新发布到 Rational Asset Manager,而重新发布的资产与 Rational Asset Manager 中的原始资产建立了 Publish by 关系;
- Service Registry 中的一个文档关系映射到一个资产关系;
- 一个治理周期可以被同步到 Rational Asset Manager;
- 如果删除 Service Registry 中的一个文档,Rational Asset Manager 中的对应资产也将在下一次同步中删除。
本文介绍了 Service Registry 治理概要文件中定义的生命周期和治理策略,提供了一个场景展示如何使用它们,并提供了对 Service Registry ALE 的介绍,Service Registry ALE 用于在设计和运行时在 Service Registry 和 Rational Asset Manager 之间进行集成元数据管理。
| 样例 WSDL 文件 | SampleWSDLs.zip | 3KB | HTTP |
学习
- 适用于面向服务架构的资产生命周期管理, Grant Larsen and Jack Wilber (developerWorks,2005):本文审视了在开发面向服务架构(SOA)解决方案期间对资产生命周期管理实践、工具和标准的应用。有效的服务生命周期管理使组织能够应用工具和方法来治理、管理、应用以及重用这些资产,从而增强 SOA 开发的优势。
- 定制 WebSphere Service Registry and Repository 治理概要文件 (developerWorks,2007):提供治理概要文件的概述,并描述了如何对其进行定制。
- WebSphere Service Registry and Repository Version 6.2 信息中心 :获得完整的产品文档。
- Multiple lifecycles with WebSphere Service Registry and Repository (developerWorks,2007):本文介绍如何使用 Websphere Service Registry and Repository 在单个状态机定义中支持多个生命周期。
- Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 2.0 Part 1: Core Language :WSDL 规范。
- IBM WebSphere Service Registry and Repository Advanced Lifecycle Edition, V6.2 :获得产品信息。
- developerWorks BPM 专区 :获得有关 IBM BPM 解决方案的最新技术资源,包括下载、演示、文章、教程、活动、网络广播等等。
- IBM developerWorks 中国 WebSphere 专区 :为使用 WebSphere 产品的开发人员准备的技术信息和资料。这里提供产品下载、how-to 信息、支持资源以及免费技术库,包含 2000 多份技术文章、教程、最佳实践、IBM Redbook 和在线产品手册。
原文:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/websphere/library/techarticles/1002_wang/1002_wang.html