转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kentyshang/archive/2007/08/16/858367.html
swt的常用组件button ,text ,combo,list ,还有一些容器类composite ,group,这里选择几个,列写简单的用法
不写解释了,因为代码很简单,而且代码上的注释足以说明.
1,combo 和text

package com.test;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionAdapter;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionEvent;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Combo;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.List;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
public class CTShow {
private static List list;
private static Combo combo;
private static Text text;
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Display display = Display.getDefault();
final Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setSize(478, 120);
shell.setText("combo and text");
shell.open();
//构造text
text = new Text(shell, SWT.BORDER);
text.setBounds(160, 34, 281, 20);
//构造combo
combo = new Combo(shell, SWT.NONE);
combo.setItems(new String[] {"one", "two", "three", "four"});
combo.setData("one", "1");
combo.setData("two", "2");
combo.setData("three", "3");
combo.setData("four", "4");
combo.setBounds(28, 34, 102, 20);
//添加监听器
combo.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter(){
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e){
String selText = combo.getText();
String selValue = (String)combo.getData(selText);
text.setText("text: " + selText + " value: " + selValue);
}});
shell.layout();
//消息循环
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
}
效果如图:
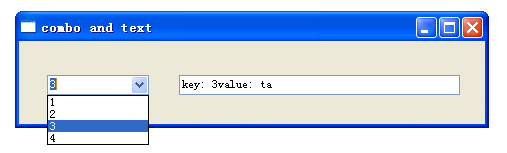

2,list、 button 、messagebox
package com.test;
import org.eclipse.jface.dialogs.MessageDialog;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionAdapter;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionEvent;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.List;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
public class LBMShow {
private static List list;
/**
* Launch the application
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Display display = Display.getDefault();
final Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setSize(192, 217);
shell.setText("list and button and messagebox");
//
shell.open();
//构造list
list = new List(shell, SWT.BORDER|SWT.MULTI|SWT.V_SCROLL);
list.setItems(new String[] {"语文", "数学", "英语", "物理", "化学"});
list.setData("化学", "HX");
list.setData("物理", "WL");
list.setData("语文", "YW");
list.setData("数学", "SX");
list.setData("英语", "YY");
list.setBounds(29, 25, 100, 75);
//构造button
final Button button = new Button(shell, SWT.NONE);
button.setText("提示");
button.setBounds(48, 121, 58, 22);
//添加监听器
button.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter(){
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e){
for (String str : list.getSelection()) {
//messagebox提示
MessageDialog.openInformation(null, null, str);
}
}
});
shell.layout();
//消息循环
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
}
效果:
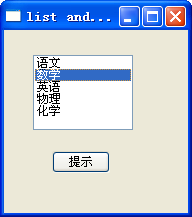

3,group组

package com.test;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Group;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
public class GroupShow {
private static Text text;
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Display display = Display.getDefault();
Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setText("group");
shell.open();
//构造group
final Group group = new Group(shell, SWT.NONE);
group.setText(" 组 ");
group.setBounds(41, 28, 143, 100);
//把按钮放在group中,注意new Button(group这里
final Button button = new Button(group, SWT.NONE);
button.setText("按钮");
button.setBounds(42, 59, 48, 22);
//构造text
text = new Text(group, SWT.BORDER);
text.setBounds(32, 28, 80, 25);
//
shell.layout();
while(!shell.isDisposed()){
if (!display.readAndDispatch()){
display.sleep();
}
}
}
}
效果;
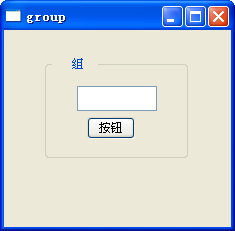
====================================================
1,简单显示,表格的式样见注释中的内容
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.TableViewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.TableViewer;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;

 public
class
TestTableViewer
{
public
class
TestTableViewer
{
 privatestaticTabletable;
privatestaticTabletable;
 /**
/**
 *Launchtheapplication
*Launchtheapplication
 *@paramargs
*@paramargs
 */
*/
 publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
 finalDisplaydisplay=Display.getDefault();
finalDisplaydisplay=Display.getDefault();
 finalShellshell=newShell();
finalShellshell=newShell();
 shell.setSize(500,375);
shell.setSize(500,375);
 shell.setText("SWTApplication");
shell.setText("SWTApplication");
 //注意这里,SWT.NULTI代表可以选择多行,SWT.FULL_SELECTION代表可以整行选择,SWT.BORDER边框,SWT.V_SCROLL ,SWT.H_SCROLL滚动条
//注意这里,SWT.NULTI代表可以选择多行,SWT.FULL_SELECTION代表可以整行选择,SWT.BORDER边框,SWT.V_SCROLL ,SWT.H_SCROLL滚动条
 finalTableViewertableViewer=newTableViewer(shell,SWT.MULTI|SWT.FULL_SELECTION|SWT.BORDER|SWT.V_SCROLL|SWT.H_SCROLL);
finalTableViewertableViewer=newTableViewer(shell,SWT.MULTI|SWT.FULL_SELECTION|SWT.BORDER|SWT.V_SCROLL|SWT.H_SCROLL);

 table=tableViewer.getTable();
table=tableViewer.getTable();
 table.setLinesVisible(true);
table.setLinesVisible(true);
 table.setHeaderVisible(true);
table.setHeaderVisible(true);
 table.setBounds(97,79,373,154);
table.setBounds(97,79,373,154);

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn.setWidth(39);
newColumnTableColumn.setWidth(39);
 newColumnTableColumn.setText("ID");
newColumnTableColumn.setText("ID");

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_1=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_1=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_1.setWidth(85);
newColumnTableColumn_1.setWidth(85);
 newColumnTableColumn_1.setText("姓名");
newColumnTableColumn_1.setText("姓名");

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_2=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_2=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_2.setWidth(41);
newColumnTableColumn_2.setWidth(41);
 newColumnTableColumn_2.setText("性别");
newColumnTableColumn_2.setText("性别");

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_3=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_3=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_3.setWidth(43);
newColumnTableColumn_3.setWidth(43);
 newColumnTableColumn_3.setText("年龄");
newColumnTableColumn_3.setText("年龄");

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_4=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_4=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_4.setWidth(126);
newColumnTableColumn_4.setWidth(126);
 newColumnTableColumn_4.setText("创建日期");
newColumnTableColumn_4.setText("创建日期");

 shell.open();
shell.open();
 while(!shell.isDisposed()){
while(!shell.isDisposed()){
 if(!display.readAndDispatch())
if(!display.readAndDispatch())
 display.sleep();
display.sleep();
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
2,加入布局
显示的效果不好,我们要加入布局,让view填充整个画面在shell.open()后加上
ok,效果达到
3,为TableViewer加上数据,光突突的样子不好看。这里是demo所以不再从数据库里边取数据了。自己构造一个List用来做数据。实际使用中也是这么使用,不过不同的是这里是随意构造的list,而显示实际使用中是从数据库取出数据构造list.
(1)构造一个people类,同时给People类提供一个构造假数据的方法getPeople()
 import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.ArrayList;
 import
java.util.Date;
import
java.util.Date;
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List;
 public
class
People
{
public
class
People
{
 privateLongid;
privateLongid;
 privateStringname;
privateStringname;
 privateStringsex;
privateStringsex;
 privateIntegerage;
privateIntegerage;
 privateDatecreateDate;
privateDatecreateDate;
 publicPeople(Longid,Stringname,Stringsex,Integerage,DatecreateDate){
publicPeople(Longid,Stringname,Stringsex,Integerage,DatecreateDate){
 this.id=id;
this.id=id;
 this.name=name;
this.name=name;
 this.sex=sex;
this.sex=sex;
 this.age=age;
this.age=age;
 this.createDate=createDate;
this.createDate=createDate;
 }
}
 publicIntegergetAge(){
publicIntegergetAge(){
 returnage;
returnage;
 }
}
 publicvoidsetAge(Integerage){
publicvoidsetAge(Integerage){
 this.age=age;
this.age=age;
 }
}
 publicDategetCreateDate(){
publicDategetCreateDate(){
 returncreateDate;
returncreateDate;
 }
}
 publicvoidsetCreateDate(DatecreateDate){
publicvoidsetCreateDate(DatecreateDate){
 this.createDate=createDate;
this.createDate=createDate;
 }
}
 publicLonggetId(){
publicLonggetId(){
 returnid;
returnid;
 }
}
 publicvoidsetId(Longid){
publicvoidsetId(Longid){
 this.id=id;
this.id=id;
 }
}
 publicStringgetName(){
publicStringgetName(){
 returnname;
returnname;
 }
}
 publicvoidsetName(Stringname){
publicvoidsetName(Stringname){
 this.name=name;
this.name=name;
 }
}
 publicStringgetSex(){
publicStringgetSex(){
 returnsex;
returnsex;
 }
}
 publicvoidsetSex(Stringsex){
publicvoidsetSex(Stringsex){
 this.sex=sex;
this.sex=sex;
 }
}
 publicstaticListgetPeople(){
publicstaticListgetPeople(){
 Listlist=newArrayList();
Listlist=newArrayList();
 intn=30;
intn=30;
 for(inti=1;i<n;i++){
for(inti=1;i<n;i++){
 Longid=newLong(i);
Longid=newLong(i);
 Stringname="张"+i;
Stringname="张"+i;
 Stringsex="男";
Stringsex="男";
 if((i%2)==0){
if((i%2)==0){
 sex="女";
sex="女";
 }
}
 Integerage;
Integerage;
 if(i<10){
if(i<10){
 age=newInteger(i*10);
age=newInteger(i*10);
 }elseif(i>10&&i<100){
}elseif(i>10&&i<100){
 age=newInteger(i);
age=newInteger(i);
 }elseif(i>100&&i<1000){
}elseif(i>100&&i<1000){
 age=newInteger(i/10);
age=newInteger(i/10);
 }else{
}else{
 age=newInteger(22);
age=newInteger(22);
 }
}
 DatecreateDate=newDate();
DatecreateDate=newDate();
 Peoplepeople=newPeople(id,name,sex,age,createDate);
Peoplepeople=newPeople(id,name,sex,age,createDate);
 list.add(people);
list.add(people);
 }
}
 returnlist;
returnlist;
 }
}
 }
}
(2)给tableViewer提供内容器(IStructuredContentPorvider)和标签器(ITableLabelProvider)
如果想一个tableviewer显示数据,那必须给它提供内容器和标签器,内容器的作用是从List(也可以是其他的集合类)中提取出一个对象(例如People对应着表格的一行,数据库的一条记录),标签器的作用是从一个对象中提取出一个字段(例如年龄,对应着表格中的一个单元格,数据库中某一列的一个值)下边是内容器和标签器的代码:
内容器:
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List;

 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.IStructuredContentProvider;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.IStructuredContentProvider;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;

 public
class
ContentProvider
implements
IStructuredContentProvider
{
public
class
ContentProvider
implements
IStructuredContentProvider
{
 publicObject[]getElements(ObjectinputElement){
publicObject[]getElements(ObjectinputElement){
 if(inputElementinstanceofList){
if(inputElementinstanceofList){
 return((List)inputElement).toArray();
return((List)inputElement).toArray();
 }else{
}else{
 returnnewObject[0];
returnnewObject[0];
 }
}
 }
}
 publicvoiddispose(){
publicvoiddispose(){
 }
}
 publicvoidinputChanged(Viewerviewer,ObjectoldInput,ObjectnewInput){
publicvoidinputChanged(Viewerviewer,ObjectoldInput,ObjectnewInput){
 }
}
 }
}
标签器:
 import
java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import
java.text.SimpleDateFormat;

 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ITableLabelProvider;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ITableLabelProvider;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.LabelProvider;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.LabelProvider;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image;
import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image;

 public
class
TableLabelProvider
extends
LabelProvider
implements
ITableLabelProvider
{
public
class
TableLabelProvider
extends
LabelProvider
implements
ITableLabelProvider
{
 publicStringgetColumnText(Objectelement,intcolumnIndex){
publicStringgetColumnText(Objectelement,intcolumnIndex){
 if(elementinstanceofPeople){
if(elementinstanceofPeople){
 Peoplep=(People)element;
Peoplep=(People)element;
 if(columnIndex==0){
if(columnIndex==0){
 returnp.getId().toString();
returnp.getId().toString();
 }elseif(columnIndex==1){
}elseif(columnIndex==1){
 returnp.getName();
returnp.getName();
 }elseif(columnIndex==2){
}elseif(columnIndex==2){
 returnp.getSex();
returnp.getSex();
 }elseif(columnIndex==3){
}elseif(columnIndex==3){
 returnp.getAge().toString();
returnp.getAge().toString();
 }elseif(columnIndex==4){
}elseif(columnIndex==4){
 SimpleDateFormatsdf=newSimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
SimpleDateFormatsdf=newSimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
 returnsdf.format(p.getCreateDate());
returnsdf.format(p.getCreateDate());
 }
}
 }
}
 returnnull;
returnnull;
 }
}
 publicImagegetColumnImage(Objectelement,intcolumnIndex){
publicImagegetColumnImage(Objectelement,intcolumnIndex){
 returnnull;
returnnull;
 }
}
 }
}
注意这里:extends LabelProvider,为什么要加这个呢? 因为如果不加这个,因为实现ITableLabelProvider的缘故我们还要写四个空函数,而我们本身不需要在这四个空函数中实现什么,所以让它继承自LabelProvider,就可以避免四个空函数。
(3)把标签器和内容器给tableviewer
在shell.open()前边加上这几行
 //
设置内容器
//
设置内容器
 tableViewer.setContentProvider(
new
ContentProvider());
tableViewer.setContentProvider(
new
ContentProvider());
 //
设置标签器
//
设置标签器
 tableViewer.setLabelProvider(
new
TableLabelProvider());
tableViewer.setLabelProvider(
new
TableLabelProvider());
 //
把数据集合给tableView
//
把数据集合给tableView
 tableViewer.setInput(People.getPeople());
tableViewer.setInput(People.getPeople());
 //
这样利用内容器和标签器就能从setInput得到的数据集合分解出显示表格需要的数据。这是一个典型的mvc的实现.
//
这样利用内容器和标签器就能从setInput得到的数据集合分解出显示表格需要的数据。这是一个典型的mvc的实现.
4,样式改变
如果想在每一列前加入一个checkbox
只需要在开始的式样中加入SWT.CHECK
好了到此一个简单的样子选择出来了,但这仅仅是开始,下边将继续介绍按列排序、过滤器、行的颜色设置、在表格上直接编辑等功能
SourceCode
=============================================
有一个功能是我们常使用的,就是在列的头上点击一下,整个表的记录按照这个列来排序,再点击一下按照这个列的反序来排序。那JFace是如何实现这个功能的呢?
在JFace中是通过一个排序器来实现的,就是ViewerSorter下边写出详细的步骤
一、定义一个sorter继承自ViewerSorter
 import
java.util.Date;
import
java.util.Date;

 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ViewerSorter;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ViewerSorter;

 public
class
Sorter
extends
ViewerSorter
{
public
class
Sorter
extends
ViewerSorter
{
 privatestaticfinalintID=1;
privatestaticfinalintID=1;
 privatestaticfinalintNAME=2;
privatestaticfinalintNAME=2;
 privatestaticfinalintSEX=3;
privatestaticfinalintSEX=3;
 privatestaticfinalintAGE=4;
privatestaticfinalintAGE=4;
 privatestaticfinalintCREATE_DATE=5;
privatestaticfinalintCREATE_DATE=5;

 publicstaticfinalSorterID_ASC=newSorter(ID);
publicstaticfinalSorterID_ASC=newSorter(ID);
 publicstaticfinalSorterID_DESC=newSorter(-ID);
publicstaticfinalSorterID_DESC=newSorter(-ID);
 publicstaticfinalSorterNAME_ASC=newSorter(NAME);
publicstaticfinalSorterNAME_ASC=newSorter(NAME);
 publicstaticfinalSorterNAME_DESC=newSorter(-NAME);
publicstaticfinalSorterNAME_DESC=newSorter(-NAME);
 publicstaticfinalSorterSEX_ASC=newSorter(SEX);
publicstaticfinalSorterSEX_ASC=newSorter(SEX);
 publicstaticfinalSorterSEX_DESC=newSorter(-SEX);
publicstaticfinalSorterSEX_DESC=newSorter(-SEX);
 publicstaticfinalSorterAGE_ASC=newSorter(AGE);
publicstaticfinalSorterAGE_ASC=newSorter(AGE);
 publicstaticfinalSorterAGE_DESC=newSorter(-AGE);
publicstaticfinalSorterAGE_DESC=newSorter(-AGE);
 publicstaticfinalSorterCREATE_DATE_ASC=newSorter(CREATE_DATE);
publicstaticfinalSorterCREATE_DATE_ASC=newSorter(CREATE_DATE);
 publicstaticfinalSorterCREATE_DATE_DESC=newSorter(-CREATE_DATE);
publicstaticfinalSorterCREATE_DATE_DESC=newSorter(-CREATE_DATE);

 privateintsortType;
privateintsortType;
 privateSorter(intsortType){
privateSorter(intsortType){
 this.sortType=sortType;
this.sortType=sortType;
 }
}
 publicintcompare(Viewerviewer,Objecte1,Objecte2){
publicintcompare(Viewerviewer,Objecte1,Objecte2){
 Peoplep1=(People)e1;
Peoplep1=(People)e1;
 Peoplep2=(People)e2;
Peoplep2=(People)e2;
 switch(sortType){
switch(sortType){
 caseID:{
caseID:{
 Longl1=p1.getId();
Longl1=p1.getId();
 Longl2=p2.getId();
Longl2=p2.getId();
 returnl1.compareTo(l2);
returnl1.compareTo(l2);
 }
}
 case-ID:{
case-ID:{
 Longl1=p1.getId();
Longl1=p1.getId();
 Longl2=p2.getId();
Longl2=p2.getId();
 returnl2.compareTo(l1);
returnl2.compareTo(l1);
 }
}
 caseNAME:{
caseNAME:{
 Strings1=p1.getName();
Strings1=p1.getName();
 Strings2=p2.getName();
Strings2=p2.getName();
 returns1.compareTo(s2);
returns1.compareTo(s2);
 }
}
 case-NAME:{
case-NAME:{
 Strings1=p1.getName();
Strings1=p1.getName();
 Strings2=p2.getName();
Strings2=p2.getName();
 returns2.compareTo(s1);
returns2.compareTo(s1);
 }
}
 caseSEX:{
caseSEX:{
 Strings1=p1.getSex();
Strings1=p1.getSex();
 Strings2=p2.getSex();
Strings2=p2.getSex();
 returns1.compareTo(s2);
returns1.compareTo(s2);
 }
}
 case-SEX:{
case-SEX:{
 Strings1=p1.getSex();
Strings1=p1.getSex();
 Strings2=p2.getSex();
Strings2=p2.getSex();
 returns2.compareTo(s1);
returns2.compareTo(s1);
 }
}
 caseAGE:{
caseAGE:{
 Integeri1=p1.getAge();
Integeri1=p1.getAge();
 Integeri2=p2.getAge();
Integeri2=p2.getAge();
 returni1.compareTo(i2);
returni1.compareTo(i2);
 }
}
 case-AGE:{
case-AGE:{
 Integeri1=p1.getAge();
Integeri1=p1.getAge();
 Integeri2=p2.getAge();
Integeri2=p2.getAge();
 returni2.compareTo(i1);
returni2.compareTo(i1);
 }
}
 caseCREATE_DATE:{
caseCREATE_DATE:{
 Dated1=p1.getCreateDate();
Dated1=p1.getCreateDate();
 Dated2=p2.getCreateDate();
Dated2=p2.getCreateDate();
 d1.compareTo(d2);
d1.compareTo(d2);
 }
}
 case-CREATE_DATE:{
case-CREATE_DATE:{
 Dated1=p1.getCreateDate();
Dated1=p1.getCreateDate();
 Dated2=p2.getCreateDate();
Dated2=p2.getCreateDate();
 d2.compareTo(d1);
d2.compareTo(d1);
 }
}
 }
}
 return0;
return0;
 }
}
 }
}
二、在TableViewer上,为每一列加入事件监听器类似这样的结构
 newColumnTableColumn.addSelectionListener(
new
SelectionAdapter()
{
newColumnTableColumn.addSelectionListener(
new
SelectionAdapter()
{
 booleanasc=true;
booleanasc=true;
 publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
 tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.ID_ASC:Sorter.ID_DESC);
tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.ID_ASC:Sorter.ID_DESC);
 asc=!asc;
asc=!asc;
 }
}
 }
);
}
);
都加入后TestTableViewer的结果:
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.TableViewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.TableViewer;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionAdapter;
import
org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionAdapter;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionEvent;
import
org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionEvent;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;
import
org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;

 public
class
TestTableViewer
{
public
class
TestTableViewer
{
 privatestaticTabletable;
privatestaticTabletable;
 /**
/**
 *Launchtheapplication
*Launchtheapplication
 *@paramargs
*@paramargs
 */
*/
 publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
 finalDisplaydisplay=Display.getDefault();
finalDisplaydisplay=Display.getDefault();
 finalShellshell=newShell();
finalShellshell=newShell();
 shell.setSize(500,375);
shell.setSize(500,375);
 shell.setText("SWTApplication");
shell.setText("SWTApplication");
 //
//
 finalTableViewertableViewer=newTableViewer(shell,SWT.CHECK|SWT.MULTI|SWT.FULL_SELECTION|SWT.BORDER|SWT.V_SCROLL|SWT.H_SCROLL);
finalTableViewertableViewer=newTableViewer(shell,SWT.CHECK|SWT.MULTI|SWT.FULL_SELECTION|SWT.BORDER|SWT.V_SCROLL|SWT.H_SCROLL);

 table=tableViewer.getTable();
table=tableViewer.getTable();
 table.setLinesVisible(true);
table.setLinesVisible(true);
 table.setHeaderVisible(true);
table.setHeaderVisible(true);
 table.setBounds(97,79,373,154);
table.setBounds(97,79,373,154);

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn.setWidth(39);
newColumnTableColumn.setWidth(39);
 newColumnTableColumn.setText("ID");
newColumnTableColumn.setText("ID");
 //加入事件监听器
//加入事件监听器
 newColumnTableColumn.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
newColumnTableColumn.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
 booleanasc=true;
booleanasc=true;
 publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
 tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.ID_ASC:Sorter.ID_DESC);
tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.ID_ASC:Sorter.ID_DESC);
 asc=!asc;
asc=!asc;
 }
}
 });
});

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_1=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_1=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_1.setWidth(85);
newColumnTableColumn_1.setWidth(85);
 newColumnTableColumn_1.setText("姓名");
newColumnTableColumn_1.setText("姓名");
 //加入事件监听器
//加入事件监听器
 newColumnTableColumn_1.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
newColumnTableColumn_1.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
 booleanasc=true;
booleanasc=true;
 publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
 tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.NAME_ASC:Sorter.NAME_DESC);
tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.NAME_ASC:Sorter.NAME_DESC);
 asc=!asc;
asc=!asc;
 }
}
 });
});

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_2=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_2=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_2.setWidth(41);
newColumnTableColumn_2.setWidth(41);
 newColumnTableColumn_2.setText("性别");
newColumnTableColumn_2.setText("性别");
 //加入事件监听器
//加入事件监听器
 newColumnTableColumn_2.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
newColumnTableColumn_2.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
 booleanasc=true;
booleanasc=true;
 publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
 tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.SEX_ASC:Sorter.SEX_DESC);
tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.SEX_ASC:Sorter.SEX_DESC);
 asc=!asc;
asc=!asc;
 }
}
 });
});

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_3=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_3=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_3.setWidth(43);
newColumnTableColumn_3.setWidth(43);
 newColumnTableColumn_3.setText("年龄");
newColumnTableColumn_3.setText("年龄");
 //加入事件监听器
//加入事件监听器
 newColumnTableColumn_3.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
newColumnTableColumn_3.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
 booleanasc=true;
booleanasc=true;
 publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
 tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.AGE_ASC:Sorter.AGE_DESC);
tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.AGE_ASC:Sorter.AGE_DESC);
 asc=!asc;
asc=!asc;
 }
}
 });
});

 finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_4=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
finalTableColumnnewColumnTableColumn_4=newTableColumn(table,SWT.NONE);
 newColumnTableColumn_4.setWidth(126);
newColumnTableColumn_4.setWidth(126);
 newColumnTableColumn_4.setText("创建日期");
newColumnTableColumn_4.setText("创建日期");
 //加入事件监听器
//加入事件监听器
 newColumnTableColumn_4.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
newColumnTableColumn_4.addSelectionListener(newSelectionAdapter(){
 booleanasc=true;
booleanasc=true;
 publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
publicvoidwidgetSelected(SelectionEvente){
 tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.CREATE_DATE_ASC:Sorter.CREATE_DATE_DESC);
tableViewer.setSorter(asc?Sorter.CREATE_DATE_ASC:Sorter.CREATE_DATE_DESC);
 asc=!asc;
asc=!asc;
 }
}
 });
});

 tableViewer.setContentProvider(newContentProvider());
tableViewer.setContentProvider(newContentProvider());
 tableViewer.setLabelProvider(newTableLabelProvider());
tableViewer.setLabelProvider(newTableLabelProvider());
 tableViewer.setInput(People.getPeople());
tableViewer.setInput(People.getPeople());

 shell.open();
shell.open();
 shell.setLayout(newFillLayout());
shell.setLayout(newFillLayout());
 shell.layout();
shell.layout();
 while(!shell.isDisposed()){
while(!shell.isDisposed()){
 if(!display.readAndDispatch())
if(!display.readAndDispatch())
 display.sleep();
display.sleep();
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
试一下结果是不是出来了?
好了,最后解释几点:
1,sorter中利用了jdk的compareTo来实现比较,当然你也可以根据自己的需求来实现。
2, sorter中利用了"-"符号来得到正负数字,用来表现升序、降序。
SourceCode
======================================================
前边实现了一个表格的基本功能,但这并不够好,能否为表格实现一些更好的功能呢?答案是肯定的。下边我们来加入直接编辑的功能。
一、要实现这个功能必须提供一个实现ICellModifier的类。内容如下
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ICellModifier;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ICellModifier;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.TableViewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.TableViewer;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableItem;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableItem;

 public
class
MyCellModifier
implements
ICellModifier
{
public
class
MyCellModifier
implements
ICellModifier
{
 privateTableViewertv;
privateTableViewertv;
 publicstaticString[]NAMES={"张三","李四","小红","翠花"};
publicstaticString[]NAMES={"张三","李四","小红","翠花"};

 publicMyCellModifier(TableViewertv){
publicMyCellModifier(TableViewertv){
 this.tv=tv;
this.tv=tv;
 }
}
 publicbooleancanModify(Objectelement,Stringproperty){
publicbooleancanModify(Objectelement,Stringproperty){
 returntrue;
returntrue;
 }
}

 publicObjectgetValue(Objectelement,Stringproperty){
publicObjectgetValue(Objectelement,Stringproperty){
 Peoplep=(People)element;
Peoplep=(People)element;
 if(property.equals("name")){
if(property.equals("name")){
 returnnewInteger(getNameIndex(p.getName()));
returnnewInteger(getNameIndex(p.getName()));
 }elseif(property.equals("sex")){
}elseif(property.equals("sex")){
 returnnewBoolean(p.getSex().equals("男"));
returnnewBoolean(p.getSex().equals("男"));
 }elseif(property.equals("age")){
}elseif(property.equals("age")){
 returnString.valueOf(p.getAge());
returnString.valueOf(p.getAge());
 }
}
 thrownewRuntimeException("errorcolumnname:"+property);
thrownewRuntimeException("errorcolumnname:"+property);
 }
}
 privateintgetNameIndex(Stringname){
privateintgetNameIndex(Stringname){
 for(inti=0;i<NAMES.length;i++){
for(inti=0;i<NAMES.length;i++){
 if(NAMES[i].equals(name)){
if(NAMES[i].equals(name)){
 returni;
returni;
 }
}
 }
}
 return-1;
return-1;
 }
}

 publicvoidmodify(Objectelement,Stringproperty,Objectvalue){
publicvoidmodify(Objectelement,Stringproperty,Objectvalue){
 TableItemitem=(TableItem)element;
TableItemitem=(TableItem)element;
 Peoplep=(People)item.getData();
Peoplep=(People)item.getData();
 if(property.equals("name")){
if(property.equals("name")){
 IntegercomboIndex=(Integer)value;
IntegercomboIndex=(Integer)value;
 if(comboIndex.intValue()==-1){
if(comboIndex.intValue()==-1){
 return;
return;
 }
}
 StringnewName=NAMES[comboIndex.intValue()];
StringnewName=NAMES[comboIndex.intValue()];
 p.setName(newName);
p.setName(newName);
 }elseif(property.equals("sex")){
}elseif(property.equals("sex")){
 BooleannewValue=(Boolean)value;
BooleannewValue=(Boolean)value;
 System.out.println(newValue);
System.out.println(newValue);
 if(newValue.booleanValue()){
if(newValue.booleanValue()){
 p.setSex("男");
p.setSex("男");
 }else{
}else{
 p.setSex("女");
p.setSex("女");
 }
}
 }elseif(property.equals("age")){
}elseif(property.equals("age")){
 StringnewValue=(String)value;
StringnewValue=(String)value;
 if(newValue.equals("")){
if(newValue.equals("")){
 return;
return;
 }
}
 IntegernewAge=newInteger(newValue);
IntegernewAge=newInteger(newValue);
 p.setAge(newAge);
p.setAge(newAge);
 }else{
}else{
 thrownewRuntimeException("错误列名:"+property);
thrownewRuntimeException("错误列名:"+property);
 }
}
 tv.update(p,null);
tv.update(p,null);
 }
}

 }
}
二、好了,有了这个类,下一部就是如何把它和TestTableViewer关联起来,在TestTableViewer中setInput()后加入如下内容
 tableViewer.setColumnProperties(
new
String[]
{"id","name","sex","age","createDate"}
);
tableViewer.setColumnProperties(
new
String[]
{"id","name","sex","age","createDate"}
);
 CellEditor[]cellEditor
=
new
CellEditor[
5
];
CellEditor[]cellEditor
=
new
CellEditor[
5
];
 cellEditor[
0
]
=
null
;
cellEditor[
0
]
=
null
;
 cellEditor[
1
]
=
new
ComboBoxCellEditor(tableViewer.getTable(),MyCellModifier.NAMES,SWT.READ_ONLY);
cellEditor[
1
]
=
new
ComboBoxCellEditor(tableViewer.getTable(),MyCellModifier.NAMES,SWT.READ_ONLY);
 cellEditor[
2
]
=
new
CheckboxCellEditor(tableViewer.getTable());
cellEditor[
2
]
=
new
CheckboxCellEditor(tableViewer.getTable());
 cellEditor[
3
]
=
new
TextCellEditor(tableViewer.getTable());
cellEditor[
3
]
=
new
TextCellEditor(tableViewer.getTable());
 cellEditor[
4
]
=
null
;
cellEditor[
4
]
=
null
;
 tableViewer.setCellEditors(cellEditor);
tableViewer.setCellEditors(cellEditor);
 ICellModifiermodifier
=
new
MyCellModifier(tableViewer);
ICellModifiermodifier
=
new
MyCellModifier(tableViewer);
 tableViewer.setCellModifier(modifier);
tableViewer.setCellModifier(modifier);
我们让名字这一列用下拉条来编辑,让性别这一列变成类似checkbox的操作,让年龄这一类变成直接输入
ok,尝试一下。
三、问题出现,如果年龄的地方我们输入一个非数字呢,所以为了安全起见,我们加入一个验证器,禁止用户输入非数字
在上边的内容下加入
 Texttext
=
(Text)cellEditor[
3
].getControl();
Texttext
=
(Text)cellEditor[
3
].getControl();
 text.addVerifyListener(
new
VerifyListener()
{
text.addVerifyListener(
new
VerifyListener()
{
 publicvoidverifyText(VerifyEvente){
publicvoidverifyText(VerifyEvente){
 StringinStr=e.text;
StringinStr=e.text;
 if(inStr.length()>0){
if(inStr.length()>0){
 try{
try{
 Integer.parseInt(inStr);
Integer.parseInt(inStr);
 e.doit=true;
e.doit=true;
 }catch(Exceptionep){
}catch(Exceptionep){
 e.doit=false;
e.doit=false;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }
);
}
);
好了,再试试是否不能输入非整数了?解决。其实还是有些问题的,试着输入个0,呵呵。这里就需要你自己按照自己的实际需求来实现了。
但作为demo这个的目的已经达到了。
SourceCode
=======================================================
如果我们想根据某一列来过滤记录,如何实现呢?很简单,定义一个过滤器filter。这里只演示定义一个过滤器的情况。
现实中你可以定义多个灵活的过滤器,通过替换过滤器来实现各种各样的过滤。
一、过滤器代码:
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ViewerFilter;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ViewerFilter;

 public
class
MyFilter
extends
ViewerFilter
{
public
class
MyFilter
extends
ViewerFilter
{
 publicbooleanselect(Viewerviewer,ObjectparentElement,Objectelement){
publicbooleanselect(Viewerviewer,ObjectparentElement,Objectelement){
 Peoplep=(People)element;
Peoplep=(People)element;
 returnp.getName().startsWith("张1");
returnp.getName().startsWith("张1");
 }
}
 }
}
然后在testTableViewer的shell.open前加入这个过滤器
 tableViewer.addFilter(
new
MyFilter());
tableViewer.addFilter(
new
MyFilter());
好了,看一下效果
二、如果我们想凸显某一条记录,想改变一下它的颜色,如果实现呢,简单,只要几句话就可以了。
Colorcolor
=
Display.getDefault().getSystemColor(SWT.COLOR_RED);
table.getItems()[table.getItemCount()
-
1
].setBackground(color);
table.redraw();
三、这里提一下,使用tabeViewer.setUseHashlookup(true)可以在tableviewer内部为数据记录和tableItem之间的映射创建一个hash表,这样可以加快tableItem的和记录间的查找速度,注意,这条语句必须在setInput之前加入才有效。
好了,到此tableviewer的基本的东西介绍的差不多了
source下载:sourcecode
四:在现实的开发中,我们更多的是喜欢把一些简单的类用匿名类或者内部类的方式来实现。像之前例子中每个都单独一个类的情况并不多。
下边是和前边的source效果等同的source,不过是使用了匿名类和内部类。
source下载:SourceCode
=============================================
上边介绍了,tableviewer,这里介绍一下treeViewer,总的流程类似。
一、构造一个树形结构的数据出来,这里选择国家、城市、人来构造一个树形结构,代码如下:
1,定义一个接口
package model;
import java.util.List;
public interface Itree {
public String getName();
public void setName(String name);
public void setChildren(List Children);
public List getChildren();
}
2,国家
package model;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Country implements Itree{
private Long id;
private String name;
private List children = new ArrayList();
public Country(){
}
public Country(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public List getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List children) {
this.children = children;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
3,城市
package model;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class City implements Itree{
private Long id;
private String name;
private List children = new ArrayList();
public City(){
}
public City(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public List getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List children) {
this.children = children;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
4,人
package model;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class People implements Itree{
private Long id;
private String name;
public People(){
}
public People(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public List getChildren() {
return null;
}
public void setChildren(List children) {
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
5,把这些元素组织起来
package model;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Factory {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static List createTree(){
//生成国家
Country cn = new Country("中国");
Country us = new Country("美国");
Country jp = new Country("日本");
//生成城市
City beijing = new City("北京");
City shanghai = new City("上海");
City newyork = new City("纽约");
City la = new City("洛杉矶");
City tokyo = new City("东京");
City osaka = new City("大阪");
//北京人
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new People("张三"));
list.add(new People("李四"));
list.add(new People("王五"));
beijing.setChildren(list);
//上海人
list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new People("翠花"));
list.add(new People("小红"));
list.add(new People("小崔"));
shanghai.setChildren(list);
//纽约人
list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new People("tom"));
list.add(new People("rose"));
list.add(new People("john"));
newyork.setChildren(list);
//洛杉矶人
list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new People("Sofia"));
list.add(new People("sarah"));
list.add(new People("Jennifer"));
la.setChildren(list);
//东京人
list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new People("渡边"));
list.add(new People("鬼冢"));
list.add(new People("山本"));
tokyo.setChildren(list);
//大阪人
list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new People("奈奈子"));
list.add(new People("菜菜子"));
list.add(new People("新垣结衣"));
osaka.setChildren(list);
//关联城市与国家
//中国
ArrayList citys = new ArrayList();
citys.add(beijing);
citys.add(shanghai);
cn.setChildren(citys);
//美国
citys = new ArrayList();
citys.add(newyork);
citys.add(la);
us.setChildren(citys);
//日本
citys = new ArrayList();
citys.add(tokyo);
citys.add(osaka);
jp.setChildren(citys);
//国家列表
ArrayList countrys = new ArrayList();
countrys.add(cn);
countrys.add(us);
countrys.add(jp);
return countrys;
}
}
二、定义内容器和标签器
1,内容器
import java.util.List;
import model.Itree;
import org.eclipse.jface.viewers.IStructuredContentProvider;
import org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ITreeContentProvider;
import org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
public class TreeContentProvider implements IStructuredContentProvider, ITreeContentProvider {
public Object[] getElements(Object inputElement) {
if (inputElement instanceof List){
List input = (List)inputElement;
return input.toArray();
}
return new Object[0];
}
public Object[] getChildren(Object parentElement) {
Itree node = (Itree)parentElement;
List list = node.getChildren();
if(list == null){
return new Object[0];
}
return list.toArray();
}
public boolean hasChildren(Object element) {
Itree node = (Itree)element;
List list = node.getChildren();
return !(list == null || list.isEmpty());
}
//以下三个函数根据需要填充
public Object getParent(Object element) {
return null;
}
public void inputChanged(Viewer viewer, Object oldInput, Object newInput) {
}
public void dispose() {
}
}
2,标签器:
import model.Itree;
import org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ILabelProvider;
import org.eclipse.jface.viewers.LabelProvider;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image;
public class TreeLabelProvider extends LabelProvider implements ILabelProvider {
public String getText(Object element) {
Itree node = (Itree)element;
return node.getName();
}
public Image getImage(Object element) {
return null;
}
}
三、好了,准备工作做好了,把上边的内容利用起来就好了。
import model.Factory;
import org.eclipse.jface.viewers.TreeViewer;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Tree;
public class TestTreeViewer {
private static Tree tree;
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Display display = Display.getDefault();
final Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setSize(500, 375);
shell.setText("SWT Application");
//
final TreeViewer treeViewer = new TreeViewer(shell, SWT.BORDER|SWT.H_SCROLL);
tree = treeViewer.getTree();
tree.setBounds(83, 75, 264, 185);
treeViewer.setLabelProvider(new TreeLabelProvider());
treeViewer.setContentProvider(new TreeContentProvider());
treeViewer.setInput(Factory.createTree());
shell.open();
shell.setLayout(new FillLayout());
shell.layout();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
}

看看是不是已经实现了treeViewer
四、上边是简单的treeViewer,如果我们需要带checkbox的treeViewer,简单,只需要更改
 final
TreeViewertreeViewer
=
new
TreeViewer(shell,SWT.BORDER
|
SWT.H_SCROLL);
final
TreeViewertreeViewer
=
new
TreeViewer(shell,SWT.BORDER
|
SWT.H_SCROLL);

把TreeViewer换成CheckboxTreeViewer。这就是mvc的好处了。
但现实中我们多用ContainerCheckedTreeViewer代替CheckboxTreeViewer,因为这个提供了更多的功能。
CheckboxTreeViewer是TreeViewer的子类, ContainerCheckedTreeViewer是CheckboxTreeViewer的子类,所以可以随便替换。
替换后:
 final
ContainerCheckedTreeViewertreeViewer
=
new
ContainerCheckedTreeViewer(shell,SWT.BORDER
|
SWT.H_SCROLL);
final
ContainerCheckedTreeViewertreeViewer
=
new
ContainerCheckedTreeViewer(shell,SWT.BORDER
|
SWT.H_SCROLL);
五、treeviewer和tableviewer都介绍过了,考虑一下把两个结合起来是不是我们经常需要的情况。尝试一下吧。
效果;

========================================================
前边将过了TableViewer和TreeViewer再来看ListViewer就简单了,操作步骤一样,但更简单。这里只给出使用的代码
一、代码,这个实现不同于前边是分开实现(都是public 的类),这里给出的是内部类的实现方式。
 import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.ArrayList;
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List;

 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.IStructuredContentProvider;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.IStructuredContentProvider;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.LabelProvider;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.LabelProvider;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ListViewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ListViewer;
 import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
import
org.eclipse.jface.viewers.Viewer;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image;
import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;
import
org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;


 public
class
TestListViewer
{
public
class
TestListViewer
{

 staticclassListLabelProviderextendsLabelProvider{
staticclassListLabelProviderextendsLabelProvider{
 publicStringgetText(Objectelement){
publicStringgetText(Objectelement){
 Countrycountry=(Country)element;
Countrycountry=(Country)element;
 returncountry.getName();
returncountry.getName();
 }
}
 publicImagegetImage(Objectelement){
publicImagegetImage(Objectelement){
 returnnull;
returnnull;
 }
}
 }
}
 staticclassContentProviderimplementsIStructuredContentProvider{
staticclassContentProviderimplementsIStructuredContentProvider{
 publicObject[]getElements(ObjectinputElement){
publicObject[]getElements(ObjectinputElement){
 if(inputElementinstanceofList){
if(inputElementinstanceofList){
 Listlist=(List)inputElement;
Listlist=(List)inputElement;
 returnlist.toArray();
returnlist.toArray();
 }
}
 returnnewObject[0];
returnnewObject[0];
 }
}
 publicvoiddispose(){
publicvoiddispose(){
 }
}
 publicvoidinputChanged(Viewerviewer,ObjectoldInput,ObjectnewInput){
publicvoidinputChanged(Viewerviewer,ObjectoldInput,ObjectnewInput){
 }
}
 }
}
 staticclassCountry{
staticclassCountry{
 privateStringname;
privateStringname;

 publicCountry(){
publicCountry(){
 }
}
 publicCountry(Stringname){
publicCountry(Stringname){
 this.name=name;
this.name=name;
 }
}
 publicStringgetName(){
publicStringgetName(){
 returnname;
returnname;
 }
}

 publicvoidsetName(Stringname){
publicvoidsetName(Stringname){
 this.name=name;
this.name=name;
 }
}
 publicstaticListgetCountryList(){
publicstaticListgetCountryList(){
 Listlist=newArrayList();
Listlist=newArrayList();
 list.add(newCountry("中国"));
list.add(newCountry("中国"));
 list.add(newCountry("美国"));
list.add(newCountry("美国"));
 list.add(newCountry("日本"));
list.add(newCountry("日本"));
 returnlist;
returnlist;
 }
}

 }
}
 privatestaticorg.eclipse.swt.widgets.Listlist;
privatestaticorg.eclipse.swt.widgets.Listlist;
 /**
/**
 *Launchtheapplication
*Launchtheapplication
 *@paramargs
*@paramargs
 */
*/
 publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
 finalDisplaydisplay=Display.getDefault();
finalDisplaydisplay=Display.getDefault();
 finalShellshell=newShell();
finalShellshell=newShell();
 shell.setSize(500,375);
shell.setSize(500,375);
 shell.setText("SWTApplication");
shell.setText("SWTApplication");
 //
//

 shell.open();
shell.open();

 finalListViewerlistViewer=newListViewer(shell,SWT.BORDER);
finalListViewerlistViewer=newListViewer(shell,SWT.BORDER);
 listViewer.setLabelProvider(newListLabelProvider());
listViewer.setLabelProvider(newListLabelProvider());
 listViewer.setContentProvider(newContentProvider());
listViewer.setContentProvider(newContentProvider());
 listViewer.setInput(newObject());
listViewer.setInput(newObject());
 list=listViewer.getList();
list=listViewer.getList();
 list.setBounds(122,63,100,100);
list.setBounds(122,63,100,100);

 listViewer.setContentProvider(newContentProvider());
listViewer.setContentProvider(newContentProvider());
 listViewer.setLabelProvider(newListLabelProvider());
listViewer.setLabelProvider(newListLabelProvider());
 listViewer.setInput(Country.getCountryList());
listViewer.setInput(Country.getCountryList());
 //可以直接添加
//可以直接添加
 listViewer.add(newCountry("英国"));
listViewer.add(newCountry("英国"));
 shell.setLayout(newFillLayout());
shell.setLayout(newFillLayout());
 shell.layout();
shell.layout();
 while(!shell.isDisposed()){
while(!shell.isDisposed()){
 if(!display.readAndDispatch())
if(!display.readAndDispatch())
 display.sleep();
display.sleep();
 }
}
 }
}

 }
}

二、注意代码的注释部分,可以直接添加和移除。
===================================================
Jface的hello World网上到处都是,但简单的Hello world能引出很多需要注意的问题.
首先大部分网上的jface helloworld如下:
 import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Point;
import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Point;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;


 public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{
public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{

 publicTestWindow(){
publicTestWindow(){
 super(null);
super(null);
 }
}
 protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){
protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){
 Texttext=newText(parent,SWT.NONE);
Texttext=newText(parent,SWT.NONE);
 text.setText("helloworld");
text.setText("helloworld");
 returnparent;
returnparent;
 }
}
 publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
 try{
try{
 TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
 window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
 window.open();
window.open();
 Display.getCurrent().dispose();
Display.getCurrent().dispose();
 }catch(Exceptione){
}catch(Exceptione){
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}

这个代码是可以运行的,而且运行的结果也看不出什么问题。但看不出来并不代表没有问题。下边我们来让问题显现
在createContents()函数中再加入一个Text代码变成
 import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;


 public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{
public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{

 publicTestWindow(){
publicTestWindow(){
 super(null);
super(null);
 }
}
 protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){
protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){
 Texttext=newText(parent,SWT.NONE);
Texttext=newText(parent,SWT.NONE);
 text.setText("helloworld");
text.setText("helloworld");
 Texttext1=newText(parent,SWT.NONE);
Texttext1=newText(parent,SWT.NONE);
 text1.setText("it'sme");
text1.setText("it'sme");
 returnparent;
returnparent;
 }
}
 publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
 try{
try{
 TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
 window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
 window.open();
window.open();
 Display.getCurrent().dispose();
Display.getCurrent().dispose();
 }catch(Exceptione){
}catch(Exceptione){
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}

运行,并没有看到第二个Text,为什么?
是否没有设置text的Bounds?好设置一下
 import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Point;
import
org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Point;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;


 public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{
public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{

 publicTestWindow(){
publicTestWindow(){
 super(null);
super(null);
 }
}
 protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){
protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){

 Texttext=newText(parent,SWT.BORDER);
Texttext=newText(parent,SWT.BORDER);
 text.setText("helloworld");
text.setText("helloworld");
 text.setBounds(59,112,80,25);
text.setBounds(59,112,80,25);

 Texttext_1=newText(parent,SWT.BORDER);
Texttext_1=newText(parent,SWT.BORDER);
 text_1.setText("it'sme");
text_1.setText("it'sme");
 text_1.setBounds(72,221,80,25);
text_1.setBounds(72,221,80,25);
 returnparent;
returnparent;
 }
}
 publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
 try{
try{
 TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
 window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
 window.open();
window.open();
 Display.getCurrent().dispose();
Display.getCurrent().dispose();
 }catch(Exceptione){
}catch(Exceptione){
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();
 }
}
 }
}
 privatevoidcreateActions(){
privatevoidcreateActions(){
 }
}
 }
}

效果依旧,那是为什么呢?
这是因为在createContents()方法中直接使用了参数中的parent,造成了布局(layout)的混乱,在只有一个的text的情况下看不出来,现在就看出来了。
解决办法:再构造一个composite,在我们平时使用的时候记得一定要构造一个自己的composite,设置自己的布局,不要直接使用参数中的composite
 import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
import
org.eclipse.jface.window.ApplicationWindow;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import
org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Control;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
 import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
import
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;


 public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{
public
class
TestWindow
extends
ApplicationWindow
{

 publicTestWindow(){
publicTestWindow(){
 super(null);
super(null);
 }
}
 protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){
protectedControlcreateContents(Compositeparent){
 Compositecontainer=newComposite(parent,SWT.NONE);
Compositecontainer=newComposite(parent,SWT.NONE);

 Texttext=newText(container,SWT.BORDER);
Texttext=newText(container,SWT.BORDER);
 text.setText("helloworld");
text.setText("helloworld");
 text.setBounds(59,112,80,25);
text.setBounds(59,112,80,25);

 Texttext_1=newText(container,SWT.BORDER);
Texttext_1=newText(container,SWT.BORDER);
 text_1.setText("it'sme");
text_1.setText("it'sme");
 text_1.setBounds(72,221,80,25);
text_1.setBounds(72,221,80,25);
 returncontainer;
returncontainer;
 }
}
 publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
 try{
try{
 TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
TestWindowwindow=newTestWindow();
 window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
window.setBlockOnOpen(true);
 window.open();
window.open();
 Display.getCurrent().dispose();
Display.getCurrent().dispose();
 }catch(Exceptione){
}catch(Exceptione){
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();
 }
}
 }
}
 privatevoidcreateActions(){
privatevoidcreateActions(){
 }
}
 }
}



