Android学习——MediaScanner源码分析
神马是MediaScanner呢?在Android的SDK里面是看不到这个类的,因为被google隐藏了。通过Android的源码我们可以看到MediaScanner的类注解多了一个@hide的标注。所以对于一般应用开发者,此文意义不是很大,大家可以绕道。
在 前两篇文章中,最后我们都了解了Android的媒体文件的扫描是在MediaScannerService中调用MediaScanner的 scanDirectories或者scanSingleFile完成最终的扫描的。那么MediaScanner是如何工作的呢?
转载请注明出处
google对MediaScanner写了一大堆的类注释,如下:
1: /* In summary:
2: * Java MediaScannerService calls
3: * Java MediaScanner scanDirectories, which calls
4: * Java MediaScanner processDirectory (native method), which calls
5: * native MediaScanner processDirectory, which calls
6: * native MyMediaScannerClient scanFile, which calls
7: * Java MyMediaScannerClient scanFile, which calls
8: * Java MediaScannerClient doScanFile, which calls
9: * Java MediaScanner processFile (native method), which calls
10: * native MediaScanner processFile, which calls
11: * native parseMP3, parseMP4, parseMidi, parseOgg or parseWMA, which calls
12: * native MyMediaScanner handleStringTag, which calls
13: * Java MyMediaScanner handleStringTag.
14: * Once MediaScanner processFile returns, an entry is inserted in to the database.
15: *
16: * {@hide}
17: */
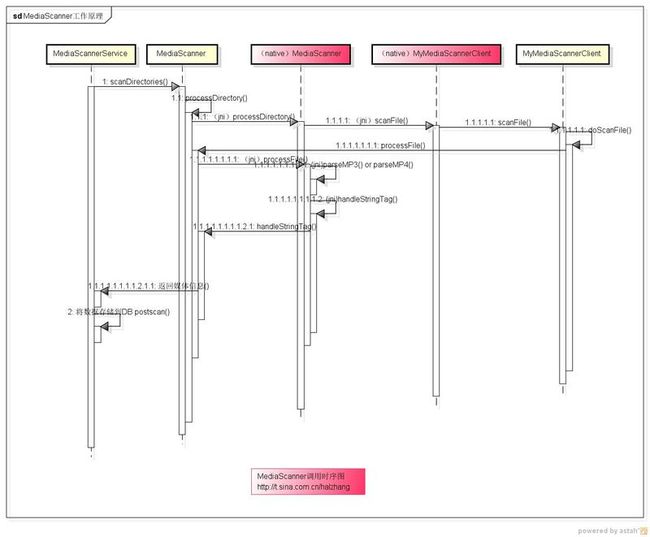
下面为调用时序图,如下:
这时序图好像不是很规范!点击看大图 !请见谅。![]() 开始看代码把……
开始看代码把……
1,scanDirectories。
初始化数据并调用processDirectory 处理扫描。
1: public void scanDirectories(String[] directories, String volumeName) {
2: try {
3: long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
4: //初始化
5:
initialize(volumeName);
6: //将数据库中的数据缓存到mFileCache
7: /*
8: * mFileCache.put(key, new FileCacheEntry(uri, rowId, path, lastModified));
9: */
10: prescan(null );
11: long prescan = System.currentTimeMillis();
12:
13: for (int i = 0; i < directories.length; i++) {
14: //扫描处理
15:
processDirectory(directories[i], MediaFile.sFileExtensions, mClient);
16:
}
17: long scan = System.currentTimeMillis();
18: //处理后续数据
19:
postscan(directories);
20: long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
2,processDirectory
这是一个native方法,所以我们直接转向jni,代码如下:
1: static void
2:
android_media_MediaScanner_processDirectory(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring path, jstring extensions, jobject client)
3: { //获取MediaScanner
4:
MediaScanner *mp = (MediaScanner *)env->GetIntField(thiz, fields.context);
5: //参数判断,并抛出异常
6: if (path == NULL) {
7: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException" , NULL);
8: return ;
9:
}
10: if (extensions == NULL) {
11: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException" , NULL);
12: return ;
13:
}
14:
15: const char *pathStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(path, NULL);
16: if (pathStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
17: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException" , "Out of memory" );
18: return ;
19:
}
20: const char *extensionsStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(extensions, NULL);
21: if (extensionsStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
22:
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
23: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException" , "Out of memory" );
24: return ;
25:
}
26: //初始化client实例
27:
MyMediaScannerClient myClient(env, client);
28: //mp调用processDirectory
29:
mp->processDirectory(pathStr, extensionsStr, myClient, ExceptionCheck, env);
30: //gc
31:
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
32:
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(extensions, extensionsStr);
33:
}
3,mp->processDirectory(pathStr, extensionsStr, myClient, ExceptionCheck, env);
1: status_t MediaScanner::processDirectory(const char *path, const char * extensions,
2: MediaScannerClient& client, ExceptionCheck exceptionCheck, void * exceptionEnv)
3: {//这方法不知道干吗的,估计跟线程有关
4:
InitializeForThread();
5:
6: int pathLength = strlen(path);
7: if (pathLength >= PATH_MAX) {
8: return PVMFFailure;
9:
}
10: char * pathBuffer = (char *)malloc(PATH_MAX + 1);
11: if (!pathBuffer) {
12: return PVMFFailure;
13:
}
14:
15: int pathRemaining = PATH_MAX - pathLength;
16:
strcpy(pathBuffer, path);
17: if (pathBuffer[pathLength - 1] != '/' ) {
18: pathBuffer[pathLength] = '/' ;
19:
pathBuffer[pathLength + 1] = 0;
20:
--pathRemaining;
21:
}
22:
23:
client.setLocale(mLocale);
24: //有是一个关键点
25:
status_t result = doProcessDirectory(pathBuffer, pathRemaining, extensions, client, exceptionCheck, exceptionEnv);
26: //释放内存
27:
free(pathBuffer);
28: return result;
29:
}
4,doProcessDirectory
1: status_t MediaScanner::doProcessDirectory(char *path, int pathRemaining, const char * extensions,
2: MediaScannerClient& client, ExceptionCheck exceptionCheck, void * exceptionEnv)
3:
{
4:
……
5:
……
6: if (type == DT_REG || type == DT_DIR) {
7: int nameLength = strlen(name);
8: bool isDirectory = (type == DT_DIR);
9:
10: if (nameLength > pathRemaining || (isDirectory && nameLength + 1 > pathRemaining)) {
11: // path too long!
12: continue ;
13:
}
14:
15:
strcpy(fileSpot, name);
16: if (isDirectory) {
17: // ignore directories with a name that starts with '.'
18: // for example, the Mac ".Trashes" directory
19: if (name[0] == '.' ) continue ;
20:
21: strcat(fileSpot, "/" );
22: //文件夹,递归调用
23: int err = doProcessDirectory(path, pathRemaining - nameLength - 1, extensions, client, exceptionCheck, exceptionEnv);
24: if (err) {
25: // pass exceptions up - ignore other errors
26: if (exceptionCheck && exceptionCheck(exceptionEnv)) goto failure;
27: LOGE("Error processing '%s' - skipping\n" , path);
28: continue ;
29:
}
30: } else if (fileMatchesExtension(path, extensions)) {
31: //文件,扩展名符合
32: struct stat statbuf;
33:
stat(path, &statbuf);
34: if (statbuf.st_size > 0) {
35: //调用client的scanFile方法
36:
client.scanFile(path, statbuf.st_mtime, statbuf.st_size);
37:
}
38: if (exceptionCheck && exceptionCheck(exceptionEnv)) goto failure;
39:
}
40:
}
41:
……
42:
……
5,client.scanFile
1: // returns true if it succeeded, false if an exception occured in the Java code
2: virtual bool scanFile(const char * path, long long lastModified, long long fileSize)
3:
{
4:
jstring pathStr;
5: if ((pathStr = mEnv->NewStringUTF(path)) == NULL) return false ;
6: //有点反射的感觉,调用java里面mClient中的scanFile方法
7:
mEnv->CallVoidMethod(mClient, mScanFileMethodID, pathStr, lastModified, fileSize);
8:
9:
mEnv->DeleteLocalRef(pathStr);
10: return (!mEnv->ExceptionCheck());
11:
}
6,mEnv->CallVoidMethod(mClient, mScanFileMethodID, pathStr, lastModified, fileSize); 让我们回到Java![]()
在android.media.MediaScanner.MyMediaScannerClient中的scanFile方法是直接调用doScanFile的,来看看doScanFile
1:
2: public Uri doScanFile(String path, String mimeType, long lastModified, long fileSize,
3:
boolean scanAlways) {
4: Uri result = null ;
5: // long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
6: try {
7:
FileCacheEntry entry = beginFile(path, mimeType, lastModified, fileSize);
8: // rescan for metadata if file was modified since last scan
9: if (entry != null && (entry.mLastModifiedChanged || scanAlways)) {
10:
String lowpath = path.toLowerCase();
11:
boolean ringtones = (lowpath.indexOf(RINGTONES_DIR) > 0);
12:
boolean notifications = (lowpath.indexOf(NOTIFICATIONS_DIR) > 0);
13:
boolean alarms = (lowpath.indexOf(ALARMS_DIR) > 0);
14:
boolean podcasts = (lowpath.indexOf(PODCAST_DIR) > 0);
15:
boolean music = (lowpath.indexOf(MUSIC_DIR) > 0)
16:
|| (!ringtones && !notifications && !alarms && !podcasts);
17:
18: if (isMetadataSupported(mFileType)) {
19: // 调用jni方法
20: processFile(path, mimeType, this );
21: } else if (MediaFile.isImageFileType(mFileType)) {
22: // we used to compute the width and height but it's not
23: // worth it
24:
}
25:
26:
result = endFile(entry, ringtones, notifications, alarms, music, podcasts);
27:
}
28: } catch (RemoteException e) {
29: Log.e(TAG, "RemoteException in MediaScanner.scanFile()" , e);
30:
}
31: // long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
32: // Log.v(TAG, "scanFile: " + path + " took " + (t2-t1));
33: return result;
34:
}
7,接着是native的 processFile
1: static void
2:
android_media_MediaScanner_processFile(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring path, jstring mimeType, jobject client)
3:
{
4:
MediaScanner *mp = (MediaScanner *)env->GetIntField(thiz, fields.context);
5:
6: if (path == NULL) {
7: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException" , NULL);
8: return ;
9:
}
10:
11: const char *pathStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(path, NULL);
12: if (pathStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
13: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException" , "Out of memory" );
14: return ;
15:
}
16: const char *mimeTypeStr = (mimeType ? env->GetStringUTFChars(mimeType, NULL) : NULL);
17: if (mimeType && mimeTypeStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
18:
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
19: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException" , "Out of memory" );
20: return ;
21:
}
22:
23:
MyMediaScannerClient myClient(env, client);
24: //调用MediaScanner的processFile
25:
mp->processFile(pathStr, mimeTypeStr, myClient);
26:
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
27: if (mimeType) {
28:
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(mimeType, mimeTypeStr);
29:
}
30:
}
1: status_t MediaScanner::processFile(const char *path, const char * mimeType, MediaScannerClient& client)
2:
{
3:
status_t result;
4:
InitializeForThread();
5: //初始化client
6:
client.setLocale(mLocale);
7:
client.beginFile();
8:
9: //LOGD("processFile %s mimeType: %s\n", path, mimeType);
10: const char * extension = strrchr(path, '.' );
11: //根据扩展名调用不同的解析方法
12: if (extension && strcasecmp(extension, ".mp3" ) == 0) {
13:
result = parseMP3(path, client);
14: } else if (extension &&
15: (strcasecmp(extension, ".mp4" ) == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".m4a" ) == 0 ||
16: strcasecmp(extension, ".3gp" ) == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".3gpp" ) == 0 ||
17: strcasecmp(extension, ".3g2" ) == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".3gpp2" ) == 0)) {
18:
result = parseMP4(path, client);
19: } else if (extension && strcasecmp(extension, ".ogg" ) == 0) {
20:
result = parseOgg(path, client);
21: } else if (extension &&
22: ( strcasecmp(extension, ".mid" ) == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".smf" ) == 0
23: || strcasecmp(extension, ".imy" ) == 0)) {
24:
result = parseMidi(path, client);
25: } else if (extension &&
26: (strcasecmp(extension, ".wma" ) == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".aac" ) == 0)) {
27: //TODO: parseWMA needs to be renamed to reflect what it is really doing,
28: //ie. using OpenCORE frame metadata utility(FMU) to retrieve metadata.
29:
result = parseWMA(path, client);
30: } else {
31:
result = PVMFFailure;
32:
}
33: //调用client
34:
client.endFile();
35:
36: return result;
37:
}
9,client.endFile()
1: void MediaScannerClient::endFile()
2:
{
3: if (mLocaleEncoding != kEncodingNone) {
4: int size = mNames->size();
5:
uint32_t encoding = kEncodingAll;
6:
7: // compute a bit mask containing all possible encodings
8: for (int i = 0; i < mNames->size(); i++)
9:
encoding &= possibleEncodings(mValues->getEntry(i));
10:
11: // if the locale encoding matches, then assume we have a native encoding.
12: if (encoding & mLocaleEncoding)
13:
convertValues(mLocaleEncoding);
14:
15: // finally, push all name/value pairs to the client
16: for (int i = 0; i < mNames->size(); i++) {
17: //在handleStringTag中是通过类反射的方法调用java中的handleStringTag
18: if (!handleStringTag(mNames->getEntry(i), mValues->getEntry(i)))
19: break ;
20:
}
21:
}
22: // else addStringTag() has done all the work so we have nothing to do
23:
24:
delete mNames;
25:
delete mValues;
26:
mNames = NULL;
27:
mValues = NULL;
28:
}
10,java中的handleStringTag ,这个方法主要处理那些在底层解析后的数据返回到java层
1: public void handleStringTag(String name, String value ) {
2: if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("title" ) || name.startsWith("title;" )) {
3: // Don't trim() here, to preserve the special \001 character
4: // used to force sorting. The media provider will trim() before
5: // inserting the title in to the database.
6: mTitle = value ;
7: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("artist" ) || name.startsWith("artist;" )) {
8: mArtist = value .trim();
9: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("albumartist" ) || name.startsWith("albumartist;" )) {
10: mAlbumArtist = value .trim();
11: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("album" ) || name.startsWith("album;" )) {
12: mAlbum = value .trim();
13: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("composer" ) || name.startsWith("composer;" )) {
14: mComposer = value .trim();
15: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("genre" ) || name.startsWith("genre;" )) {
16: // handle numeric genres, which PV sometimes encodes like "(20)"
17: if (value .length() > 0) {
18: int genreCode = -1;
19: char ch = value .charAt(0);
20: if (ch == '(' ) {
21: genreCode = parseSubstring(value , 1, -1);
22: } else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) {
23: genreCode = parseSubstring(value , 0, -1);
24:
}
25: if (genreCode >= 0 && genreCode < ID3_GENRES.length) {
26: value = ID3_GENRES[genreCode];
27:
}
28:
}
29: mGenre = value ;
30: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("year" ) || name.startsWith("year;" )) {
31: mYear = parseSubstring(value , 0, 0);
32: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("tracknumber" ) || name.startsWith("tracknumber;" )) {
33: // track number might be of the form "2/12"
34: // we just read the number before the slash
35: int num = parseSubstring(value , 0, 0);
36:
mTrack = (mTrack / 1000) * 1000 + num;
37: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("discnumber" ) ||
38: name.equals("set" ) || name.startsWith("set;" )) {
39: // set number might be of the form "1/3"
40: // we just read the number before the slash
41: int num = parseSubstring(value , 0, 0);
42:
mTrack = (num * 1000) + (mTrack % 1000);
43: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("duration" )) {
44: mDuration = parseSubstring(value , 0, 0);
45: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("writer" ) || name.startsWith("writer;" )) {
46: mWriter = value .trim();
47:
}
48:
}
此致,此文结束,累。![]()