SQL Server 2005 – Automating Creation of Database Snapshots
SQL Server 2005 is packed with many new features. One of the new features that I would like to discuss in this article is Database Snapshots, which are read only static views of a database. SQL Server 2005 allows you to create multiple snapshots on a database. In this article, I would like to demonstrate the creation of database snapshots and automating the creation of database snapshots.
First let's simulate the whole snapshot creation process.
Step 1
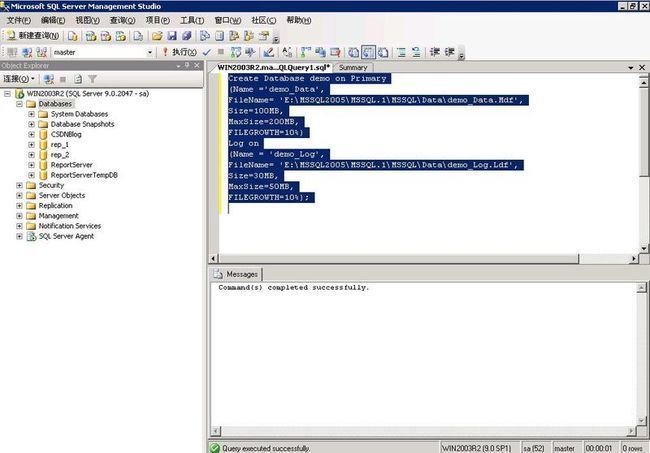
Copy and paste the query below into the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio's Query window and execute it. This statement creates the database demo.
Create Database demo on Primary
(Name ='demo_Data',
FileName= 'E:\MSSQL2005\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\Data\demo_Data.Mdf',
Size=100MB,
MaxSize=200MB,
FILEGROWTH=10%)
Log on
(Name = 'demo_Log',
FileName= 'E:\MSSQL2005\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\Data\demo_Log.Ldf',
Size=30MB,
MaxSize=50MB,
FILEGROWTH=10%);
Figure 1
Setp 2
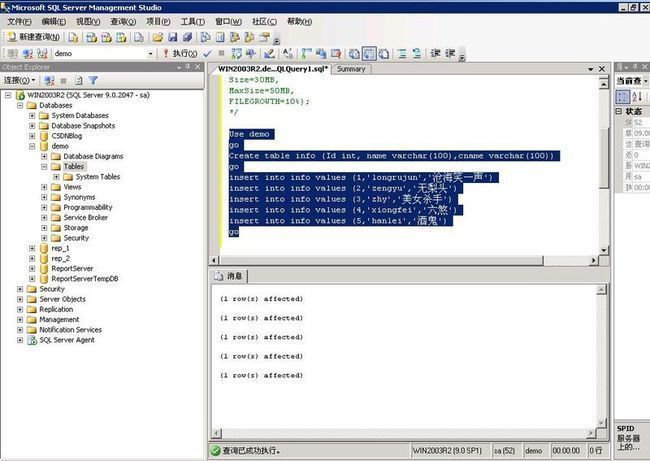
Let us create a table and insert some rows.
Copy and paste the query below into the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio's Query window and execute it. This statement creates the table info and inserts 5 rows to the table.
Use demo
go
Create table info (Id int, name varchar(100),cname varchar(100))
go
insert into info values (1,'longrujun','沧海笑一声')
insert into info values (2,'zengyu','无梨头')
insert into info values (3,'zhy','美女杀手')
insert into info values (4,'xiongfei','六煞')
insert into info values (5,'hanlei','酒鬼')
go
Figure 2
Step 3
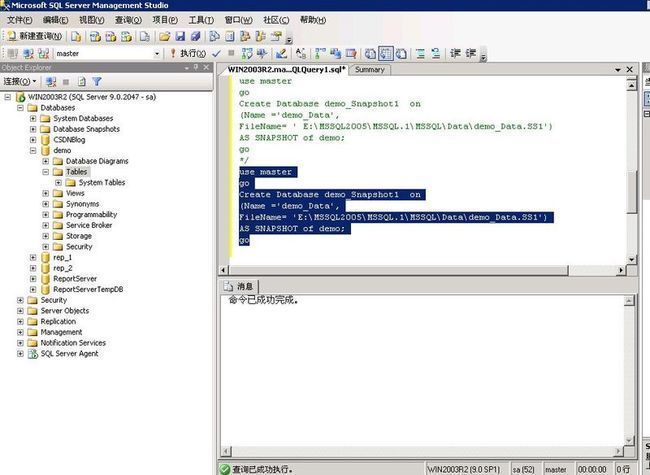
Now let's create a snapshot for the database demo.
Copy and paste the query below into the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio's Query window and execute it. This statement creates the snapshot demo_Snapshot1 for the database demo.
use master
go
Create Database demo_Snapshot1 on
(Name ='demo_Data',
FileName= 'E:\MSSQL2005\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\Data\demo_Data.SS1')
AS SNAPSHOT of demo;
Go
This would create a file E:\MSSQL2005\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\Data\demo_Data.SS1 as shown in the following Figure
Figure 3,4
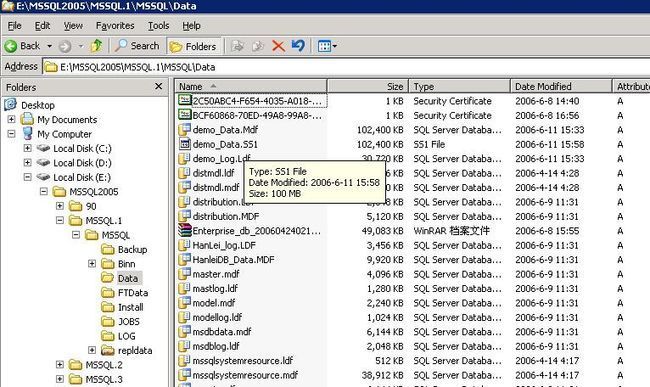
Step 4
Now let's delete some rows from the original database.
Copy and paste the query below into the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio's Query window and execute it. This statement deletes two rows from the demo database.
Use demo
Go
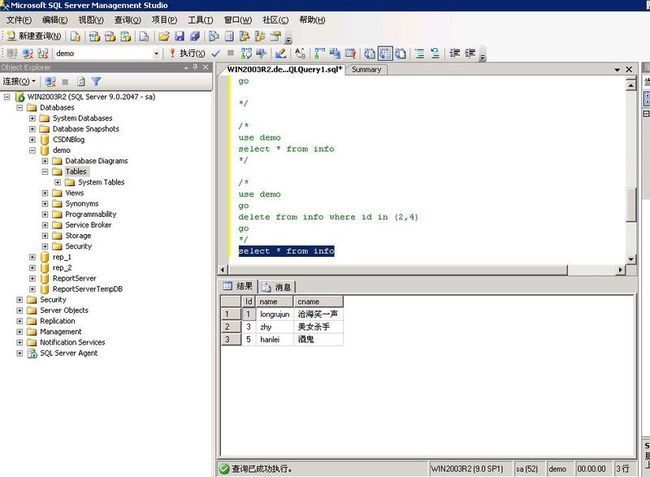
Select * from info
Figure 5
use demo go delete from info where id in (2,4) go
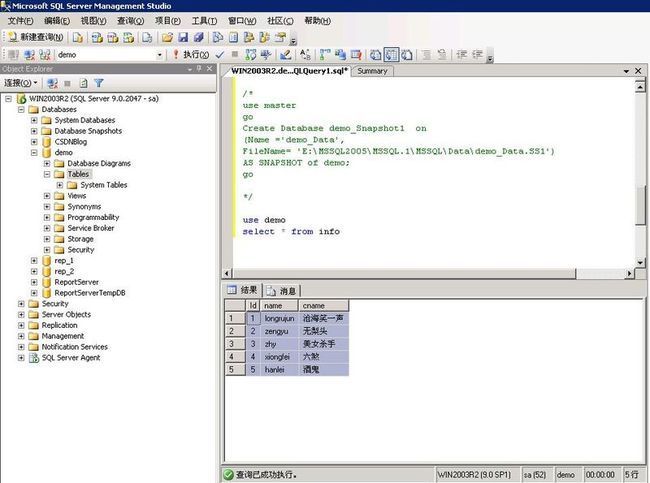
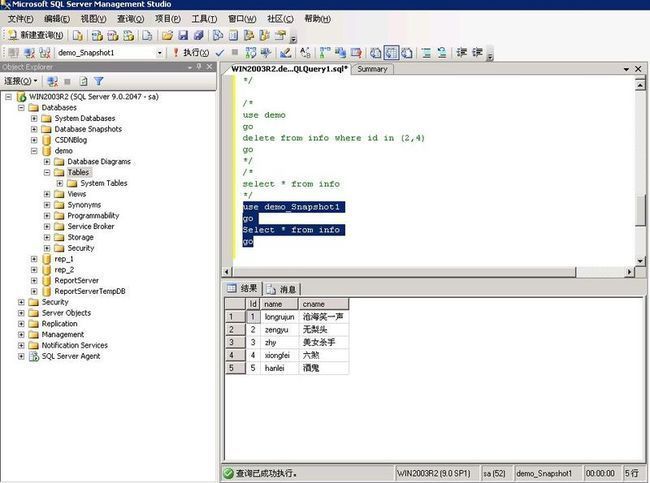
Step 5 Now let's query the table info from the original database demo and from the SnapShot view demo_Snapshot1.
Copy and paste the query below into the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio's Query window and execute it. This statement displays all of the rows from the table info from the database demo. [Refer Fig ]
use demogoSelect * from infogoFigure 6
Copy and paste the query below into the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio's Query window and execute it. This statement displays all of the rows from the table info, from the snapshot demo_Snapshot1 (the snapshot view of the database info.)use demo_Snapshot1goSelect * from infogoFigure 7
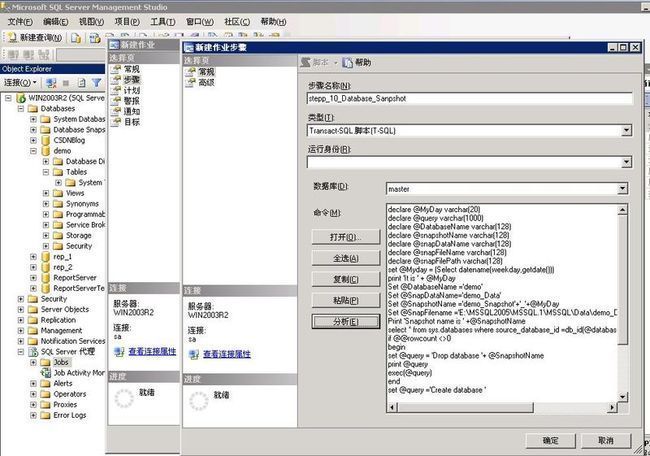
Now, let's automate creation of a daily database snapshot and let's keep one week worth of snapshots.
Create a SQL Server Scheduled job [Refer Fig 8,9,10,11] to execute the following statement every night at 3:00 am
Figure 8
Figure 9
the code is here
declare @query varchar(1000)
declare @DatabaseName varchar(128)
declare @snapshotName varchar(128)
declare @snapDataName varchar(128)
declare @snapFileName varchar(128)
declare @snapFilePath varchar(128)
declare @nalja varchar(12)
set @nalja=convert(varchar(4), datepart(yyyy, getdate())) + convert
(varchar(4), datepart(mm, getdate())) + convert(varchar(4), datepart
(dd, getdate()))
print 'It is ' + @nalja
Set @DatabaseName ='demo'
Set @SnapDataName='demo_Data'
Set @SnapshotName ='demo_Snapshot'+'_'+@nalja
Set @SnapFilename ='"E:\MSSQL2005\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\Data\demo_Data'+'_'+@nalja+'.ss"'
Print 'Snapshot name is ' +@SnapshotName
select * from sys.databases where source_database_id =db_id(@databasename) and name = @SnapshotName
if @@rowcount <>0
begin
set @query = 'Drop database '+ @SnapshotName
print @query
exec(@query)
end
set @query ='Create database ' + @SnapshotName + ' on (Name = ' +@snapDataName +', FileName=' +@SnapFilename +') AS SNAPSHOT of ' + @databasename+';'
print @query
exec(@query)
Figure 10
The naming convention of the database snapshot is demo_Snapshot_Day
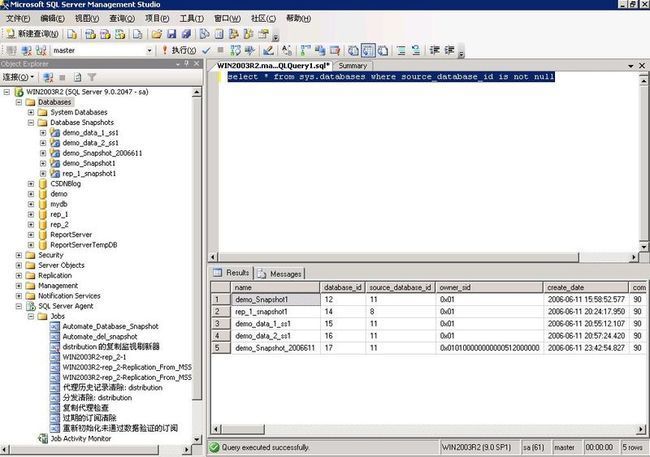
The following SQL statement will list all of the database snapshots available on a SQL Server instance. [Refer Fig 11]
select * from sys.databases where source_database_id is not null
Figure 11
Note: By changing the naming convention and the schedule of this process,you can convert this daily database snapshot process to a weekly or monthlydatabase snapshot process.
Conclusion
This article demonstrated the creation of a database snapshot and the automating of the creation of database snapshots.By creating a database snapshot everyday, it would be more convenient to go back to a particular day to get data, or compareor to monitor the status of the data. The database can be reverted to a database snapshot using the RESTORE command.