Mybatis源码学习(一)-整体框架理解
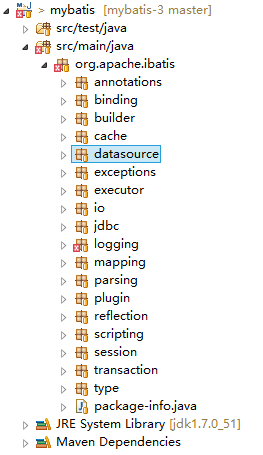
一、对源码先上一个结构图:
源代码主要在org.apache.ibatis目录下,18个包,其中在应用中主要的包有:builder、session、cache、type、transaction、datasource、jdbc、mapping,提供支撑服务的包有annotation、binding、io、logging、plugin、reflection、scripting、exception、executor、parsing
二、从使用入手
MyBatis使用的三板斧是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder和SqlSessionFactory、SqlSession
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
支持9种构造方法,其实最主要的是包含Configuration对象的构造方法,目的是为了通过加载配置文件创造SqlSessionFactory对象,真实最终返回的是DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
所有的构造方法最终都是调用build(Configuratiron)方法,这就要来研究一下Configuration对象,其实他就是对xml配置文件的对象映射,关于xml文件结构组成可从源码中看出如下:
本文介绍一下Configuration的大框架,后续开个专辑专门研究Configuration的细节
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //加载资源文件属性和当前文件属性
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
环境元素(数据源和事务)、 属性、类型别名、typeHandler、mapper、setting、插件
属性:
先来看属性的加载,属性的加载最重要的是了解三种属性来源(属性配置文件、当前文件的属性、java代码输入)和三种属性的加载顺序(先加载配置文件,在加载config文件的属性,最后加载java代码输入)
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
if (resource != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
parser.setVariables(defaults);
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
类型别名
主要是类的完整路径和简单别名的对应关系加载,保存在容器typeAliasRegistry中,最终映射到configuratiron对象中
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else {
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
if (alias == null) {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
typeHandler
用户自定义类型处理器,保存在typeHandlerRegistry容器中,最终保存在configuration对象中
private void typeHandlerElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeHandlerPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerPackage);
} else {
String javaTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String handlerTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("handler");
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaTypeName);
JdbcType jdbcType = resolveJdbcType(jdbcTypeName);
Class<?> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(handlerTypeName);
if (javaTypeClass != null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass);
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, jdbcType, typeHandlerClass);
}
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerClass);
}
}
}
}
}
mapper
主要是加载mapper.xml文件,同构mapperParser对文件进行解析,保存在容器mapperRegistry中,最终保存到configuration对象中
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
环境元素
主要加载数据源、和事务配置信息,由Environment.Builder对象进行处理,并将信息保存到configuratiron对象
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
setting
加载ibatis自身工作需要配置的所有设置信息,为configuration对象进行赋值
private void settingsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class);
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), true));
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
configuration.setLogImpl(resolveClass(props.getProperty("logImpl")));
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
configuration.setInjectionFilterEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("injectionFilterEnabled"), false));
configuration.setInjectionFilter(parseExpression(props.getProperty("injectionFilter"), "^[a-zA-Z0-9._]*$"));
}
}
2、SqlSessionFactory,真实干活的DefaultSqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory的作用是承上启下,作为SqlSession的工厂,主要是工作必须是提供获取SqlSession的方法,同时还提供了一个获取Configuration的方法
其中SqlSessionFactory提供了8种获取SqlSession的方法,主要涉及4个参数:是否自动提交、事务级别、ExecutorType(Statement类型【普通、预处理、批处理】)、自定义Connection
其中需要注意的是openSession()方法默认不是自动commit的。
SqlSession openSession(); SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit); SqlSession openSession(Connection connection); SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level); SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection); Configuration getConfiguration();
揭开如何提供SqlSession的秘密(在这里发现了Configuration还可以提供创造Executor的工作,Connection被封装在Transaction 中,Configuration做了两件事情,一个是配置信息存储,还有内部对象的组装工作,需要深入研究这种模式是否可以通过另一个Action对象进行管理呢?)
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromConnection(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection) {
try {
boolean autoCommit;
try {
autoCommit = connection.getAutoCommit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Failover to true, as most poor drivers
// or databases won't support transactions
autoCommit = true;
}
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
final Transaction tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(connection);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
这个需要重点关注。创建事务,将Connection传递给tx的过程。
3、SqlSession,真实干活的是DefaultSqlSession
SqlSession类主要封装了Configuration对象、Executor对象、是否自动提交
SqlSession是在程序中真实干活的人,我们在使用Mybatis中打交道最频繁的就是SqlSessinon对象,上个结构图,看看他都在干啥
看到图了,就没有什么秘密了,他就是在干数据的日常操作的活,只不过是用他自己封装的一套东西,比如说Configuration(封装Connection【来源可以使Pool】)、Executor(封装Statement)、ResultHandler(封装处理ResultSet对象)、RowBounds(封装分页对象),提供了CRUD,提供了缓存机制,提供了根据配置文件获取Sql语句的方法,提供了事务的提交和回滚等。