毕业设计(三)---spring学习笔记(1)之-IOC
框架搭建完毕,准备开始动手,理了一下思路,发现struts2 和 hibernate3 的各种公用都比较清楚,唯独对spring2.5 的里各种知识点有点模糊,特此复习!
Spring简介:
Spring 框架是一个分层架构,由 7 个定义良好的模块组成。Spring 模块构建在核心容器之上,核心容器定义了创建、配置和管理 bean 的方式,如图 所示。
图 1. Spring 框架的 7 个模块
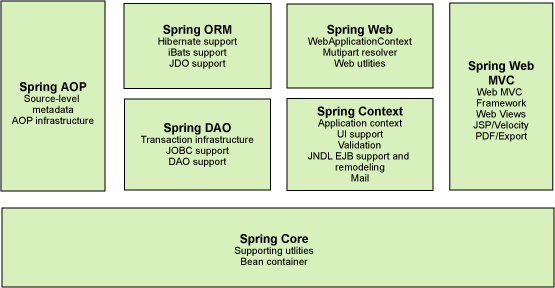
组成 Spring 框架的每个模块(或组件)都可以单独存在,或者与其他一个或多个模块联合实现。每个模块的功能如下:
- 核心容器:核心容器提供 Spring 框架的基本功能。核心容器的主要组件是
BeanFactory,它是工厂模式的实现。BeanFactory使用控制反转 (IOC) 模式将应用程序的配置和依赖性规范与实际的应用程序代码分开。 - Spring 上下文:Spring 上下文是一个配置文件,向 Spring 框架提供上下文信息。Spring 上下文包括企业服务,例如 JNDI、EJB、电子邮件、国际化、校验和调度功能。
- Spring AOP:通过配置管理特性,Spring AOP 模块直接将面向方面的编程功能集成到了 Spring 框架中。所以,可以很容易地使 Spring 框架管理的任何对象支持 AOP。Spring AOP 模块为基于 Spring 的应用程序中的对象提供了事务管理服务。通过使用 Spring AOP,不用依赖 EJB 组件,就可以将声明性事务管理集成到应用程序中。
- Spring DAO:JDBC DAO 抽象层提供了有意义的异常层次结构,可用该结构来管理异常处理和不同数据库供应商抛出的错误消息。异常层次结构简化了错误处理,并且极大地降低了需要编写的异常代码数量(例如打开和关闭连接)。Spring DAO 的面向 JDBC 的异常遵从通用的 DAO 异常层次结构。
- Spring ORM:Spring 框架插入了若干个 ORM 框架,从而提供了 ORM 的对象关系工具,其中包括 JDO、Hibernate 和 iBatis SQL Map。所有这些都遵从 Spring 的通用事务和 DAO 异常层次结构。
- Spring Web 模块:Web 上下文模块建立在应用程序上下文模块之上,为基于 Web 的应用程序提供了上下文。所以,Spring 框架支持与 Jakarta Struts 的集成。Web 模块还简化了处理多部分请求以及将请求参数绑定到域对象的工作。
- Spring MVC 框架:MVC 框架是一个全功能的构建 Web 应用程序的 MVC 实现。通过策略接口,MVC 框架变成为高度可配置的,MVC 容纳了大量视图技术,其中包括 JSP、Velocity、Tiles、iText 和 POI。
Spring 框架的功能可以用在任何 J2EE 服务器中,大多数功能也适用于不受管理的环境。Spring 的核心要点是:支持不绑定到特定 J2EE 服务的可重用业务和数据访问对象。毫无疑问,这样的对象可以在不同 J2EE 环境 (Web 或 EJB)、独立应用程序、测试环境之间重用。
一:IOC
1) 定义:
bean:在spring 中 ,那些组成应用程序的主体(backbone)及由spring ioc 容器所管理的对象成为bean。
简单来说,bean是又Spring进行初始化,装配及管理的对象,除此之外,bean就是于应用程序其他对象没有什么区别了。而bean的定义以及bean相互间的依赖关系将通过配置元素来描述。
控制反转 IoC(Inversion of Control) : ioc 是一种编程思想,主要是协调各组件间相互的依赖关系。 Ioc 就是由容器来控制业务对象之间的依赖关系,而非传统方式中由代码来直接操控,控制反转的本质,是控制权由应用代码转到了外部容器,控制权的转移即是所谓的反转,控制权的转移带来的好处就是降低了业务对象之间的依赖程度,即实现了解耦。
2)配置元数据
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="..." class="com.xxx.xxx.类名"> <!-- id也可以使用name ,区别是name可以使用特殊字符 -->
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="..." class="...">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions go here -->
</beans>
3)实例化容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String[] {"services.xml", "daos.xml"});
// an ApplicationContext is also a BeanFactory (via inheritance)
BeanFactory factory = context;
使用bean容器的小代码:
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
Chinese c = ctx.getBean("chinese");
4)注入依赖:
构造器注入(少):
package x.y;
public class Foo {
public Foo(Bar bar, Baz baz) {
// ...
}
}
<beans>
<bean name="foo" class="x.y.Foo">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="x.y.Bar"/>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="x.y.Baz"/>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
setter注入(多):
public class ExampleBean {
private AnotherBean beanOne;
private YetAnotherBean beanTwo;
private int i;
public void setBeanOne(AnotherBean beanOne) {
this.beanOne = beanOne;
}
public void setBeanTwo(YetAnotherBean beanTwo) {
this.beanTwo = beanTwo;
}
public void setIntegerProperty(int i) {
this.i = i;
}
}
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean"> <!-- setter injection using the nested <ref/> element --> <property name="beanOne"> <ref bean="anotherExampleBean"/> </property>
<!-- setter injection using the neater 'ref' attribute -->
<property name="beanTwo" ref="yetAnotherBean"/>
<property name="integerProperty" value="1"/>
</bean>
<bean id="anotherExampleBean" class="examples.AnotherBean"/>
<bean id="yetAnotherBean" class="examples.YetAnotherBean"/>
5)bean的作用域
Singleton:在每个Spring IoC容器中一个bean定义对应一个对象实例。
Prototype:一个bean定义对应多个对象实例。
<bean id="accountService" class="com.foo.DefaultAccountService"/> <!-- the following is equivalent, though redundant (singleton scope is the default); using spring-beans-2.0.dtd --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.foo.DefaultAccountService" scope="singleton"/> <!-- the following is equivalent and preserved for backward compatibility in spring-beans.dtd --><bean name="userDAO2" class="com.bjsxt.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl"> <property name="daoId" value="2"></property> </bean> <bean id="userService" class="com.bjsxt.service.UserService" scope="prototype" autowire="byType|byName"> </bean> ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService service = (UserService)ctx.getBean("userService"); System.out.println(service.getUserDAO());//自动装配了 name="userDAO2" 的bean.
<bean id="accountService" class="com.foo.DefaultAccountService" singleton="true"/> 6)自动装配byName:
根据属性名自动装配。此选项将检查容器并根据名字查找与属性完全一致的bean,并将其与属性自动装配。例如,在bean定义中将autowire设置为by name,而该bean包含master属性(同时提供setMaster(..)方法),Spring就会查找名为
master的bean定义,并用它来装配给master属性。byType:
如果容器中存在一个与指定属性类型相同的bean,那么将与该属性自动装配。如果存在多个该类型的bean,那么将会抛出异常,并指出不能使用byType方式进行自动装配。若没有找到相匹配的bean,则什么事都不发生,属性也不会被设置。
6)使用Annotation注解!
a. 修改 applicationContext.xml 文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config><!-- 隐式的向spring容器注册4个BeanProcessor,为了能让系统识别相应的注解 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.myblog" /><!-- 扫描所有的component, 从com.myblog 开始扫描,扫描其下的所有的包,此项 该配置项其实也包含了自动注入上述processor的功能, 可以移除 上一项了 --></beans>
b.基于注解的 @Autowired默认使用的是 byType
public class SimpleMovieLister { private MovieFinder movieFinder; @Autowired public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) { this.movieFinder = movieFinder; } // ... }c.基于注解的 @Resource 和 @Component (重要)
public class SimpleMovieLister { private MovieFinder movieFinder; @Resource(name="myMovieFinder")//@Resource 只有一个属性name ,如果缺省,默认为 movieFinder public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) { this.movieFinder = movieFinder; } }通过 @Autowired 或者 @Resource 在Bean类中使用自动注入功能, bean 是在xml中定义的,也可以使用注解的方法定义bean , 那就是
@Component 需要在applicationContext.xml上加上
<context:component-scan base-package="com.myblog" />@Component 有一个可选的入参,用于指定 Bean 的名称,一般情况下,Bean 都是 singleton 的,需要注入 Bean 的地方仅需要通过 byType 策略就可以自动注入了,所以大可不必指定 Bean 的名称
@Component("daoPost")//不指定名字, 默认就是 daoPost , 或者不写,通过byType 自动注入~~ public class DaoPostImpl implements DaoPost { ... }
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。