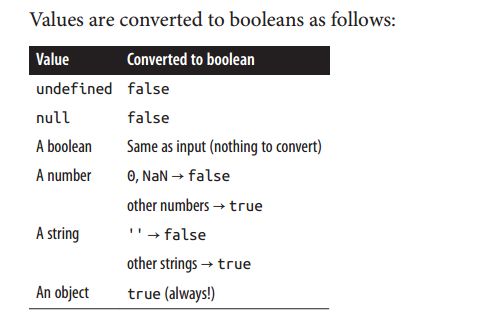
JS转换为布尔值、逻辑运算符、操作符==和===
以下都会使用实例来说明转换规则
value ? true : false方式转换为布尔值
//JS的boolean的转换
//Values are converted to booleans as follows:
var exp = undefined;
console.log(exp ? "undefined->true" : "undefined->false");//undefined->false
var exp2 = null;
console.log(exp2 ? "null->true" : "null->false");//null->false
var exp3 = 0;
console.log(exp3 ? "number 0->true" : "number 0->false");//number 0->false
var nan = NaN;
console.log(nan ? "NaN->true" : "NaN->false");//NaN->false
var exp4 = -1;
console.log(exp4 ? "other numbers(except 0)->true" : "other numbers(except 0)->false");//"other numbers(except 0)->true"
var exp5 = '';
console.log(exp5 ? "a string '' -> false" : "other string -> true");//a string '' -> false
var exp6 = 'abcd';
console.log(exp6 ? "a string '' -> false" : "other string -> true");//other string -> true
var obj = new Object();//all objects are truthy
console.log(obj ? "always true" : ">>>>>>>");//always true
console.log({} ? "always true" : ">>>>>>>>");//always true
console.log([] ? "always true" : ">>>>>>>>");//always true
Boolean(value) 方式转换为布尔值
(Invoked as a function, not as a constructor)
/////////////////////////////////////
//Manually Converting to Boolean
//使用Boolean(value) (Invoked as a function, not as a constructor)
var v1 = Boolean("false");
console.log(v1 ? "true" : "false"); //true
var v2 = Boolean('');
console.log(v2 ? "true" : "false"); //false
var v3 = Boolean(undefined);
console.log(v3 ? "true" : "false"); //false
!!value方式转换为布尔值
//使用(!!value)->A single “not” converts to negated boolean; use twice for the nonnegated conversion var v4 = null; console.log(!!v4 ? "true" : "false"); //false var v5 = 0; console.log(!!v5 ? "true" : "false"); //false
typeof 六种返回值
typeof的返回值有六种可能:number、string、boolean、object、function、undefined。
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//typeof的返回值有六种可能:number、string、boolean、object、function、undefined。
console.log(typeof new Object()); //object
console.log(typeof 123);//number
console.log(typeof function () {
});//function
function hello() {
alert("say hello~~");
}
console.log(typeof hello); //function
console.log(typeof "hello"); //string
console.log(typeof romantic);//undefined
var good = null;
console.log(typeof good); //object
console.log(typeof true); //boolean
JS逻辑运算符
Logical And (&&)
If the first operand can be converted to false, return it. Otherwise, return the second operand:
if (true && false) { //true
console.log("true");
} else {
console.log("false");
}
if (0 && 123) { //false
console.log("true");
} else {
console.log("false");
}
if (undefined && 123) { //false
console.log("true");
} else {
console.log("false");
}
console.log(null && "1234"); //null-因为第一个操作数被转换为false,所以返回第一个操作数null
console.log("123" && undefined); //返回第二个操作数undefined
Logical Or (||)
If the first operand can be converted to true, return it. Otherwise, return the second operand:
console.log(null || "1234"); //null-因为第一个操作数被转换为false,所以返回第二个操作数1234
console.log("123" || undefined); //返回第一个操作数123
Logical Not (!)
The logical not operator !converts its operand to boolean and then negates it:
console.log(!null); //true console.log(!"123"); //false
JS操作符==和===
JavaScript has two ways of determining whether two values are equal:
Strict equality (===) and strict inequality (!==) consider only values that have the
same type to be equal.(Values with different types are never strictly equal. )
Normal (or “lenient”) equality (==) and inequality (!=) try to convert values of
different types before comparing them as with strict (in)equality.
Strict Equality (===, !==)
console.log(undefined === undefined ? "true" : "false"); //true
console.log(undefined == undefined ? "true" : "false"); //true
console.log(NaN === NaN ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(NaN == NaN ? "true" : "false"); //false
//Two objects (including arrays and functions): x === yif and only if xand yare the
//same object; that is, if you want to compare different objects, you have to implement
//your own comparison algorithm:
var b = {}, c = {};
console.log(b === c ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(b === b ? "true" : "false"); //true
console.log(undefined === null ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(undefined == null ? "true" : "false"); //true
其中比较特殊的就是
var b = {}, c = {};
console.log(b === c ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(b === b ? "true" : "false"); //true
js中的每个对象都是唯一的,它仅仅和自己相等。
还有关于NaN的相等关系
console.log(NaN === NaN ? "true" : "false"); //false console.log(NaN == NaN ? "true" : "false"); //false
Normal (Lenient) Equality (==, !=)
If both operands have the same type (one of the six specification types—Undefined, Null, Boolean, Number, String, and Object), then compare them via strict equality.
Otherwise, if the operands are:
1. undefinedand null, then they are considered leniently equal:
> undefined == null true2. A string and a number, then convert the string to a number and compare both operands via strict equality.
3. A boolean and a nonboolean, then convert the boolean to a number and compare leniently (again).
4. An object and a number or a string, then try to convert the object to a primitive (via the algorithm described in “Algorithm: ToPrimitive()—Converting a Value to a Primitive” on page 79) and compare leniently (again).
Otherwise-if none of the aforementioned cases apply—the result of the lenient comparison is false.
上面这段英文描述了比较规则。(摘自Speaking JavaScript)
我做的例子:
console.log("1234" == 1234 ? "true" : "false"); //true//根据上面的规则,把字符串转为数字,然后再使用===
console.log(12345 == "12345" ? "true" : "false"); //true
console.log(12345 == "12325" ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(true == 1 ? "true" : "false"); //true
console.log(true == 2 ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(true == 3 ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(false == 0 ? "true" : "false"); //true//把布尔值转换为数字,然后再与数字进行==比较
var str = new String("134");
console.log(str == 134 ? "true" : "false"); //true//根据上面的规则,一个对象要转换为他的原始值,然后在进行==比较
var obj2 = new Object();
console.log(obj2.valueOf()); //{}
console.log(obj2.toString());//[object Object]
console.log(obj2 == '' ? "true" : "false"); //false
console.log(obj2 == {} ? "true" : "false"); //false
最近整理了这些东西,我感觉做开发基本够用,有些太迷惑人的东西就舍弃了。。
====持续补充====