ThreadLocal的细节和设计模式
提要:
1.都知道ThreadLocal都是线程局部变量,可以比作是个Thread->T的MAP,那么有个问题了,如果一个类维护了一个TL的局部变量,随着不同的线程访问,这个TL会变得很大么?我们需要在线程结束前调用TL.remove来删除TL变量么,如果不删除会不会空间无法释放导致OOM呢?
2.在写某些会被多线程访问的代码时,某些实例变量需要做成线程私有,那么就会出现在使用这些变量时都使用threadLocal.get(),这样的junk code,有好的代码结构可以优化他么?
============================================================================
解答:
1.其实ThreadLocal并不把变量保存在自己里,而是保存到线程t里,
摘自ThreadLocal
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
摘自Thread
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
因此,TheadLocal本身并不保存变量,而是委托线程去保存。而这里又有个问题,这样做可以保证ThreadLocal不会受到线程的生命周期影响,我们也不需要显示remove。那么这里又有个问题了,线程Map里始终维护了TheadLocal->T的变量,如果维护ThreadLocal的对象被GC掉,线程本地变量里的ThreadLocal变量却依然被引用,并不会被gc。这样会不会有内存泄露呢?
实际上是不会的,这个归功于WeakReference的使用
WeakReference是一种引用容器,他虽然会维持R的引用,但是如果除了WeakReference外没有其他Object引用R,那么weakreference会在R被GC时,删除他。
所以回到ThreadLocal,如果已经没有对象引用ThreadLocal,那么线程中的ThreadLocaMap就会踢掉这个被回收的ThreadLocal。
详见Thread.ThreadLocalMap
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
.....
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
*/
private Entry[] table;
}
可以看到Entry是一个TheadLocal的弱引用,其成员变量保存了映射的value,Entry[]是线程的所有ThreadLocal变量。类似一个LinkedHashMap。
2.如何避免使用ThreadLocal的线程安全类满屏的t.get()这样的junkcode
在Ibatis中sqlMapClient配置为一个bean,但是每个线程在使用smc时总有自己的局部变量,例如Transaction,这样就跟我们的场景一样。但是我们并没有看到sqlMapClient使用t.get()这样的代码。他是怎么做到的呢:
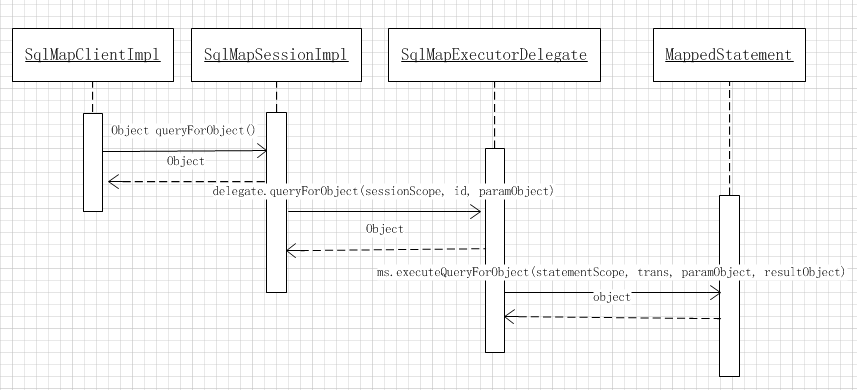
如图,sqlMapClient是全局共享的,他的queryForObject其实是委托一个sqlMapSessionImpl实现的,
sqlMapSessionImpl是线程成私有的,保存在smc的TheadLocal变量里的。
摘自SqlMapClient
protected SqlMapSessionImpl getLocalSqlMapSession() {
SqlMapSessionImpl sqlMapSession = (SqlMapSessionImpl) localSqlMapSession.get();
if (sqlMapSession == null || sqlMapSession.isClosed()) {
sqlMapSession = new SqlMapSessionImpl(this);
localSqlMapSession.set(sqlMapSession);
}
return sqlMapSession;
}
而sqlMapSessionImpl作为一个实例变量,他是不可能完成数据库操作的,他是委托了SqlMapExecutorDelegate的方法,SMED是在sqlMapClient里的变量,可以理解为是变相的回调操作。而SMSI里维护了一个SessionScope,这个是一个线程上下文里的变量,
摘自SqlMapSessionImpl
public class SqlMapSessionImpl implements SqlMapSession {
protected SqlMapExecutorDelegate delegate;
protected SessionScope sessionScope;
protected boolean closed;
...
}
摘自SessionScope
public class SessionScope {
private static long nextId;
private long id;
// Used by Any
private SqlMapClient sqlMapClient;
private SqlMapExecutor sqlMapExecutor;
private SqlMapTransactionManager sqlMapTxMgr;
private int requestStackDepth;
// Used by TransactionManager
private Transaction transaction;
private TransactionState transactionState;
...
} SqlMapExecutorDelegate才是数据库执行的真正地方,那么既然要实现线程安全的操作,势必有个SqlMapExecutorDelegate不能再维护TheadLocal变量了,因此SqlMapExecutorDelegate的操作都带有SessionScope这个入参。
摘自SqlMapExecutorEelegate
public Object queryForObject(SessionScope sessionScope, String id, Object paramObject) throws SQLException {
return queryForObject(sessionScope, id, paramObject, null);
} 因此通过这样的回调,巧妙的解决了junkcode,让代码更加清晰。
================================================================================
模仿一下
我们需要抽象一个数据源DataProvider,DataProvider可以有很多实现类,例如FileDataProvider,MysqlDataProvider,这个DataProvider数据的获取方式变成Iterator的方式。
public abstract class DataProvider implements Iterator<Row> {
public abstract Set<String> listFieldsName();
public abstract Long size();
public abstract void setPath(String path);
public String getName() {
return this.getClass().toString();
}
public abstract String getDesc();
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
那么junk-code的写法(代码只截取部分,有个意思)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
@Component
public class FileDataProvider extends DataProvider {
private ThreadLocal<ReaderInfo> readerInfo = new ThreadLocal<ReaderInfo>();
class ReaderInfo {
public String csvFullPath = null;
public BufferedReader reader = null;
public File file = null;
public boolean hasMore = false;
public boolean isColumn = true;
public List<String> columnNameList = null;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
try {
if (readerInfo.get().file == null)
readerInfo.get().file = new File(readerInfo.get().csvFullPath);
if (readerInfo.get().reader == null)
readerInfo.get().reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(readerInfo.get().file));
if (readerInfo.get().reader.ready()) {
readerInfo.get().hasMore = true;
if (readerInfo.get().isColumn) {
readerInfo.get().isColumn = false;
readerInfo.get().columnNameList = new ArrayList<String>();
String line = readerInfo.get().reader.readLine();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(line, ",");
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
readerInfo.get().columnNameList.add(st.nextToken());
}
}
return true;
} else {
readerInfo.get().hasMore = false;
readerInfo.get().reader.close();
readerInfo.get().reader = null;
return false;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
...
}
在hashNext中需要访问readerInfo里的path和file都用到了readerInfo.get()。
-------------以下是模仿sqlMapClient做的改造--------------------
1.把readerfino独立出来(变个名字sessionScope)
public class SessionScope {
public String csvFullPath = null;
public BufferedReader reader = null;
public File file = null;
public boolean hasMore = false;
public boolean isColumn = true;
public List<String> columnNameList = null;
}
2.编写一个使用sessionScope作为入参的读取器FileProviderExecutor
import com.alibaba.cainiao.hellomaven.impl.Field;
import com.alibaba.cainiao.hellomaven.impl.Row;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class FileProviderExecutor {
public boolean hasNext(SessionScope sessionScope) {
try {
if (sessionScope.file == null)
sessionScope.file = new File(sessionScope.csvFullPath);
if (sessionScope.reader == null)
sessionScope.reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sessionScope.file));
if (sessionScope.reader.ready()) {
sessionScope.hasMore = true;
if (sessionScope.isColumn) {
sessionScope.isColumn = false;
sessionScope.columnNameList = new ArrayList<String>();
String line = sessionScope.reader.readLine();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(line, ",");
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
sessionScope.columnNameList.add(st.nextToken());
}
}
return true;
} else {
sessionScope.hasMore = false;
sessionScope.reader.close();
sessionScope.reader = null;
return false;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
...
}
3.写一个FileDataSessionProvider,维护sessionScope,和FileProviderExecutor,FPE使用构造函数传递进来(当然也可以吧FPE换成FileDataProvider)
public class FileDataSessionProvider {
private SessionScope sessionScope;
private FileProviderExecutor fileProviderExecutor = null;
public FileDataSessionProvider(FileProviderExecutor executor) {
this.fileProviderExecutor = executor ;
sessionScope = new SessionScope();
}
public Set<String> listFieldsName() {
return fileProviderExecutor.listFieldsName(sessionScope);
}
public Long size() {
return fileProviderExecutor.size(sessionScope);
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.sessionScope.csvFullPath = path;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return fileProviderExecutor.hasNext(sessionScope);
}
public Row next() {
return fileProviderExecutor.next(sessionScope);
}
}
所有的函数委托Executor执行,传入参数sessionScope
4.最后,封装FileDataProvider,维护一个TheadLocal变量,里面存放FileDataSessionProvider,实现DataProvider,获取TheadLocal变量进行调用。
public class FileDataProvider extends DataProvider {
FileProviderExecutor fileProviderExecutor = new FileProviderExecutor();
private ThreadLocal<FileDataSessionProvider> fileDataSessionProviderThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<FileDataSessionProvider>();
private FileDataSessionProvider getLocalSessionProvider() {
FileDataSessionProvider fileDataSessionProvider = fileDataSessionProviderThreadLocal.get();
if (fileDataSessionProvider == null) {
fileDataSessionProvider = new FileDataSessionProvider(this.fileProviderExecutor);
fileDataSessionProviderThreadLocal.set(fileDataSessionProvider);
}
return fileDataSessionProvider;
}
@Override
public Set<String> listFieldsName() {
return this.getLocalSessionProvider().listFieldsName();
}
@Override
public Long size() {
return this.getLocalSessionProvider().size();
}
@Override
public void setPath(String path) {
this.getLocalSessionProvider().setPath(path);
}
@Override
public String getDesc() {
return "测试下";
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return this.getLocalSessionProvider().hasNext();
}
public Row next() {
return this.getLocalSessionProvider().next();
}
public FileProviderExecutor getFileProviderExecutor() {
return fileProviderExecutor;
}
public void setFileProviderExecutor(FileProviderExecutor fileProviderExecutor) {
this.fileProviderExecutor = fileProviderExecutor;
}
}
在getLocalSessionProvider()中,如果该线程没有访问过就创建sessionProvider,传入Executor。这样就完成了封装,绕过了对ThreadLocal变量内部成员变量的反复读取。这样的设计模式让代码层次更清晰,但是呢缺增加了代码量和理解难度,所以可以看情况选择使用。
不过这样的写法在设计模式里能找到对应的类型么?
FINISH