设计模式——Spring IoC中用到的模板方法模式
基本概念
什么是模板方法(Template method):父类定义了骨架(调用哪些方法及顺序),某些特定方法由子类实现。
最大的好处:代码复用,减少重复代码。除了子类要实现的特定方法,其他方法及方法调用顺序都在父类中预先写好了。
所以父类模板方法中有两类方法:
1、共同的方法:所有子类都会用到的代码
2、不同的方法:子类要覆盖的方法,分为两种:
A、抽象方法:父类中的是抽象方法,子类必须覆盖
B、钩子方法:父类中是一个空方法,子类继承了默认也是空的
注:为什么叫钩子,子类可以通过这个钩子(方法),控制父类,因为这个钩子实际是父类的方法(空方法)!
模板方法模式,和现实中的模板很像,一个文档的模板通常是一个完成了部分内容的表格(表格模板就像一个模板方法),每个人都会拿到表格的副本(具体的实现类)进行某些项的填写,每个人都可以对指定项(抽象方法或钩子方法)进行填写,表格中的必填项就像抽象方法必须实现,表格中的非必填项就是钩子方法。当然只是比喻和实际情况不完全一样。
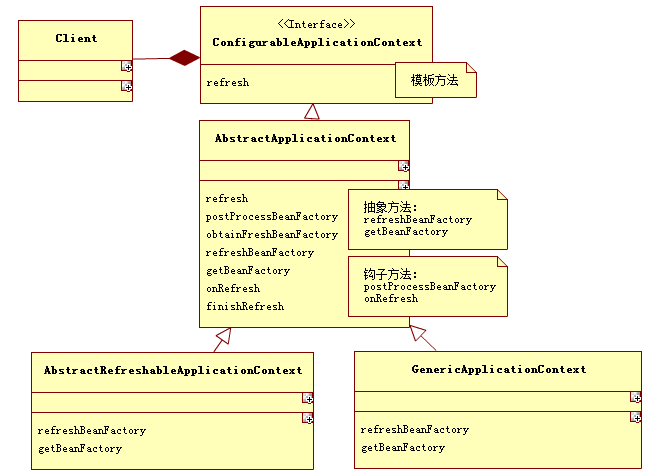
UML图
Java代码展示
下面的代码展示了,模板方法模式在Java代码中通常是怎样的:
1、先定义一个接口,主要是定义了模板方法
public interface TemplateInterface { public void execute(); }
2、抽象类实现了接口,主要是实现了模板方法的逻辑,模板方法中调用了自己的逻辑方法,还有最重要的钩子方法和抽象方法
public abstract class TemplateAbstractClass implements TemplateInterface{ /**模板方法*/ @Override public void execute() { preDoSomething(); abstractMethod(); hookMethod(); afterDoSomething(); } private void preDoSomething(){ System.out.println("before do some thing in abstract class"); } private void afterDoSomething(){ System.out.println("after do some thing in abstract class"); } /**抽象方法*/ public abstract void abstractMethod(); /**钩子方法*/ public void hookMethod(){ } }
3、两个子类,One只实现了抽象方法,Two实现了抽象方法并覆盖了钩子方法
public class SubClassOne extends TemplateAbstractClass{ /**抽象方法*/ @Override public void abstractMethod() { System.out.println("do another thing by subClassOne"); } }
public class SubClassTwo extends TemplateAbstractClass{ /**抽象方法*/ @Override public void abstractMethod() { System.out.println("do another thing by subClassTwo"); } /**钩子方法*/ @Override public void hookMethod() { System.out.println("hook method in subClassTwo"); } }
Spring中的模板方法模式
Spring中几乎所有的扩展,都使用了模板方法模式,JdbcTemplate中应该很多,不过还没学到那里,这里说下IoC部分的模板方法模式!
注:貌似在业务系统中很少看到,是开发者的编码能力问题还是对实际情况不适用,但是在框架中很多,Java IO、Spring、Hibernate等,可能是作为一个框架来说考虑更多的是扩展问题!
下面的代码展示了Spring IOC容器初始化时运用到的模板方法模式。(截取部分关键代码)
1、首先定义一个接口ConfigurableApplicationContext,声明模板方法refresh
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable { /**声明了一个模板方法*/ void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException; }
2、抽象类AbstractApplicationContext实现了接口,主要实现了模板方法refresh(这个方法很重要,是各种IOC容器初始化的入口)的逻辑
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean { /**模板方法的具体实现*/ public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); //注意这个方法是,里面调用了两个抽象方法refreshBeanFactory、getBeanFactory // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { //注意这个方法是钩子方法 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); //注意这个方法是钩子方法 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } } }
这里最主要有一个抽象方法obtainFreshBeanFactory、两个钩子方法postProcessBeanFactory和onRefresh,看看他们在类中的定义
两个钩子方法:
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { } protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException { // For subclasses: do nothing by default. }
再看看获取Spring容器的抽象方法:
/**其实他内部只调用了两个抽象方法**/ protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; } protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException; public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
具体要取那种BeanFactory容器的决定权交给了子类!
3、具体实现的子类,实现了抽象方法getBeanFactory的子类有:
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext:
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext { @Override public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() { synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { if (this.beanFactory == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - " + "call 'refresh' before accessing beans via the ApplicationContext"); } //这里的this.beanFactory在另一个抽象方法refreshBeanFactory的设置的 return this.beanFactory; } } }
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry { @Override public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() { //同样这里的this.beanFactory在另一个抽象方法中设置 return this.beanFactory; } }
其实这里的差别还不是很大,我们可以看看另一个抽象方法refreshBeanFactory的实现,两个抽象方法的配合使用。
所以这里的UML是: