ASP.NET 开发必备知识点(1):如何让Asp.net网站运行在自定义的Web服务器上
一、前言
大家都知道,在之前,我们Asp.net 的网站都只能部署在IIS上,并且IIS也只存在于Windows上,这样Asp.net开发的网站就难以做到跨平台。由于微软的各项技术的开源,所以微软自然要对跨平台做出支持的。OWIN技术就可以使得Web 服务器不再依赖于IIS,从而使得Asp.net 网站不再依赖于Windows。是不是有了OWIN,就不需要安装MONO就可以实现跨平台呢?显然不是,有了OWIN要实现跨平台还是要依赖与MONO,因为MONO提供了在Liunx环境下.NET代码的运行环境,而OWIN只是分离了Web应用程序与Web Server之间的紧耦合罢了。
二、使Asp.net网站跨平台成为可能的机制——OWIN
前面我们已经引出了使得Asp.net网站跨平台成为可能的机制就是OWIN,下面让我们具体看看什么是OWIN。
OWIN全称是——Open Web Interface For .NET。从名字上可以看出,它是一套接口定义,它完整定义如下:
OWIN在.NET Web Servers与Web Application之间定义了一套标准接口,OWIN的目标是用于解耦Web Server和Web Application。基于此标准,鼓励开发者开发简单、灵活的模块,从而推进.NET Web Development开源生态系统的发展。
至于为什么需要OWIN,在前面部分已经介绍过了,就是为了使得Web Application和Web Server解耦,这样就可以使得Asp.net 网站不再依赖与IIS Web Server,从而就不会紧耦合与Windows 操作系统了。(看到这里,你是不是和我学习OWIN有一样的疑问呢?问题是:之前没有OWIN规范不是照样可以通过Mono来实现asp.net 网站的跨平台吗?现在还需要OWIN干什么的?)
对于这个上面的疑问,我后面给出答案。既然OWIN是一套规范,则自然有它定义规范了。OWIN规范中定义了4个组件:
Host:主要负责托管应用程序的进程,可以是IIS,也可以自己写的程序等。主要用来启动,加载OWIN组件,以及合理地管理它们。
Server:指的实际的Web Server,负责绑定套接字并对Http请求进行监听,将Request和ReponsedeBody、Header封装成服务OWIN规范的字典并发送到OWIN Middleware Pipeline中进行处理。
Middleware:这个中间件就是用来在OWIN管道中处理请求的组件(可以把它想象成一个自定义的Http Module),它会被注册到Owin管道中一起处理Http request。
Application:这个就是我们自己开发的应用程序,或者是网站。
应用程序代理(Application Delegate)
Owin规范另一个重要的组成部分是接口的定义,它通过将服务器与应用程序之间的交互归纳为一个方法签名,称之为“应用程序代理”(Applacation Delegate)。具体定义如下:
AppFunc = Func<IDictionary<string, object>, Task>;
上面委托的定义中第一参数称为环境字典,而第二个参数Task指的异步执行的方法。之前我们通过HttpContext对象来获得request、Response等对象,基于Owin的应用是通过这个环境字典来获得相应的对象。有了Owin之后,我们就不再与Asp.net管道打交道了,取而代之则是Owin管道。
Microsoft对OWIN规范的实现——Katana
既然OWIN是一套规范,自然就有其具体的实现,微软根据OWIN规范在Windows下实现了Katana(武士刀)。其开源地址:http://katanaproject.codeplex.com/。
Katana实现了OWIN的4个组件。
1)Host: Kataba为我们提供了3种Host的选择:
- IIS:使用IIS是最简单和向后兼容方式。在这种场景中OWIN管道通过标准的HttpModule和HttpHandler启动。使用此Host你必须使用System.Web作为OWIN Server
- Custom Host: 你也可以选择创建一个自定义宿主来托管应用程序
- OwinHost:Katana自己实现了宿主程序——OwinHost.exe。我们可以利用该宿主来宿主我们的应用程序。
2)Server: Katana对Owin Server的实现提供如下几类实现:
- System.Web: System.Web与IIS两者彼此耦合,当你选择使用System.Web作为Server,此时必须选择IIS为宿主。
- HttpListener:这是OwinHost.exe和定义Host默认的Server。
- WebListener:这是ASP.NET vNext默认的轻量级Server。它目前无法使用在Katana张。
3) Middleware: 中间件(Middleware)用来处理Pipeline中的请求。Middleware是Owin Pipeline中处理请求的单元,它可以是Log组件,也可以是Asp.net Web API、SignlR等组件。
4)Application:应用程序的实现代码,可以为Asp.net MVC站点,也可以为Asp.net Web API和SignalR具体的应用实现。
Katana,它只能够运行在Windows中,使得在Windows环境下,我们的Asp.net 网站不完全依赖于IIS;而在Liunx环境下也有OWIN规范的具体实现,就是Jexus Web Server(简称JWS)。所以,我们可以利用Mono+OWIN+Jexus在Liunx环境下部署我们的Asp.net站点,具体部署参考:ASP.NET Linux部署(2) - MS Owin + WebApi + Mono + Jexus。
到这里,你们还记得我文章开头的疑问吗?大家应该都知道,在OWIN规范出现之前,我们就已经可以利用Mono来讲我们的Asp.net 站点部署在Liunx环境下了,之前采用的部署方式是:Mono+Apache/nginx + XSP2。具体部署请参考:Linux下的.NET之旅:第一站,CentOS+Mono+Xsp构建最简单的ASP.NET服务器。既然以前也可以实现Asp.net 网站在liunx环境下部署,则利用Owin的实现Jexus自然就有其优势,不能也就没有其存在的意义了,这里就涉及到Mono Xsp与基于Owin实现Jexus的一个对比:
Mono Xsp 和Jexus有什么区别呢:
- 速度方面: 对于ASP.NET网页,大压力访问时Jexus处理速度更快; 对于静态文件,Jexus远快于XSP,而且对磁盘的要求和影响小N倍;
- 功能方面: XSP是以ASP.NET测试工作开发的,功能单调,而Jexus是作为生产环境使用的真实的WEB服务开发的,功能全面,因此,xsp与Jexus在功能上可比性
- 稳定性方面: Jexus有良好的容错和自动纠错能力,可以长期不间断运行,而XSP是单进程程序,没有任何自动纠错机制,无法保持不间断运行。
- 安全性方面: Jexus有关键的入侵检测功能,XSP没有任何安全检测功能,没有可比性;
- 多站点支持: XSP支持一站,Jexus支持任意多网站。
更详细内容请参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/alsw/p/3255984.html。
三、使用IIS托管Katana-based Asp.net网站
因为Katana为了向后兼容,依然支持IIS作为宿主,下面通过一个例子看看如何将Asp.net 站点托管在Katana-based的IIS中。
1. 创建一个空的Web Application:
2. 从Nuget中添加 Microsoft.Owin.Host.SystemWeb包
3. 添加OWIN Startup类,并添加如下代码在Startup1.Configuration方法中:
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app) { // 有关如何配置应用程序的详细信息,请访问 http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=316888 app.Run(context => { context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain"; return context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello, world."); }); }
按F5运行,你将看到浏览器中打印出“Hello, world”的字样。
虽然同样是托管在IIS,但是所有的请求都会被OWIN来处理。Kanata除了支持IIS托管外,还支持自定义宿主,接下来介绍就是通过创建一个控制台程序来宿主Web 应用程序。
四、利于Microsoft.Owin.Host.HttpListener实现自寄宿
OWIN目标就是使得Web Server与Web Application解耦,接下来就具体看看如何将Web应用程序实现自我宿主。
1. 首先创建一个控制台应用程序
2. 通过Nuget安装Microsoft.Owin.Hosting和Microsoft.Owin.HttpListener包
3. 创建OWIN Startup类,该类的具体实现代码:
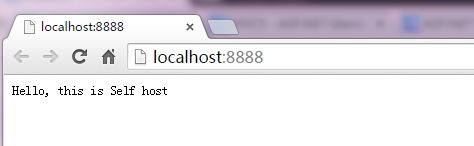
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app) { // 有关如何配置应用程序的详细信息,请访问 http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=316888 app.Run(context => { context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain"; return context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello, this is Self host"); }); }
4. 在Main方法中加入下面代码来启动我们的网站:
static void Main(string[] args) { using (WebApp.Start<Startup>( new StartOptions(url: "http://localhost:8888"))) { Console.ReadLine(); } Console.ReadLine(); }
运行该控制台程序,然后在浏览器中输入“http://localhost:8888/”将看到如下界面:
当然,Katana还支持OwinHost.exe程序来进行宿主,其实现步骤如下所示:
1. 创建一个空的Web应用程序
2. 通过Nuget安装OwinHost包
3. 添加OWIN Startup类,并添加如下代码:
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app) { // 有关如何配置应用程序的详细信息,请访问 http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=316888 app.Run(context => { context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain"; return context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello, This is host in OwinHost.exe."); }); }
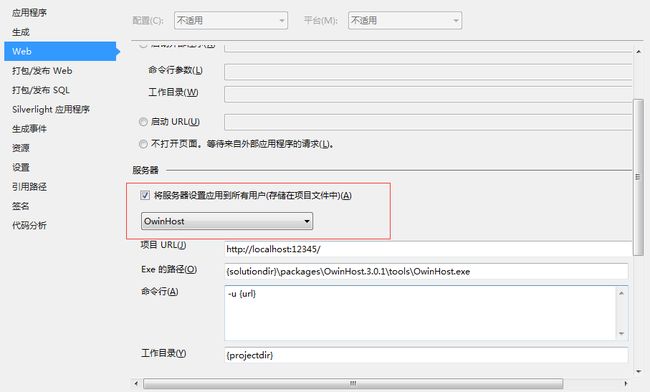
4. 设置Web应用程序属性,将宿主从IIS Express更改为OwinHost。具体设置如下图所示:
然后运行该网站,你将在浏览器中看到“Hello, This is host in OwinHost.exe.”的字样。
五、让Asp.net网站运行在定义的Web服务器上
前面我们简单应用了Kanata支持的三种宿主方式。但如果我们想将我们的Asp.net 网站运行到自定义的Web 服务器上该怎么办呢?朋友们,你们是否还记到,我在C#网络编程系列中,已经实现一个轻量的Web 服务器了。既然OWIN规范可以使得我们可以将Asp.net网站不再依赖于IIS Web 服务器,那自然我们就可以通过自定义Web 服务器,然后让Asp.net运行在我们自定义的Web 服务器上了。接下来让我们具体看看,如何实现Asp.net网站运行在我们自定义的Web 服务器上的。
1. 首先自定义Web 服务器。具体的实现代码如下所示:
using System.Net; using System.Net.Sockets; using AppFunc = Func<IDictionary<string, object>, Task>; public class CustomServer { public CustomServer() { // Create a configurable instance } public void Start(AppFunc next, IList<IDictionary<string, object>> addresses) { // 获得本机的Ip地址,即127.0.0.1 IPAddress localaddress = IPAddress.Loopback; // 创建可以访问的断点,49155表示端口号,如果这里设置为0,表示使用一个由系统分配的空闲的端口号 IPEndPoint endpoint = new IPEndPoint(localaddress, 8888); // 创建Tcp 监听器 TcpListener tcpListener = new TcpListener(endpoint); // 启动监听 tcpListener.Start(); Console.WriteLine("Wait an connect Request..."); while (true) { // 等待客户连接 TcpClient client = tcpListener.AcceptTcpClient(); if (client.Connected == true) { // 输出已经建立连接 Console.WriteLine("Created connection"); } // 获得一个网络流对象 // 该网络流对象封装了Socket的输入和输出操作 // 此时通过对网络流对象进行写入来返回响应消息 // 通过对网络流对象进行读取来获得请求消息 NetworkStream netstream = client.GetStream(); // 把客户端的请求数据读入保存到一个数组中 byte[] buffer = new byte[2048]; int receivelength = netstream.Read(buffer, 0, 2048); string requeststring = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer, 0, receivelength); // 在服务器端输出请求的消息 Console.WriteLine(requeststring); // 服务器端做出相应内容 // 响应的状态行 string statusLine = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"; byte[] responseStatusLineBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(statusLine); string responseBody = "<html><head><title>Default Page</title></head><body><p style='font:bold;font-size:24pt'>Welcome my custom server</p></body></html>"; string responseHeader = string.Format( "Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTf-8\r\nContent-Length: {0}\r\n", responseBody.Length); byte[] responseHeaderBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(responseHeader); byte[] responseBodyBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(responseBody); // 写入状态行信息 netstream.Write(responseStatusLineBytes, 0, responseStatusLineBytes.Length); // 写入回应的头部 netstream.Write(responseHeaderBytes, 0, responseHeaderBytes.Length); // 写入回应头部和内容之间的空行 netstream.Write(new byte[] { 13, 10 }, 0, 2); // 写入回应的内容 netstream.Write(responseBodyBytes, 0, responseBodyBytes.Length); // 关闭与客户端的连接 client.Close(); Console.ReadKey(); break; } // 关闭服务器 tcpListener.Stop(); } } using AppFunc = Func<IDictionary<string, object>, Task>; public static class OwinServerFactory { /// <summary> /// Optional. This gives the server the chance to tell the application about what capabilities are supported. /// </summary> /// <param name="properties"></param> public static void Initialize(IDictionary<string, object> properties) { // TODO: Add Owin.Types.BuilderProperties for setting capabilities, etc.. // Consider adding a configurable object to the properties if the application needs to set some specific server settings. properties[typeof(CustomServer).FullName] = new CustomServer(); } public static CustomServer Create(AppFunc app, IDictionary<string, object> properties) { object obj; // Get the user configured server instance, if any. CustomServer server = null; if (properties.TryGetValue(typeof(CustomServer).FullName, out obj)) { server = obj as CustomServer; } server = server ?? new CustomServer(); // Get the address collection IList<IDictionary<string, object>> addresses = null; if (properties.TryGetValue("host.Addresses", out obj)) { addresses = obj as IList<IDictionary<string, object>>; } server.Start(app, addresses); return server; } }
2. 创建一个控制台应用程序来对Web应用程序进行自我宿主。
3. 通过Nuget添加“Microsoft.Owin.Hosting”包
4. 添加OWIN Startup类
5. 往Main方法中添加下面代码:
static void Main(string[] args) { using (WebApp.Start<Startup>( new StartOptions(url: "http://localhost:8888") { ServerFactory = "CustomWebServer" })) { Console.WriteLine("Started, Press any key to stop."); Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("Stopped"); } }
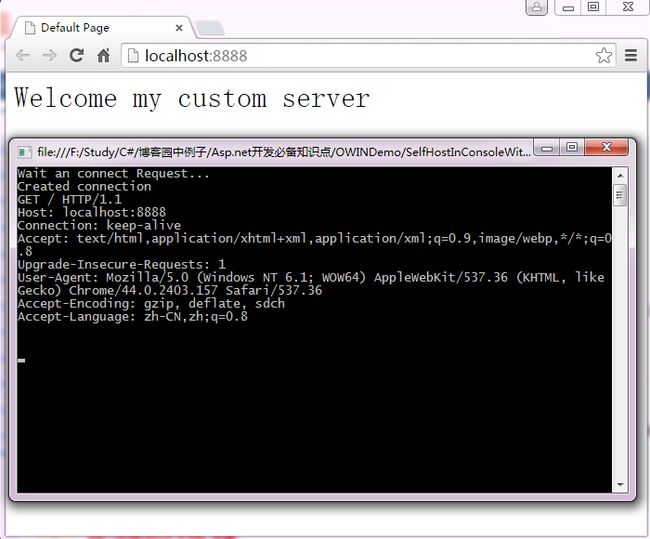
此时,运行该控制台程序,然后在浏览器中输入“localhost:8888”,你将看到如下结果:
到此,我们已经将Asp.net站点运行在我们自定义的Web 服务器上了。
六、总结
到这里,关于OWIN的介绍就到此结束了,接下来将介绍Asp.net最新的用户权限管理:Asp.net Identity的相关内容。
本文的所有源码下载:OWINDemo