equals()与hashCode()方法协作约定
翻译人员: 铁锚
翻译时间: 2013年11月15日
原文链接: Java equals() and hashCode() Contract
本文先用示例演示如何使用它们,然后解释 equals()方法和hashCode是如何协同工作.
1. 错误使用方式
下面是一个常见的错误用法:
上述代码的输出结果是: null. 但通过断点调试,可以确定此对象已经存在于hashMap中,截图如下:
问题的原因是 没有重写"hashCode()"方法.
equals()方法与hashCode()的通用协定是:
2.1 如果两个对象相等(equal),那么必须拥有相同的哈希码(hash code)
2.2 即使两个对象有相同的哈希值(hash code),他们不一定相等.
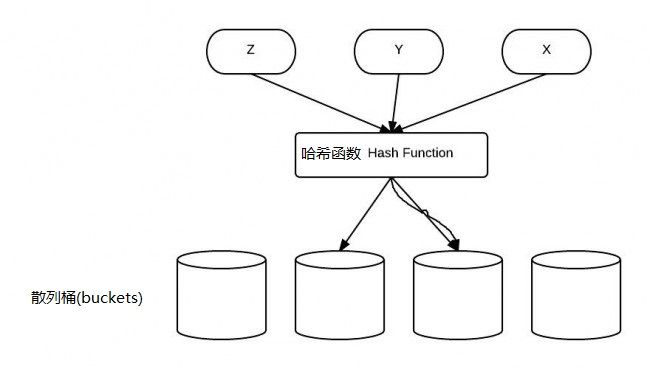
Map的核心思想就是可以比线性查找更快. 通过散列值(hash)作为键(key)来定位对象的过程分为两步:
在Map内部,存储着一个顶层数组,顶层数组的每个元素指向其他的数组,查找或存储的时候,先根据key对象的hashCode()值计算出数组的索引,然后到这个索引找到所指向的第二层线性数组,使用equals方法来比较是否有相应的值(以返回或者存储).
Object类中的hashCode()默认为每个对象返回不同的int值,因此在上面的例子中,两个相等(equal)的对象,返回了不同的hashCode值.
解决方法是为此类添加hashCode方法,比如,使用color字符串的长度作为示范:
翻译时间: 2013年11月15日
原文链接: Java equals() and hashCode() Contract
图1
Java所有对象的超类 java.lang.Object 有两个非常重要的方法定义:
public boolean equals(Object obj) public int hashCode()实践证明这两个方法是非常重要的,特别是用Map存储用户自定义对象时.然而,有些高级开发者也不一定知道如何合适的使用它们。
本文先用示例演示如何使用它们,然后解释 equals()方法和hashCode是如何协同工作.
1. 错误使用方式
下面是一个常见的错误用法:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Apple {
private String color;
public Apple(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (!(obj instanceof Apple))
return false;
if (obj == this)
return true;
return this.color == ((Apple) obj).color;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple a1 = new Apple("green");
Apple a2 = new Apple("red");
//hashMap stores apple type and its quantity
HashMap<Apple, Integer> m = new HashMap<Apple, Integer>();
m.put(a1, 10);
m.put(a2, 20);
System.out.println(m.get(new Apple("green")));
}
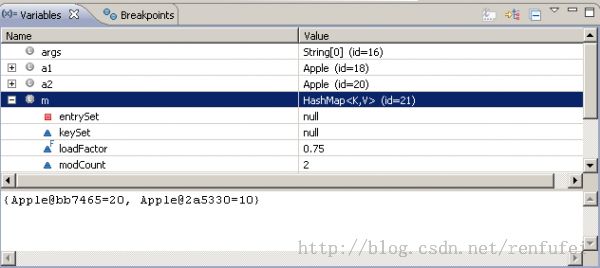
}在此示例中,hashMap 已经保存了一个绿色的Apple对象,但想(通过程序中的方式)从map获取此对象时,apple 对象并未被找到.
上述代码的输出结果是: null. 但通过断点调试,可以确定此对象已经存在于hashMap中,截图如下:
图2
2. 此问题由hashCode()引起
问题的原因是 没有重写"hashCode()"方法.
equals()方法与hashCode()的通用协定是:
2.1 如果两个对象相等(equal),那么必须拥有相同的哈希码(hash code)
2.2 即使两个对象有相同的哈希值(hash code),他们不一定相等.
Map的核心思想就是可以比线性查找更快. 通过散列值(hash)作为键(key)来定位对象的过程分为两步:
在Map内部,存储着一个顶层数组,顶层数组的每个元素指向其他的数组,查找或存储的时候,先根据key对象的hashCode()值计算出数组的索引,然后到这个索引找到所指向的第二层线性数组,使用equals方法来比较是否有相应的值(以返回或者存储).
Object类中的hashCode()默认为每个对象返回不同的int值,因此在上面的例子中,两个相等(equal)的对象,返回了不同的hashCode值.
解决方法是为此类添加hashCode方法,比如,使用color字符串的长度作为示范:
public int hashCode(){
// 此种实现,要求 color值定以后就不得修改
// 否则同一个物理对象,前后有两个不同的hashCode,逻辑上就是错的。
return this.color.length();
}
相关文章:
- Java中Set的contains()方法
- HashMap vs. TreeMap vs. Hashtable vs. LinkedHashMap
- Top 8 Diagrams for Understanding Java
- Yet Another “Java Passes By Reference or By Value”?