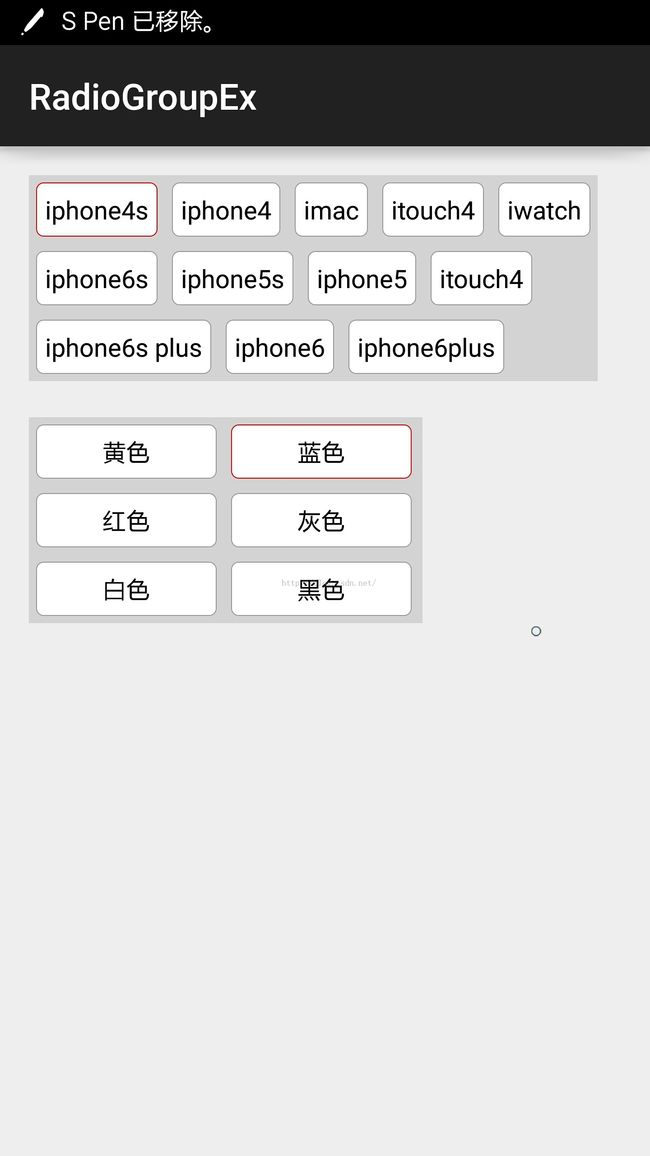
可自动换行的单选 RadioGroupEx
今天要说的,并不是很复杂的,但确是很常见的。下面这个图,就是今天的主角(可换行的RadioGroup):
可换行的单选效果,在大多网购的app中选择物品可以看到。有时候,项目中可能需要,直接拿过来用,这样就方便多了。
我们要实现可换行的单选效果,可以选择这种方式:
1.继承RadioGroup,改变RadioGroup的布局结构。
2.继承ViewGroup,写一个类似RadioGroup的容器,控制子View的单选;并且继承View,写一个类似RadioButton的子View,并重写这个子View的onTouchEvent(),使用onDraw()方法绘制需要的效果。
这两种实现方法,显然第一种是比较简单的。在这里,我也是介绍第一种方式。 我们继承了RadioGroup,只需要重写布局方式即可,其它逻辑,都不用自己处理,却拥有RadioGroup对外开放的功能。要重写RadioGroup的布局效果,需要重写的方法 onMeasure()和onLayout() (我们需要从宏观上了解ViewGroup的绘制流程,即先调用onMeasure()再调用onLayout()最后onDraw(),至于onDraw(),一般不再ViewGroup中重写该方法)。 重写的过程中,我们需要考虑到ViewGroup的padding值,和RaidoButton的margin值。 下面还是先看代码,能够从感官上了解大致流程:
最核心的类,RadioGroupEx
<span style="font-size:18px;">package com.mjc.radiogroupex;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
/**
* Created by mjc on 2016/1/20.
* 重新对RadioGroup进行布局,可以折行
* 默认水平开始排布
*/
public class RadioGroupEx extends RadioGroup {
private static final String TAG = "RadioGroupEx";
public RadioGroupEx(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public RadioGroupEx(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//调用ViewGroup的方法,测量子view
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//最大的宽
int maxWidth = 0;
//累计的高
int totalHeight = 0;
//当前这一行的累计行宽
int lineWidth = 0;
//当前这行的最大行高
int maxLineHeight = 0;
//用于记录换行前的行宽和行高
int oldHeight;
int oldWidth;
int count = getChildCount();
//假设 widthMode和heightMode都是AT_MOST
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//得到这一行的最高
oldHeight = maxLineHeight;
//当前最大宽度
oldWidth = maxWidth;
int deltaX = child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
if (lineWidth + deltaX + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() > widthSize) {//如果折行,height增加
//和目前最大的宽度比较,得到最宽。不能加上当前的child的宽,所以用的是oldWidth
maxWidth = Math.max(lineWidth, oldWidth);
//重置宽度
lineWidth = deltaX;
//累加高度
totalHeight += oldHeight;
//重置行高,当前这个View,属于下一行,因此当前最大行高为这个child的高度加上margin
maxLineHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
Log.v(TAG, "maxHeight:" + totalHeight + "---" + "maxWidth:" + maxWidth);
} else {
//不换行,累加宽度
lineWidth += deltaX;
//不换行,计算行最高
int deltaY = child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
maxLineHeight = Math.max(maxLineHeight, deltaY);
}
if (i == count - 1) {
//前面没有加上下一行的搞,如果是最后一行,还要再叠加上最后一行的最高的值
totalHeight += maxLineHeight;
//计算最后一行和前面的最宽的一行比较
maxWidth = Math.max(lineWidth, oldWidth);
}
}
//加上当前容器的padding值
maxWidth += getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
totalHeight += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
setMeasuredDimension(widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? widthSize : maxWidth,
heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? heightSize : totalHeight);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
//pre为前面所有的child的相加后的位置
int preLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int preTop = getPaddingTop();
//记录每一行的最高值
int maxHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//r-l为当前容器的宽度。如果子view的累积宽度大于容器宽度,就换行。
if (preLeft + params.leftMargin + child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.rightMargin + getPaddingRight() > (r - l)) {
//重置
preLeft = getPaddingLeft();
//要选择child的height最大的作为设置
preTop = preTop + maxHeight;
maxHeight = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
} else { //不换行,计算最大高度
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin);
}
//left坐标
int left = preLeft + params.leftMargin;
//top坐标
int top = preTop + params.topMargin;
int right = left + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bottom = top + child.getMeasuredHeight();
//为子view布局
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
//计算布局结束后,preLeft的值
preLeft += params.leftMargin + child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.rightMargin;
}
}
}</span>
在RaidoGroupEx中,我们可以看到,主要是通过重写onMeasure()和onLayout()的方法重新布局。其中measureChildren(),是ViewGroup提供的测量子View的方法,通过它,我们能够很方便的测量出子View。以至于,下面计算子View的测量宽和测量高。
measure过程:如果当前容器的布局要求的EXACTLY,那么当前容器的宽和高就是MeasureSpec.getSize(spc)的值,即代码中的widthSize和heightSize; 如果当前的容器布局要求是AT_MOST,那么当前容器的宽和高依赖于子View的宽和高,但是不能超过MeasureSpec.getSize(spc)取出的值,即代码中的widthSize和heightSize;因此我们要判断,如果子view水平排放的宽度大于widthSize,我们就要换行,重新开始计算,但是最终的宽度,是所有行中,最宽的那个;而高度,则是每一行的最高子View的高度累加,这样来得到当前容器的最终高度。得到最终高度后,通过setMeasureDimension()设置当前容器的宽和高。
layout过程:首先考虑到padding值,所以起始地布局位置是getPaddingLeft()和getpaddingTop()。每布局一个子View后,需要判断当前是否超过了布局容器的宽和高,如果没超过,preLeft增加上新的子View的所占据的宽度吗,然后继续水平布局;如果超过了则换行,重置当前的preLeft,并给preTop累加上一行的最大行高。布局则是调用child.layout()方法。
通过重写这两个方法,我们完成了ViewGroup的换行效果。是不是很简单呢。
附源码:点击打开链接
注:如果大家发现有什么问题,请留言指教。