Java NIO Channel
Java Nio
| 1 | Java NIO Tutorial |
| 2 | Java NIO Overview |
| 3 | Java NIO Channel |
| 4 | Java NIO Buffer |
| 5 | Java NIO Scatter / Gather |
| 6 | Java NIO Channel to Channel Transfers |
| 7 | Java NIO Selector |
| 8 | Java NIO FileChannel |
| 9 | Java NIO SocketChannel |
| 10 | Java NIO ServerSocketChannel |
| 11 | Java NIO DatagramChannel |
| 12 | Java NIO Pipe |
| 13 | Java NIO vs. IO |
Java NIO Channel
- Channel Implementations
- Basic Channel Example
Java NIO Channels are similar to streams with a few differences:
- You can both read and write to a Channels. Streams are typically one-way (read or write).
- Channels can be read and written asynchronously.
- Channels always read to, or write from, a Buffer.
As mentioned above, you read data from a channel into a buffer, and write data from a buffer into a channel. Here is an illustration of that:
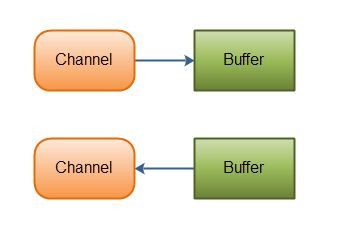 |
| Java NIO: Channels read data into Buffers, and Buffers write data into Channels |
Channel Implementations
Here are the most important Channel implementations in Java NIO:
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
The FileChannel reads data from and to files.
The DatagramChannel can read and write data over the network via UDP.
The SocketChannel can read and write data over the network via TCP.
The ServerSocketChannel allows you to listen for incoming TCP connections, like a web server does. For each incoming connection a SocketChannel is created.
Basic Channel Example
Here is a basic example that uses a FileChannel to read some data into a Buffer:
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("data/nio-data.txt", "rw");
FileChannel inChannel = aFile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf);
while (bytesRead != -1) {
System.out.println("Read " + bytesRead);
buf.flip();
while(buf.hasRemaining()){
System.out.print((char) buf.get());
}
buf.clear();
bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf);
}
aFile.close();
Notice the buf.flip() call. First you read into a Buffer. Then you flip it. Then you read out of it. I'll get into more detail about that in the next text about Buffer's.
