Android实训案例(五)——四大组件之一ContentProvider的使用,通讯录的实现以及ListView的优化
Android实训案例(五)——四大组件之一ContentProvider的使用,通讯录的实现
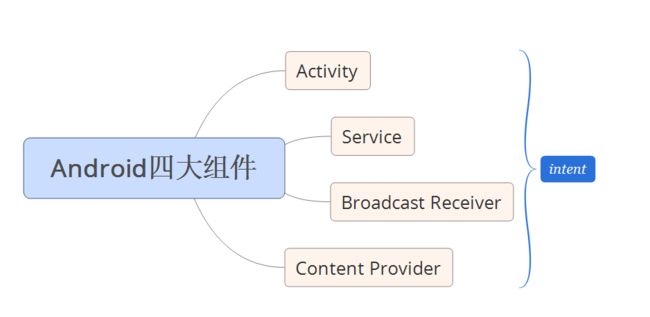
Android四大组件是啥这里就不用多说了,看图吧,他们之间通过intent通讯
我们后续也会一一的为大家讲解,今天就使用内容提供者ContentProvider查询系统的数据库来获取联系人,我们用listview装载
我们新建一个项目就叫MyPhone吧
并且添加权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS"/>一,获取联系人
我们可以新建一个Class——GetPhone,这样吧,我们先在手机里创建两个联系人
GetPhone
package com.lgl.myphone;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.provider.ContactsContract;
import android.util.Log;
/** * 获取手机联系人 * Created by LGL on 2016/1/24. */
public class GetPhone {
//获取通讯录的方法
public static String getPhone(Context context) {
/** * 1.系统给了我们一个接口访问 * 2.3.4.5也是查询条件,这我们并不需要 * 并且返回一个Cursor类型的参数 */
Cursor query = context.getContentResolver().query(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI, null, null, null, null);
//创建一个对象进行储存
String name; //联系人
String phone; //电话号码
//我们获取到这些信息之后遍历出来
while (query.moveToNext()) {
//获取名字就需要Phone.DISPLAY_NAME
name = query.getString(query.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.DISPLAY_NAME));
//获取num字段需要Phone.NUMBER
phone = query.getString(query.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER));
Log.i("字段", name + ":" + phone);
}
return null;
}
}
然后我们只要在MainActivity中调用就可以了
//调用查询
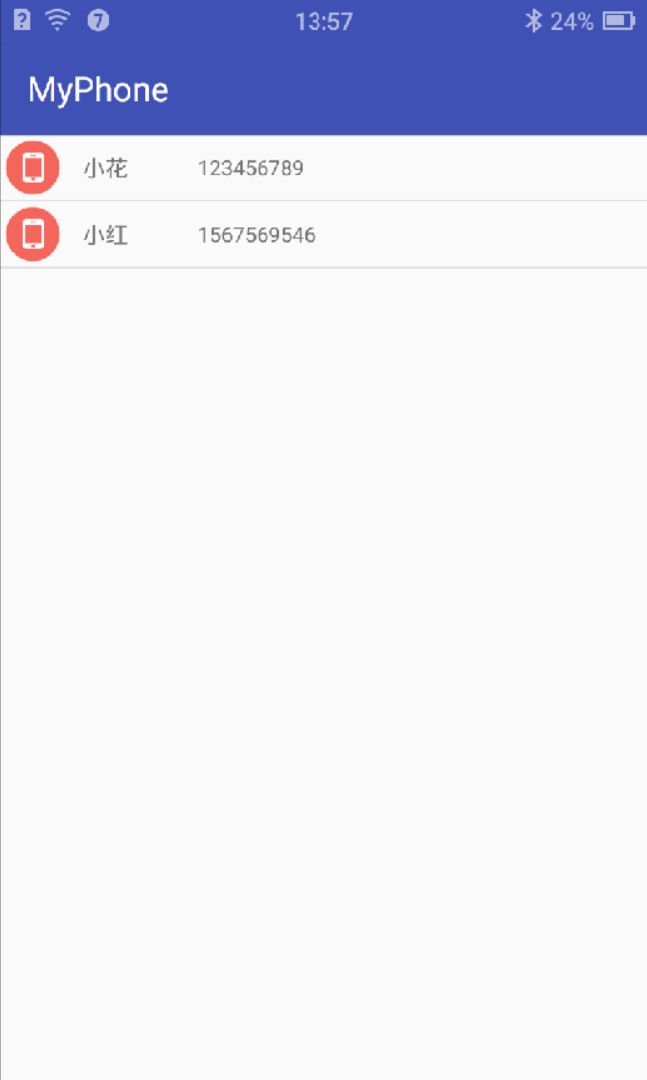
GetPhone.getPhone(this);运行一下
也是成功的打印出来了
二,数据存储
我们既然要用到这些读取出来的数据,就需要先把这些数据给存储起来,我们新建一个Class类——Bean,声明一个name和一个phone,并且生成他们的set和get方法
package com.lgl.myphone;
/** * 数据存储 * Created by LGL on 2016/1/24. */
public class Bean {
private String name;
private String phone;
public Bean(String name, String phone) {
setName(name);
setPhone(phone);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
}
这样的话我们就可以去封装了,这里封装也是很简单,直接在GetPhone这个类里面声明一个list集合
public static List<Bean>list = new ArrayList<Bean>();然后我们可以将这个写数据装载起来
Bean bean = new Bean(name,phone);
list.add(bean);三,实现自定义Adapter
考虑到这个项目的扩展性,我们的adapter一般都是自己实现继承BaseAdapter,今天,我们也来实现以下,并且放几张头像上去
ListAdapter
package com.lgl.myphone;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.List;
/** * Created by LGL on 2016/1/24. */
public class ListAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private List<Bean> list;
//承接上下文
private Context context;
private RelativeLayout layout;
//构造方法
public ListAdapter(List<Bean> list, Context context) {
this.list = list;
this.context = context;
}
//返回的是集合的数量,大小
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
//返回当前这条数据
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return list.get(position);
}
//获取当前的ID
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
//id和position是相等的
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
/** * 我们要获取当前视图的View并且加载到视图当中 */
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
layout = (RelativeLayout) inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item, null);
TextView tv_name = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
TextView tv_phone = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.tv_phone);
//添加内容
tv_name.setText(list.get(position).getName());
tv_phone.setText(list.get(position).getPhone());
return layout;
}
}
接着我们使用就可以了,在MainActivity中
//初始化listview
listview = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview);
listAdapter = new ListAdapter(GetPhone.list,this);
listview.setAdapter(listAdapter);运行一下,就知道效果了
四,ListView的优化ViewHolder
事实上,listview的优化已经见怪不怪了,当我们的通讯录需要加载几千条数据的时候,我们就有必要的进行一些优化了,那就是使用viewholder
package com.lgl.myphone;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.List;
/** * Created by LGL on 2016/1/24. */
public class ListAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private List<Bean> list;
//承接上下文
private Context context;
private RelativeLayout layout;
//构造方法
public ListAdapter(List<Bean> list, Context context) {
this.list = list;
this.context = context;
}
//返回的是集合的数量,大小
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
//返回当前这条数据
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return list.get(position);
}
//获取当前的ID
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
//id和position是相等的
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
/** * 我们要获取当前视图的View并且加载到视图当中 */
// LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
// layout = (RelativeLayout) inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item, null);
//
// TextView tv_name = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
// TextView tv_phone = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.tv_phone);
//
// //添加内容
// tv_name.setText(list.get(position).getName());
// tv_phone.setText(list.get(position).getPhone());
ViewHolder holder;
//==null代表并没有记载view
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.list_item, null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.tv_name = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
holder.tv_phone = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_phone);
//加载内容
holder.tv_name.setText(list.get(position).getName());
holder.tv_phone.setText(list.get(position).getPhone());
//第一次加载完毕后标签储存
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
//代表加载过了
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
//加载内容
holder.tv_name.setText(list.get(position).getName());
holder.tv_phone.setText(list.get(position).getPhone());
}
return convertView;
}
private static class ViewHolder {
TextView tv_name;
TextView tv_phone;
}
}
这样子就可以数据量再大也不会出现卡顿的现象了
弱弱的说一句:今天的深圳真冷啊