IOS CoreText --- 代码封装
前几节中,我转载他人的博客,详细的描述了Core Text的基本概念及使用,但看上去他所提供的demo是面向过程的,代码不容易管理及维护。接下来几节,我将逐步封装Core Text代码,让其看起来不那么凌乱(因为Core Text是纯C的语法)。下面,我们先看一张 “iOS Text Design and Rendering Architecture” 架构图。
上图中,最底层的Core Graphics是核心绘画,我在Quartz 2D章节已经进行了详细的说明,然后上面一层的就是Core Text。 先看看我实现的一个Core Text的demo效果图。
1. 我们先看看原始的代码实现过程,可以看出,代码中,将坐标系的变换,路径的初始化,字符串的处理,frame的创建及最终的绘制 全部放在一起处理了,当遇到复杂的业务需求的话,代码显的臃肿和不利于维护。
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextSetTextMatrix(context, CGAffineTransformIdentity);
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 0, self.bounds.size.height);
CGContextScaleCTM(context, 1.0, -1.0);
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddRect(path, NULL, self.bounds);
NSAttributedString *attrString = [[NSAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@"大话西游台词..."];
// 这里截断字符串,然后对每段进行文字及颜色的设置
CTFramesetterRef framesetter = CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((CFAttributedStringRef)attrString);
CTFrameRef frame = CTFramesetterCreateFrame(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0, attrString.length), path, NULL);
CTFrameDraw(frame, context);
CFRelease(frame);
CFRelease(path);
CFRelease(framesetter);
2. 考虑对代码进行封装
对于一个复杂的排版引擎来说,可以将其功能拆分成以下几个类来完成。
1)一个显示用的类,仅负责显示内容,不负责排版。
2)一个模型类,用于承载显示所需要的所有数据。
3)一个排版类,用于实现文字内容的排版。
4)一个配置类,用于实现一些排版时的可配置项。
按照以上的描述,我们可以将上面的代码内容拆分,分成4个类:
1)CTFrameParserConfig类,用于配置绘制的参数,例如文字颜色、大小、行间距等。
2)CTFrameParser类,用于生成最后绘制界面需要的CTFrameRef实例。
3)CoreTextData类,用于保存由CTFrameParser类生成的CTFrameRef实例以及CTFrameRef实际绘制需要的高度。
4)CTDisplayView类,持有CoreTextData类的实例,负责将CTFrameRef绘制到界面上。
下面我就一一介绍上面说描述的类:
1)CTFrameParserConfig类,主要是初始化了文字宽度、大小、行间距、颜色信息。 代码如下:
@interface CTFrameParserConfig : NSObject
@property (nonatomic,assign) CGFloat width;
@property (nonatomic,assign) CGFloat fontSize;
@property (nonatomic,assign) CGFloat lineSpace;
@property (nonatomic,strong) UIColor *textColor;
@end
#define RGB(A,B,C) [UIColor colorWithRed:(A/255.0) green:(B/255.0) blue:(C/255.0) alpha:1.0]
#import "CTFrameParserConfig.h"
@implementation CTFrameParserConfig
- (instancetype)init {
if (self = [super init]) {
self.width = 300.0f;
self.fontSize = 16.0f;
self.lineSpace = 8.0f;
self.textColor = RGB(108, 108, 108);
}
return self;
}
@end
2)CoreTextData类,定义了两个属性,用来存储绘制所需要的CTFrameRef及最终绘制的View的高度(因为高度是根据文字内容动态计算出来的)。
@interface CoreTextData : NSObject
@property (nonatomic,assign) CTFrameRef ctFrame;
@property (nonatomic,assign) CGFloat height;
@end
@implementation CoreTextData
- (void)setCtFrame:(CTFrameRef)ctFrame {
if (_ctFrame != ctFrame) {
if(_ctFrame != nil) {
CFRelease(_ctFrame);
}
CFRetain(ctFrame);
_ctFrame = ctFrame;
}
}
- (void)dealloc {
if (_ctFrame != nil) {
CFRelease(_ctFrame);
_ctFrame = nil;
}
}
@end
3)CTDisplayView类, 定义了属性data,用于接收外面传递进来的模型数据,然后在drwRect方法中完成绘制工作。
I. 在绘制之前先进行坐标系翻转,因为Core Text的默认坐标系原点在左下角。
II.直接调用CTFrameDraw方法,完成绘制工作。
@interface CTDisplayView : UIView
@property (nonatomic,strong) CoreTextData *data;
@end
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
[super drawRect:rect];
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextSetTextMatrix(context, CGAffineTransformIdentity);
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 0, self.bounds.size.height);
CGContextScaleCTM(context, 1.0, -1.0);
if (self.data) {
CTFrameDraw(self.data.ctFrame, context);
}
}
4)CTFrameParser类,这个类是核心类,主要完成用于生成最后绘制界面需要的CTFrameRef实例。先看看CTFrameParser.h文件中的代码:
@interface CTFrameParser : NSObject /* 对整段文字进行排版 */ + (CoreTextData *)parseContent:(NSString *)content config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config; /* 自定义自己的排版 */ + (CoreTextData *)parseTemplateFile:(NSString *)path config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config; @end
I. 对整段文字进行排版,直接操作传递过来的content字符串,最终显示出来的效果是:所有字体的大小,颜色,行间距均一致。比如:小说应用。
先来看看parseContent方法:
+ (CoreTextData *)parseContent:(NSString *)content config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config {
NSDictionary *attributes = [self attributesWithConfig:config];
NSAttributedString *contentString = [[NSAttributedString alloc] initWithString:content attributes:attributes];
return [self parseAttributedContent:contentString config:config];
}
代码中第一句attrbutesWithConfig方法就是初始化从CTFrameParserConfig中传递过来的默认信息值。
+ (NSDictionary *)attributesWithConfig:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config {
CGFloat fontSize = config.fontSize;
CTFontRef fontRef = CTFontCreateWithName((CFStringRef)@"ArialMT", fontSize, NULL);
CGFloat lineSpacing = config.lineSpace;
const CFIndex kNumberOfSettings = 3;
CTParagraphStyleSetting theSettings[kNumberOfSettings] = {
{kCTParagraphStyleSpecifierLineSpacingAdjustment,sizeof(CGFloat),&lineSpacing},
{kCTParagraphStyleSpecifierMaximumLineSpacing,sizeof(CGFloat),&lineSpacing},
{kCTParagraphStyleSpecifierMinimumLineSpacing,sizeof(CGFloat),&lineSpacing}
};
CTParagraphStyleRef theParagraphRef = CTParagraphStyleCreate(theSettings, kNumberOfSettings);
UIColor *textColor = config.textColor;
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[(id)kCTForegroundColorAttributeName] = (id)textColor.CGColor;
dict[(id)kCTFontAttributeName] = (__bridge id)fontRef;
dict[(id)kCTParagraphStyleAttributeName] = (__bridge id)theParagraphRef;
CFRelease(theParagraphRef);
CFRelease(fontRef);
return dict;
}
代码中的parseAttributeContent方法,就是要返回最终的CoreTextData模型数据,最终给CTDisplayView绘制使用。
+ (CoreTextData *)parseAttributedContent:(NSAttributedString *)content config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config {
// 创建CTFramesetterRef实例
CTFramesetterRef framesetter = CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((CFAttributedStringRef)content);
// 获得要绘制区域的高度
CGSize restrictSize = CGSizeMake(config.width, CGFLOAT_MAX);
CGSize coreTextSize = CTFramesetterSuggestFrameSizeWithConstraints(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0, 0), nil, restrictSize, nil);
CGFloat textHeight = coreTextSize.height;
// 生成CTFrameRef实例
CTFrameRef frame = [self createFrameWithFramesetter:framesetter config:config height:textHeight];
// 将生成好的CTFrameRef实例和计算好的绘制高度保存到CoreTextData实例中,并返回
CoreTextData *data = [[CoreTextData alloc] init];
data.ctFrame = frame;
data.height = textHeight;
// 内存释放
CFRelease(frame);
CFRelease(framesetter);
return data;
}
+ (CTFrameRef)createFrameWithFramesetter:(CTFramesetterRef)framesetter config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config height:(CGFloat)height {
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddRect(path, NULL, CGRectMake(0, 0, config.width, height));
CTFrameRef frame = CTFramesetterCreateFrame(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0, 0), path, NULL);
CFRelease(path);
return frame;
}
II.自定义排版,正如我文章开头贴出来的效果。
/* 自定义自己的排版 */
+ (CoreTextData *)parseTemplateFile:(NSString *)path config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config {
NSAttributedString *content = [self loadTemplateFile:path config:config];
return [self parseAttributedContent:content config:config];
}
先来看看loadTempllateFile方法,就是用来加载数据源,在“对整段文字进行排版”,数据源就是content字符串;而现在这种情况,数据源是自定义的了,它是plist,json等数据形式。为了演示方便,我这里采取的是plist形式。准备的plist结构大致如下:
loadTemplateFile方法具体实现如下:
+ (NSAttributedString *)loadTemplateFile:(NSString *)path config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config {
NSMutableAttributedString *result = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] init];
// JSON方式获取数据
// NSArray *array = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:NSJSONReadingAllowFragments error:nil];
NSArray *array = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path];
if (array) {
if ([array isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {
for (NSDictionary *dict in array) {
NSAttributedString *as = [self parseAttributedContentFromNSDictionary:dict config:config];
[result appendAttributedString:as];
}
}
}
return result;
}
可以看出,代码中,遍历plist文件中的每一个字典数据,然后再调用parseAttributedContentFromNSDictionary方法进行文字的具体处理,这样就可以保证,每段文字的风格不一致了,以达到自定义的效果。parseAttributedContentFromNSDictionary方法代码如下:
+ (NSAttributedString *)parseAttributedContentFromNSDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config {
NSMutableDictionary *attributes = (NSMutableDictionary *)[self attributesWithConfig:config];
UIColor *color = [self colorFromTemplate:dict[@"color"]];
if (color) {
attributes[(id)kCTForegroundColorAttributeName] = (id)color.CGColor;
}
CGFloat fontSize = [dict[@"size"] floatValue];
if (fontSize > 0) {
CTFontRef fontRef = CTFontCreateWithName((CFStringRef)@"ArialMT", fontSize, NULL);
attributes[(id)kCTFontAttributeName] = (__bridge id)(fontRef);
CFRelease(fontRef);
}
NSString *content = dict[@"content"];
return [[NSAttributedString alloc] initWithString:content attributes:attributes];
}
+ (UIColor *)colorFromTemplate:(NSString *)name {
if ([name isEqualToString:@"blue"]) {
return [UIColor blueColor];
} else if ([name isEqualToString:@"green"]) {
return [UIColor greenColor];
} else if ([name isEqualToString:@"red"]) {
return [UIColor redColor];
} else if ([name isEqualToString:@"purple"]) {
return [UIColor purpleColor];
} else {
return nil;
}
}
至此,所有类的定义及实现全部完成了,最终我们调用的代码如下:
CTFrameParserConfig *config = [[CTFrameParserConfig alloc] init];
config.width = self.ctView.width;
NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"TempData.plist" ofType:nil];
CoreTextData *data = [CTFrameParser parseTemplateFile:path config:config];
// 传递数据给CTDisplayView,然后绘制内容
self.ctView.data = data;
// 设置CTDisplayView的高度
self.ctView.height = data.height;
看到上面的代码,是不是瞬间觉得简单易读,并且屏蔽了那些枯燥无味的C语言接口。所以我们想实现自定义模板,只要提供好plist或者json文件的数据形式及内容。
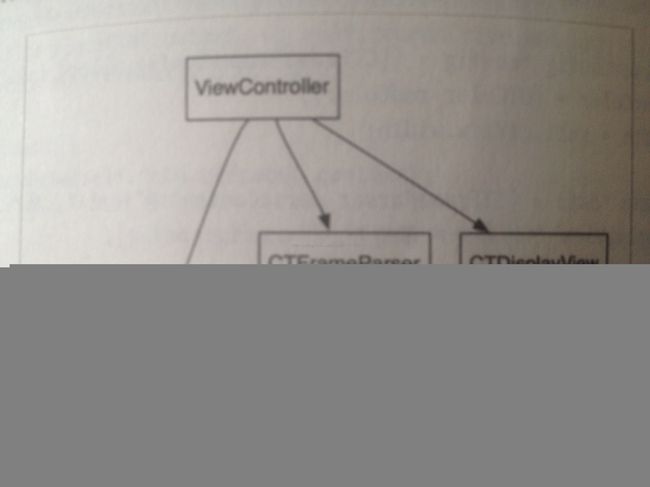
下图是框架的UML示意图:
1. CTFrameParser通过CTFrameParserConfig实例来生成CoreTextData实例。
2. CTDisplayView通过持有CoreTextData实例来获得绘制所需要的所有信息。
3. ViewController类通过配置CTFrameParserConfig实例,进而获得生成的CoreTextData实例,最后将其赋值给它的CTDisplayView成员,达到将指定内容显示在界面上得效果。