浅析SkipList跳跃表原理及代码实现
转载请注明:http://blog.csdn.net/ict2014/article/details/17394259
SkipList在leveldb以及lucence中都广为使用,是比较高效的数据结构。由于它的代码以及原理实现的简单性,更为人们所接受。我们首先看看SkipList的定义,为什么叫跳跃表?
“ Skip lists are data structures that use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing. As a result, the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees. ”
译文:跳跃表使用概率均衡技术而不是使用强制性均衡,因此,对于插入和删除结点比传统上的平衡树算法更为简洁高效。
我们看一个图就能明白,什么是跳跃表,如图1所示:
图1:跳跃表简单示例
如上图所示,是一个即为简单的跳跃表。传统意义的单链表是一个线性结构,向有序的链表中插入一个节点需要O(n)的时间,查找操作需要O(n)的时间。如果我们使用图1所示的跳跃表,就可以减少查找所需时间为O(n/2),因为我们可以先通过每个节点的最上面的指针先进行查找,这样子就能跳过一半的节点。比如我们想查找19,首先和6比较,大于6之后,在和9进行比较,然后在和12进行比较......最后比较到21的时候,发现21大于19,说明查找的点在17和21之间,从这个过程中,我们可以看出,查找的时候跳过了3、7、12等点,因此查找的复杂度为O(n/2)。查找的过程如下图2:
图2:跳跃表查找操作简单示例
其实,上面基本上就是跳跃表的思想,每一个结点不单单只包含指向下一个结点的指针,可能包含很多个指向后续结点的指针,这样就可以跳过一些不必要的结点,从而加快查找、删除等操作。对于一个链表内每一个结点包含多少个指向后续元素的指针,这个过程是通过一个随机函数生成器得到,这样子就构成了一个跳跃表。这就是为什么论文“Skip Lists : A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees ”中有“概率”的原因了,就是通过随机生成一个结点中指向后续结点的指针数目。随机生成的跳跃表可能如下图3所示:
图3:随机生成的跳跃表
跳跃表的大体原理,我们就讲述到这里。下面我们将从如下几个方面来探讨跳跃表的操作:
1、重要数据结构定义
2、初始化表
3、查找
4、插入
5、删除
6、随机数生成器
7、释放表
8、性能比较
(一)重要数据结构定义
从图3中,我们可以看出一个跳跃表是由结点组成,结点之间通过指针进行链接。因此我们定义如下数据结构:
//定义key和value的类型
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int ValueType;
//定义结点
typedef struct nodeStructure* Node;
struct nodeStructure{
KeyType key;
ValueType value;
Node forward[1];
};
//定义跳跃表
typedef struct listStructure* List;
struct listStructure{
int level;
Node header;
};每一个结点都由3部分组成,key(关键字)、value(存放的值)以及forward数组(指向后续结点的数组,这里只保存了首地址)。通过这些结点,我们就可以创建跳跃表List,它是由两个元素构成,首结点以及level(当前跳跃表内最大的层数或者高度)。这样子,基本的数据结构定义完毕了。
(二)初始化表
初始化表主要包括两个方面,首先就是header节点和NIL结点的申请,其次就是List资源的申请。
void SkipList::NewList(){
//设置NIL结点
NewNodeWithLevel(0, NIL_);
NIL_->key = 0x7fffffff;
//设置链表List
list_ = (List)malloc(sizeof(listStructure));
list_->level = 0;
//设置头结点
NewNodeWithLevel(MAX_LEVEL,list_->header);
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_LEVEL; ++i){
list_->header->forward[i] = NIL_;
}
//设置链表元素的数目
size_ = 0;
}
void SkipList::NewNodeWithLevel(const int& level,
Node& node){
//新结点空间大小
int total_size = sizeof(nodeStructure) + level*sizeof(Node);
//申请空间
node = (Node)malloc(total_size);
assert(node != NULL);
}
其中,NewNodeWithLevel是申请结点(总共level层)所需的内存空间。NIL_节点会在后续全部代码实现中可以看到。
(三)查找
查找就是给定一个key,查找这个key是否出现在跳跃表中,如果出现,则返回其值,如果不存在,则返回不存在。我们结合一个图就是讲解查找操作,如下图4所示:
图4:查找操作前的跳跃表
如果我们想查找19是否存在?如何查找呢?我们从头结点开始,首先和9进行判断,此时大于9,然后和21进行判断,小于21,此时这个值肯定在9结点和21结点之间,此时,我们和17进行判断,大于17,然后和21进行判断,小于21,此时肯定在17结点和21结点之间,此时和19进行判断,找到了。具体的示意图如图5所示:
图5:查找操作后的跳跃表
bool SkipList::Search(const KeyType& key,
ValueType& value){
Node x = list_->header;
int i;
for(i = list_->level; i >= 0; --i){
while(x->forward[i]->key < key){
x = x->forward[i];
}
}
x = x->forward[0];
if(x->key == key){
value = x->value;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
(四)插入
插入包含如下几个操作:1、查找到需要插入的位置 2、申请新的结点 3、调整指针。
我们结合下图6进行讲解,查找如下图的灰色的线所示 申请新的结点如17结点所示, 调整指向新结点17的指针以及17结点指向后续结点的指针。这里有一个小技巧,就是使用update数组保存大于17结点的位置,这样如果插入17结点的话,就指针调整update数组和17结点的指针、17结点和update数组指向的结点的指针。update数组的内容如红线所示,这些位置才是有可能更新指针的位置。
图6:插入操作示意图(感谢博主:来自cnblogs的qiang.xu )
bool SkipList::Insert(const KeyType& key,
const ValueType& value){
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
int i;
Node x = list_->header;
//寻找key所要插入的位置
//保存大于key的位置信息
for(i = list_->level; i >= 0; --i){
while(x->forward[i]->key < key){
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[0];
//如果key已经存在
if(x->key == key){
x->value = value;
return false;
}else{
//随机生成新结点的层数
int level = RandomLevel();
//为了节省空间,采用比当前最大层数加1的策略
if(level > list_->level){
level = ++list_->level;
update[level] = list_->header;
}
//申请新的结点
Node newNode;
NewNodeWithLevel(level, newNode);
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
//调整forward指针
for(int i = level; i >= 0; --i){
x = update[i];
newNode->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
x->forward[i] = newNode;
}
//更新元素数目
++size_;
return true;
}
}
(五)删除
删除操作类似于插入操作,包含如下3步:1、查找到需要删除的结点 2、删除结点 3、调整指针
图7:删除操作示意图(感谢博主qiang.xu 来自cnblogs)
bool SkipList::Delete(const KeyType& key,
ValueType& value){
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
int i;
Node x = list_->header;
//寻找要删除的结点
for(i = list_->level; i >= 0; --i){
while(x->forward[i]->key < key){
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[0];
//结点不存在
if(x->key != key){
return false;
}else{
value = x->value;
//调整指针
for(i = 0; i <= list_->level; ++i){
if(update[i]->forward[i] != x)
break;
update[i]->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
}
//删除结点
free(x);
//更新level的值,有可能会变化,造成空间的浪费
while(list_->level > 0
&& list_->header->forward[list_->level] == NIL_){
--list_->level;
}
//更新链表元素数目
--size_;
return true;
}
}
(六)随机数生成器
再向跳跃表中插入新的结点时候,我们需要生成该结点的层数,使用的就是随机数生成器,随机的生成一个层数。这部分严格意义上讲,不属于跳跃表的一部分。随机数生成器说简单很简单,说难很也很难,看你究竟是否想生成随机的数。可以采用c语言中srand以及rand函数,也可以自己设计随机数生成器。
此部分我们采用levelDB随机数生成器:
// Copyright (c) 2011 The LevelDB Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file. See the AUTHORS file for names of contributors.
#include <stdint.h>
//typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
//typedef unsigned long long uint64_t;
// A very simple random number generator. Not especially good at
// generating truly random bits, but good enough for our needs in this
// package.
class Random {
private:
uint32_t seed_;
public:
explicit Random(uint32_t s) : seed_(s & 0x7fffffffu) {
// Avoid bad seeds.
if (seed_ == 0 || seed_ == 2147483647L) {
seed_ = 1;
}
}
uint32_t Next() {
static const uint32_t M = 2147483647L; // 2^31-1
static const uint64_t A = 16807; // bits 14, 8, 7, 5, 2, 1, 0
// We are computing
// seed_ = (seed_ * A) % M, where M = 2^31-1
//
// seed_ must not be zero or M, or else all subsequent computed values
// will be zero or M respectively. For all other values, seed_ will end
// up cycling through every number in [1,M-1]
uint64_t product = seed_ * A;
// Compute (product % M) using the fact that ((x << 31) % M) == x.
seed_ = static_cast<uint32_t>((product >> 31) + (product & M));
// The first reduction may overflow by 1 bit, so we may need to
// repeat. mod == M is not possible; using > allows the faster
// sign-bit-based test.
if (seed_ > M) {
seed_ -= M;
}
return seed_;
}
// Returns a uniformly distributed value in the range [0..n-1]
// REQUIRES: n > 0
uint32_t Uniform(int n) { return (Next() % n); }
// Randomly returns true ~"1/n" of the time, and false otherwise.
// REQUIRES: n > 0
bool OneIn(int n) { return (Next() % n) == 0; }
// Skewed: pick "base" uniformly from range [0,max_log] and then
// return "base" random bits. The effect is to pick a number in the
// range [0,2^max_log-1] with exponential bias towards smaller numbers.
uint32_t Skewed(int max_log) {
return Uniform(1 << Uniform(max_log + 1));
}
};
其中核心的是 seed_ = (seed_ * A) % M这个函数,并且调用一次就重新更新一个种子seed。以达到随机性。
根据个人喜好,自己可以独立设计随机数生成器,只要能够返回一个随机的数字即可。
(七)释放表
释放表的操作比较简单,只要像单链表一样释放表就可以,释放表的示意图8如下:
图8:释放表
void SkipList::FreeList(){
Node p = list_->header;
Node q;
while(p != NIL_){
q = p->forward[0];
free(p);
p = q;
}
free(p);
free(list_);
}
(八)性能比较
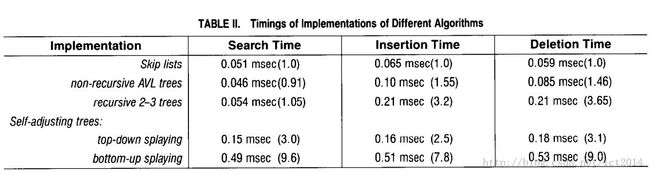
我们对跳跃表、平衡树等进行比较,如下图9所示:
图9:性能比较图
从中可以看出,随机跳跃表表现性能很不错,节省了大量复杂的调节平衡树的代码。
========自己开发的源代码,部分参照qiang.xu====================
下面我将自己用C++实现的代码贴出来,总共包含了如下几个文件:
1、Main.cpp 主要用于测试SkipList
2、skiplist.h 接口声明以及重要数据结构定义
3、skiplist.cpp 接口的具体实现
4、random.h 随机数生成器
--------------------------------------Main.cpp----------------------------------------------------
//此文件用于测试skiplist
//
//@作者:张海波
//@时间:2013-12-17
//@版权:个人所有
#include "skiplist.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
cout << "test is starting ....." << endl;
SkipList list;
//测试插入
for(int i = 0; i < 100; ++i){
list.Insert(i, i+10);
//cout << list.GetCurrentLevel() << endl;
}
cout << "The number of elements in SkipList is :"
<< list.size()
<< endl;
if(list.size() != 100){
cout << "Insert failure." << endl;
}else{
cout << "Insert success." << endl;
}
//测试查找
bool is_search_success = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; ++i){
int value;
if(!(list.Search(i,value) && (value == i+10))){
is_search_success = false;
break;
}
}
if(is_search_success){
cout << "Search success." << endl;
}else{
cout << "Search failure." << endl;
}
//测试删除
bool is_delete_success = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; ++i){
int value;
if(!(list.Delete(i,value) && (value == i+10))){
is_delete_success = false;
break;
}
}
if(is_delete_success){
cout << "Delete success." << endl;
}else{
cout << "Delete failure." << endl;
}
cout << "test is finished ...." << endl;
return 0;
}
--------------------------------------------------skiplist.h---------------------------------------------------
//跳表实现
//
//参考文章为:Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees
//
//提供如下接口:
// Search:搜索给定key的值
// Insert:插入指定的key及value
// Delete:删除指定的key
//
//@作者: 张海波
//@时间: 2013-12-17
//@版权: 个人所有
//
#include <stddef.h>
#include "random.h"
//定义调试开关
#define Debug
//最大层数
const int MAX_LEVEL = 16;
//定义key和value的类型
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int ValueType;
//定义结点
typedef struct nodeStructure* Node;
struct nodeStructure{
KeyType key;
ValueType value;
Node forward[1];
};
//定义跳跃表
typedef struct listStructure* List;
struct listStructure{
int level;
Node header;
};
class SkipList{
public:
//初始化表结构
SkipList():rnd_(0xdeadbeef)
{ NewList(); }
//释放内存空间
~SkipList(){ FreeList(); }
//搜索key,保存结果至value
//找到,返回true
//未找到,返回false
bool Search(const KeyType& key,
ValueType& value);
//插入key和value
bool Insert(const KeyType& key,
const ValueType& value);
//删除key,保存结果至value
//删除成功返回true
//未删除成功返回false
bool Delete(const KeyType& key,
ValueType& value);
//链表包含元素的数目
int size(){ return size_; }
//打印当前最大的level
int GetCurrentLevel();
private:
//初始化表
void NewList();
//释放表
void FreeList();
//创建一个新的结点,结点的层数为level
void NewNodeWithLevel(const int& level,
Node& node);
//随机生成一个level
int RandomLevel();
private:
List list_;
Node NIL_;
//链表中包含元素的数目
size_t size_;
//随机器生成器
Random rnd_;
};
-------------------------------------------------------------skiplist.cpp-----------------------------------------------------
//skiplist头文件重要函数实现
//
//@作者:张海波
//@时间:2013-12-17
//@版权:个人所有
#include "skiplist.h"
#include "time.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void DebugOutput(const string& information){
#ifdef Debug
cout << information << endl;
#endif
}
void SkipList::NewList(){
//设置NIL结点
NewNodeWithLevel(0, NIL_);
NIL_->key = 0x7fffffff;
//设置链表List
list_ = (List)malloc(sizeof(listStructure));
list_->level = 0;
//设置头结点
NewNodeWithLevel(MAX_LEVEL,list_->header);
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_LEVEL; ++i){
list_->header->forward[i] = NIL_;
}
//设置链表元素的数目
size_ = 0;
}
void SkipList::NewNodeWithLevel(const int& level,
Node& node){
//新结点空间大小
int total_size = sizeof(nodeStructure) + level*sizeof(Node);
//申请空间
node = (Node)malloc(total_size);
assert(node != NULL);
}
void SkipList::FreeList(){
Node p = list_->header;
Node q;
while(p != NIL_){
q = p->forward[0];
free(p);
p = q;
}
free(p);
free(list_);
}
bool SkipList::Search(const KeyType& key,
ValueType& value){
Node x = list_->header;
int i;
for(i = list_->level; i >= 0; --i){
while(x->forward[i]->key < key){
x = x->forward[i];
}
}
x = x->forward[0];
if(x->key == key){
value = x->value;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
bool SkipList::Insert(const KeyType& key,
const ValueType& value){
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
int i;
Node x = list_->header;
//寻找key所要插入的位置
//保存大约key的位置信息
for(i = list_->level; i >= 0; --i){
while(x->forward[i]->key < key){
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[0];
//如果key已经存在
if(x->key == key){
x->value = value;
return false;
}else{
//随机生成新结点的层数
int level = RandomLevel();
//为了节省空间,采用比当前最大层数加1的策略
if(level > list_->level){
level = ++list_->level;
update[level] = list_->header;
}
//申请新的结点
Node newNode;
NewNodeWithLevel(level, newNode);
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
//调整forward指针
for(int i = level; i >= 0; --i){
x = update[i];
newNode->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
x->forward[i] = newNode;
}
//更新元素数目
++size_;
return true;
}
}
bool SkipList::Delete(const KeyType& key,
ValueType& value){
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
int i;
Node x = list_->header;
//寻找要删除的结点
for(i = list_->level; i >= 0; --i){
while(x->forward[i]->key < key){
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[0];
//结点不存在
if(x->key != key){
return false;
}else{
value = x->value;
//调整指针
for(i = 0; i <= list_->level; ++i){
if(update[i]->forward[i] != x)
break;
update[i]->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
}
//删除结点
free(x);
//更新level的值,有可能会变化,造成空间的浪费
while(list_->level > 0
&& list_->header->forward[list_->level] == NIL_){
--list_->level;
}
//更新链表元素数目
--size_;
return true;
}
}
int SkipList::RandomLevel(){
int level = static_cast<int>(rnd_.Uniform(MAX_LEVEL));
if(level == 0){
level = 1;
}
//cout << level << endl;
return level;
}
int SkipList::GetCurrentLevel(){
return list_->level;
}
-----------------------------------------------------------random.h-------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2011 The LevelDB Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file. See the AUTHORS file for names of contributors.
#include <stdint.h>
//typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
//typedef unsigned long long uint64_t;
// A very simple random number generator. Not especially good at
// generating truly random bits, but good enough for our needs in this
// package.
class Random {
private:
uint32_t seed_;
public:
explicit Random(uint32_t s) : seed_(s & 0x7fffffffu) {
// Avoid bad seeds.
if (seed_ == 0 || seed_ == 2147483647L) {
seed_ = 1;
}
}
uint32_t Next() {
static const uint32_t M = 2147483647L; // 2^31-1
static const uint64_t A = 16807; // bits 14, 8, 7, 5, 2, 1, 0
// We are computing
// seed_ = (seed_ * A) % M, where M = 2^31-1
//
// seed_ must not be zero or M, or else all subsequent computed values
// will be zero or M respectively. For all other values, seed_ will end
// up cycling through every number in [1,M-1]
uint64_t product = seed_ * A;
// Compute (product % M) using the fact that ((x << 31) % M) == x.
seed_ = static_cast<uint32_t>((product >> 31) + (product & M));
// The first reduction may overflow by 1 bit, so we may need to
// repeat. mod == M is not possible; using > allows the faster
// sign-bit-based test.
if (seed_ > M) {
seed_ -= M;
}
return seed_;
}
// Returns a uniformly distributed value in the range [0..n-1]
// REQUIRES: n > 0
uint32_t Uniform(int n) { return (Next() % n); }
// Randomly returns true ~"1/n" of the time, and false otherwise.
// REQUIRES: n > 0
bool OneIn(int n) { return (Next() % n) == 0; }
// Skewed: pick "base" uniformly from range [0,max_log] and then
// return "base" random bits. The effect is to pick a number in the
// range [0,2^max_log-1] with exponential bias towards smaller numbers.
uint32_t Skewed(int max_log) {
return Uniform(1 << Uniform(max_log + 1));
}
};
上述程序运行的结果如下图所示: