【移动开发】如何自定义ViewGroup
本文翻译自《50 android hacks》
依照惯例,先从一个例子说起。
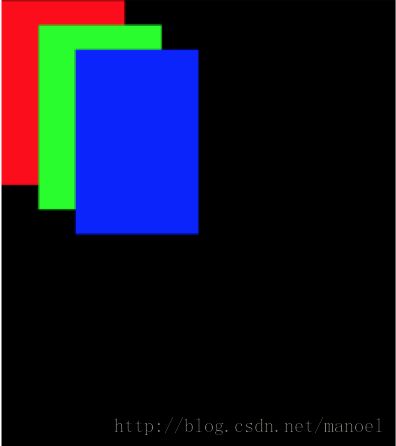
很简单,3张扑克牌叠在一起显示。这个布局效果该如何实现呢?有的同学该说了,这很简单啊,用RelativeLayout或FrameLayout,然后为每一个扑克牌设置margin就能实现了。
ok,那就看一下通过这种方式是如何实现的。代码如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#FF0000" />
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:background="#00FF00" />
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="60dp"
android:layout_marginTop="40dp"
android:background="#0000FF" />
</RelativeLayout>效果图
没错,通过这种方式是可以实现的。但是,不觉得这种方式有点low吗?!让我们用高级一点的方式去实现它,提升一下自己的逼格!
定制ViewGroup之前,我们需要先理解几个概念。
Android绘制视图的方式
这里我不会涉及太多的细节,但是需要理解Android开发文档中的一段话:
“绘制布局由两个遍历过程组成:测量过程和布局过程。测量过程由measure(int, int)方法完成,该方法从上到下遍历视图树。在递归遍历过程中,每个视图都会向下层传递尺寸和规格。当measure方法遍历结束,每个视图都保存了各自的尺寸信息。第二个过程由layout(int,int,int,int)方法完成,该方法也是由上而下遍历视图树,在遍历过程中,每个父视图通过测量过程的结果定位所有子视图的位置信息。”
简而言之,第一步是测量ViewGroup的宽度和高度,在onMeasure()方法中完成,ViewGroup遍历所有子视图计算出它的大小。第二步是根据第一步获取的尺寸去布局所有子视图,在onLayout()中完成。
创建CascadeLayout
终于到了定制ViewGroup的阶段了。假设我们已经定制了一个CascadeLayout的容器,我们会这样使用它。
<FrameLayout xmlns:cascade="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.manoel.custom"
<!-- 声明命名空间 -->
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<com.manoel.view.CascadeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
<!-- 自定义属性 -->
cascade:horizontal_spacing="30dp"
cascade:vertical_spacing="20dp" >
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#FF0000" />
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#00FF00" />
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#0000FF" />
</com.manoel.view.CascadeLayout>
</FrameLayout>
首先,定义属性。在values文件夹下面创建attrs.xml,代码如下:
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="CascadeLayout">
<attr name="horizontal_spacing" format="dimension" />
<attr name="vertical_spacing" format="dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
同时,为了严谨一些,定义一些默认的垂直距离和水平距离,以防在布局中没有提供这些属性。
在dimens.xml中添加如下代码:
<resources>
<dimen name="cascade_horizontal_spacing">10dp</dimen>
<dimen name="cascade_vertical_spacing">10dp</dimen>
</resources>准备工作已经做好了,接下来看一下CascadeLayout的源码,略微有点长,后面帮助大家分析一下。
public class CascadeLayout extends ViewGroup {
private int mHorizontalSpacing;
private int mVerticalSpacing;
public CascadeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.CascadeLayout);
try {
mHorizontalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.CascadeLayout_horizontal_spacing,
getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(
R.dimen.cascade_horizontal_spacing));
mVerticalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.CascadeLayout_vertical_spacing, getResources()
.getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.cascade_vertical_spacing));
} finally {
a.recycle();
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int width = getPaddingLeft();
int height = getPaddingTop();
int verticalSpacing;
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
verticalSpacing = mVerticalSpacing;
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
width = getPaddingLeft() + mHorizontalSpacing * i;
lp.x = width;
lp.y = height;
if (lp.verticalSpacing >= 0) {
verticalSpacing = lp.verticalSpacing;
}
width += child.getMeasuredWidth();
height += verticalSpacing;
}
width += getPaddingRight();
height += getChildAt(getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredHeight()
+ getPaddingBottom();
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec),
resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec));
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
child.layout(lp.x, lp.y, lp.x + child.getMeasuredWidth(), lp.y
+ child.getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof LayoutParams;
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new LayoutParams(p.width, p.height);
}
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
int x;
int y;
public int verticalSpacing;
public LayoutParams(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public LayoutParams(int w, int h) {
super(w, h);
}
}
}
首先,分析构造函数。
public CascadeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.CascadeLayout);
try {
mHorizontalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.CascadeLayout_horizontal_spacing,
getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(
R.dimen.cascade_horizontal_spacing));
mVerticalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.CascadeLayout_vertical_spacing, getResources()
.getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.cascade_vertical_spacing));
} finally {
a.recycle();
}
}如果在布局中使用CasecadeLayout,系统就会调用这个构造函数,这个大家都应该知道的吧。这里不解释why,有兴趣的可以去看源码,重点看系统是如何解析xml布局的。
构造函数很简单,就是通过布局文件中的属性,获取水平距离和垂直距离。
然后,分析自定义LayoutParams。
这个类的用途就是保存每个子视图的x,y轴位置。这里把它定义为静态内部类。ps:提到静态内部类,我又想起来关于多线程内存泄露的问题了,如果有时间再给大家解释一下多线程造成内存泄露的问题。
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
int x;
int y;
public int verticalSpacing;
public LayoutParams(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public LayoutParams(int w, int h) {
super(w, h);
}
}
除此之外,还需要重写一些方法,checkLayoutParams()、generateDefaultLayoutParams()等,这个方法在不同ViewGroup之间往往是相同的。
接下来,分析onMeasure()方法。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int width = getPaddingLeft();
int height = getPaddingTop();
int verticalSpacing;
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
verticalSpacing = mVerticalSpacing;
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); // 令每个子视图测量自身
LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
width = getPaddingLeft() + mHorizontalSpacing * i;
// 保存每个子视图的x,y轴坐标
lp.x = width;
lp.y = height;
if (lp.verticalSpacing >= 0) {
verticalSpacing = lp.verticalSpacing;
}
width += child.getMeasuredWidth();
height += verticalSpacing;
}
width += getPaddingRight();
height += getChildAt(getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredHeight()
+ getPaddingBottom();
// 使用计算所得的宽和高设置整个布局的测量尺寸
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec),
resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec));
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
child.layout(lp.x, lp.y, lp.x + child.getMeasuredWidth(), lp.y
+ child.getMeasuredHeight());
}
}逻辑很简单,用onMeasure()方法计算出的值为参数循环调用子View的layout()方法。
为子视图添加自定义属性
作为示例,下面将添加子视图重写垂直间距的方法。
第一步是向attrs.xml中添加一个新的属性。
<declare-styleable name="CascadeLayout_LayoutParams">
<attr name="layout_vertical_spacing" format="dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
这里的属性名是layout_vertical_spacing,因为该属性名前缀是layout_,同时,又不是View固有的属性,所以该属性会被添加到LayoutParams的属性表中。在CascadeLayout类的构造函数中读取这个新属性。
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
int x;
int y;
public int verticalSpacing;
public LayoutParams(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.CascadeLayout_LayoutParams);
try {
verticalSpacing = a
.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.CascadeLayout_LayoutParams_layout_vertical_spacing,
-1);
} finally {
a.recycle();
}
}
public LayoutParams(int w, int h) {
super(w, h);
}
}
那怎么使用这个属性呢?so easy!
<com.manoel.view.CascadeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
cascade:horizontal_spacing="30dp"
cascade:vertical_spacing="20dp" >
<!-- 注意:这张“扑克牌”使用了layout_vertical_spacing属性 -->
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
cascade:layout_vertical_spacing="90dp"
android:background="#FF0000" />
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#00FF00" />
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#0000FF" />
</com.manoel.view.CascadeLayout>

参考资料
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/how-android-draws.html
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/ViewGroup.html
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/ViewGroup.LayoutParams.html