GUI
1、GUI(图形用户界面)
GUI
Graphical User Interface(图形用户接口)。
用图形的方式,来显示计算机操作的界面,这样更方便更直观。
CLI
Command line User Interface (命令行用户接口)
就是常见的Dos命令行操作。
需要记忆一些常用的命令,操作不直观。
举例:
比如:创建文件夹,或者删除文件夹等
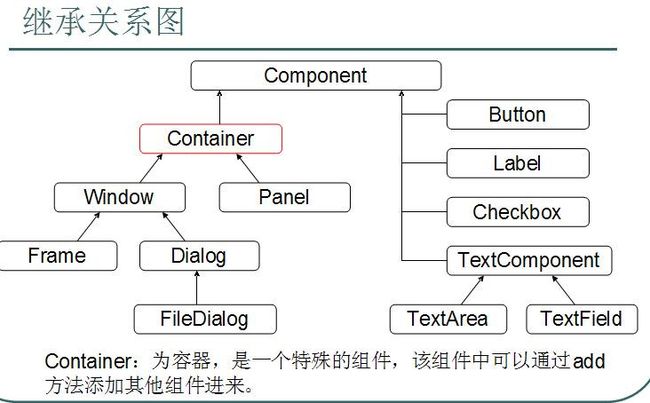
Java为GUI提供的对象都存在java.Awt和javax.Swing两个包中。
Act和Swing
Awt与 Swing
java.Awt:Abstract Window ToolKit (抽象窗口工具包),需要调用本地系统方法实现功能。属重量级控件。
javax.Swing:在AWT的基础上,建立的一套图形界面系统,其中提供了更多的组件,而且完全由Java实现。增强了移植性,属轻量级控件。
2、布局管理器
容器中的组件的排放方式,就是布局。
常见的布局管理器:
FlowLayout(流式布局管理器)//目前最常用的
从左到右的顺序排列。
Panel默认的布局管理器。
BorderLayout(边界布局管理器)
东,南,西,北,中
Frame默认的布局管理器。
GridLayout(网格布局管理器)
规则的矩阵
CardLayout(卡片布局管理器)
选项卡
GridBagLayout(网格包布局管理器)
非规则的矩阵
使用方法:new frame().setLayout(new FlowLayout());
我的总结:
创建图形化界面:
1,创建frame窗体。
2,对窗体进行基本设置。 比如大小,位置,布局。
3,定义组件。
4,将组件通过窗体的add方法添加到窗体中。
5,让窗体显示,通过setVisible(true)
Eg:一个简单的窗体
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
class SwingDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame f = new JFrame();
f.setBounds(300,100,500,400);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton but = new JButton("我是一个按钮");
f.add(but);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
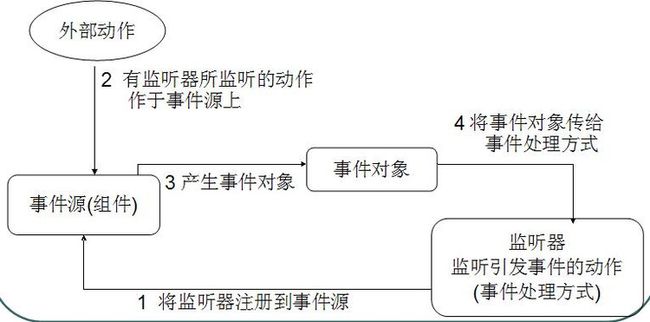
3、事件监听机制组成
事件源(组件)
事件(Event)
监听器(Listener)
事件处理(引发事件后处理方式)
事件监听机制流程图
务必记牢:
确定事件源(容器或组件)
通过事件源对象的addXXXListener()方法将侦听器注册到该事件源上。
该方法中接收XXXListener的子类对象,或者XXXListener的子类XXXAdapter的子类对象。
一般用匿名内部类来表示。
在覆盖方法的时候,方法的参数一般是XXXEvent类型的变量接收。
事件触发后会把事件打包成对象传递给该变量。(其中包括事件源对象。通过getSource()或者,getComponent()获取。)
事件源:就是awt包或者swing包中的那些图形界面组件。
事件:每一个事件源都有自己特有的对应事件和共性事件。
监听器:将可以触发某一个事件的动作(不只一个动作)都已经封装到了监听器中。
以上三者,在java中都已经定义好了。直接获取其对象来用就可以了。
我们要做的事情是,就是对产生的动作进行处理。
Eg:
package june610;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
class MyWin extends WindowAdapter{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.out.println("hahahha");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public class FrameDemo {//如果写成内部类的形式那么前面必须加上public static,因为主方法是静态的,不能调用动态类或者方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//设置窗体
Frame f = new Frame("窗体");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(500, 300);//距离左侧,距离上面
/**可以用这个方法一次性设置
* setBounds(int x, int y, int width, int height) 移动组件并调整其大小。
*/
Button b = new Button("按钮");
Button b2 = new Button("按钮2");
TextField tf = new TextField(20);
f.add(b);//把按钮添加到窗体上
f.add(b2);//把按钮添加到窗体上
f.add(tf);//在窗体上的的顺序按照添加的顺序
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());//设置容器的布局管理器
//f.addWindowListener(new MyWin());
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){//通过匿名内部类,方便 添加动作监听器
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("按钮把界面关闭了");
//System.exit(0);
}
});
//鼠标
b.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {//鼠标动作监听器
int count = 1;
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e){
System.out.println("鼠标进入"+(count++)+"次!");
}
});
b.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter(){//和上面的一样,可以写在一起
int clickCount = 1;
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e){
if(e.getClickCount() == 2){
System.out.println("双击动作"+clickCount++);
}
}
});
/*
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()//匿名内部类的写法
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.out.println("我关");
System.exit(0);
}
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e)
{
System.out.println("我活了。");
}
public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e)
{
System.out.println("我被打开了,hahahhahah");
}
});*/
//键盘:
b2.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
{
System.out.println("键盘的作用");//用鼠标按没反应,
System.out.println(e.getKeyChar()+"---"+e.getKeyCode());//f---70等、
if(e.getKeyCode() == 27){//按住esc键退出
System.out.println("ESC键把我关闭了!");
System.exit(0);
}
//组合键去关闭 CTRL + ENTER
if(e.isControlDown() && e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER){
System.out.println("CTRL + ENTER组合键把我关闭了!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
});
//文本框
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
if(!(e.getKeyCode()>=KeyEvent.VK_0 && e.getKeyCode()<=KeyEvent.VK_9)){
System.out.println(e.getKeyChar()+"不符合是数字!");
}
}
});
f.setVisible(true);//设置可见性
}
}
Eg://列出文件夹内全部的文件
package june610;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.TextArea;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.io.File;
class MyFrame {
private Frame f;
private Button b;
private TextField tf;
private TextArea ta;
MyFrame() {
init();
}
void init() {
f = new Frame("我的电脑");
f.setBounds(300, 100, 600, 500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
b = new Button("转到");
tf = new TextField(60);
ta = new TextArea(25, 70);
f.add(tf);
f.add(b);
f.add(ta);
f.setVisible(true);
action();
}
//窗体上的操作
void action() {
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
buttonAction();
keyAction();
}
void keyAction(){
//设置键盘监听器,当输入enter键的时候实现和点击鼠标同样的功能!
b.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
//if(e.getKeyCode() == 10){
//buttonAction();
//}
String dirPath = tf.getText();// 获取文本(我们想验证的是路径),接下来获取文件
File file = new File(dirPath);// 获取文件
if (file.exists() && file.isDirectory()) {// 判断,存在否以及是否是文件夹
ta.setText("");// 如果符合条件的话,清空以前的数据;
String[] names = file.list();
for (String name : names) {
ta.append(name + "\r\n");
}
System.out.println("=======");
} else {
ta.setText("");
ta.append("对不起,请确认您输入的是路径!");
}
System.out.println(e.getKeyCode());
}
});
tf.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String dirPath = tf.getText();// 获取文本(我们想验证的是路径),接下来获取文件
File file = new File(dirPath);// 获取文件
if (file.exists() && file.isDirectory()) {// 判断,存在否以及是否是文件夹
ta.setText("");// 如果符合条件的话,清空以前的数据;
String[] names = file.list();
for (String name : names) {
ta.append(name + "\r\n");
}
System.out.println("=======");
} else {
ta.setText("");
ta.append("对不起,请确认您输入的是路径!");
}
}
});
}
void buttonAction() {
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String dirPath = tf.getText();// 获取文本(我们想验证的是路径),接下来获取文件
File file = new File(dirPath);// 获取文件
if (file.exists() && file.isDirectory()) {// 判断,存在否以及是否是文件夹
ta.setText("");// 如果符合条件的话,清空以前的数据;
String[] names = file.list();
for (String name : names) {
ta.append(name + "\r\n");
}
System.out.println("=======");
} else {
ta.setText("");
ta.append("对不起,请确认您输入的是路径!");
}
}
});
}
}
public class FrameDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame();
}
}
4、Dialog
Dialog构造方法
* Dialog(Frame owner, String title, boolean modal)
构造一个最初不可见的 Dialog,它带有指定的所有者 Frame、标题和模式。
备注:Dialog的模式区别在于:
true的话对话框依附于窗体,不取消Dialog不可以操作窗体,
false的话,不取消Dialog可以操作窗体!
package june610;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Dialog;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.TextArea;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.io.File;
public class FrameDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Frame f = new Frame("我的电脑");
f.setBounds(300, 100, 600, 500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
Button b = new Button("转到");
Button okBut = new Button("确定");
final TextField tf = new TextField(60);
final TextArea ta = new TextArea(25, 70);
f.add(tf);
f.add(b);
f.add(ta);
f.setVisible(true);
final Dialog d = new Dialog(f,"提示信息",true);
final Label lab = new Label();//没有给出内容,用到的时候再给出!
d.add(lab);//label标签加到Dialog上去!
d.setBounds(400, 200, 240, 150);
d.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
d.add(okBut);
okBut.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
//只可以对鼠标有作用!
okBut.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
d.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
d.setVisible(false);//对话框不显示
}
});
//窗体上的操作
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
//设置键盘监听器,当输入enter键的时候实现和点击鼠标同样的功能!
/*tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
if (e.getKeyCode() == 10) {
// buttonAction();
run(tf,ta,f,d,lab);
}
System.out.println(e.getKeyCode());
}
});*/
//和上面被注释的代码实现的是同样的功能,也是键盘控制,不过不能设定哪个键,只有enter!
tf.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
run(tf,ta,f,d,lab);
// System.out.println(text);
}
});
//给转到添加键盘和鼠标双控制
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
run(tf,ta,f,d,lab);
// System.out.println(text);
}
});
b.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
run(tf,ta,f,d,lab);
}
});
}
//封装这一方法,为了方便使用(注意这个时候传递参数太多了,尽量避免这种情况的发生!
//在一个方法内部创建的对象只有在自己方法体里面才可以直接调用,而在外部方法必须传递参数)
public static void run(TextField tf,TextArea ta,Frame f,Dialog d,Label lab){
String dirPath = tf.getText();// 获取文本(我们想验证的是路径),接下来获取文件
File file = new File(dirPath);// 获取文件
if (file.exists() && file.isDirectory()) {// 判断,存在否以及是否是文件夹
ta.setText("");// 如果符合条件的话,清空以前的数据;
String[] names = file.list();
for (String name : names) {
ta.append(name + "\r\n");
}
} else {
//备注:应该在这里构建对话框,为了内存的优化,用到的时候才创建对象,用不到就不创建!
String info = "您输入的信息:"+dirPath+"有误,请重新输入!";
lab.setText(info);
d.setVisible(true);
/**可以这样写,但是不专业,现在弹出对话框!
* ta.setText("");
ta.append("对不起,请确认您输入的是路径!");
*/
}
}
}
5、菜单
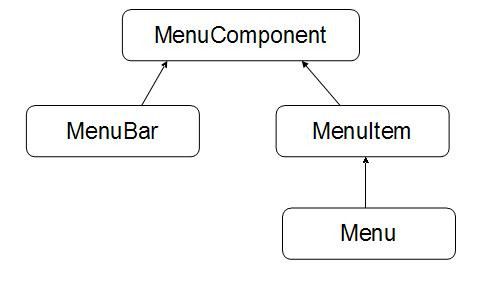
继承体系
MenuBar,Menu,MenuItem之间的关系:
先创建菜单条,再创建菜单,每一个菜单中建立菜单项。
也可以菜单添加到菜单中,作为子菜单。
通过setMenuBar()方法,将菜单添加到Frame中。
package june610;
import java.awt.FileDialog;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Menu;
import java.awt.MenuBar;
import java.awt.MenuItem;
import java.awt.TextArea;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
//最后导出jar包,用eclipse,必须要指定main函数!!不能直接点击finished!!!
/**我的总结:
* 菜单的结构MenuBar(相当于一个环境,f.set、、)
* -->Menu(菜单,m.add、、可以添加自己,也可以添加Item)
* -->MenuItem(条目 )
*/
class MyMenuDemo{
private Frame f;//首先声明对象的好处,全局可以调用!
private MenuBar mb;
private Menu m,subm;
private MenuItem mi,close,save,open;
private FileDialog openDia,saveDia;
private TextArea ta;
private File file;
MyMenuDemo(){
f = new Frame("我的电脑");
f.setBounds(400, 150, 500, 500);
//备注:此时没有设置布局管理器类型(因为不设置的话下面的TextArea会很爽!)
mb = new MenuBar();
m = new Menu("文件");
save = new MenuItem("保存");
open = new MenuItem("打开");
subm = new Menu("子菜单");
close = new MenuItem("退出");
mi = new MenuItem("子菜单2");
openDia = new FileDialog(f, "我的打开", FileDialog.LOAD);//加载
saveDia = new FileDialog(f, "我的保存", FileDialog.SAVE);//保存
ta = new TextArea();
f.setMenuBar(mb);//添加
mb.add(m);
subm.add(mi);
m.add(subm);
m.add(open);
m.add(save);
m.add(close);
f.add(ta);
f.setVisible(true);
init();
}
public void init(){
//打开文件,弹出对话框
open.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
openDia.setVisible(true);
String path = openDia.getDirectory();
String name = openDia.getFile();
//ta.append(path+"-----"+name+"\n");
if(path==null || name==null)
return ;
ta.setText("");//每次开始都清空
file = new File(path, name);
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));//缓冲流
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
ta.append(line+"\n");
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//保存文件,弹出对话框!
save.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//注意问题:只有文件第一次保存(不存在)的时候才需要你去弹出对话框,以后只保存,不弹出!
if(file == null){
saveDia.setVisible(true);//不存在才弹,创建文件
String path = saveDia.getDirectory();
String name = saveDia.getFile();
if(name == null || path == null)
return;
//目录和名字正确,但是文件不存在,就新建一个文件!
file = new File(path,name);
}
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String s = ta.getText();
bw.write(s);
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
close.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
public class MenuDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyMenuDemo();
}
}