Android 4.4 KitKat NotificationManagerService使用详解与原理分析
转载请务必注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/yihongyuelan
概况
Android在4.3的版本中(即API 18)加入了NotificationListenerService,根据SDK的描述(AndroidDeveloper)可以知道,当系统收到新的通知或者通知被删除时,会触发NotificationListenerService的回调方法。同时在Android 4.4 中新增了Notification.extras 字段,也就是说可以使用NotificationListenerService获取系统通知具体信息,这在以前是需要用反射来实现的。
重要关系
对于系统通知,三方APP使用NotificationListenerService主要目的是为了获取系统通知相关信息,主要包括:通知的新增和删除,获取当前通知数量,通知内容相关信息等。这些信息可以通过NotificationListenerService类提供的方法以及StatusBarNotification类对象来获取。
NotificationListenerService主要方法(成员变量):
cancelAllNotifications() :删除系统中所有可被清除的通知;
cancelNotification(String pkg, String tag, int id) :删除具体某一个通知;
getActiveNotifications() :返回当前系统所有通知到StatusBarNotification[];
onNotificationPosted(StatusBarNotification sbn) :当系统收到新的通知后出发回调;
onNotificationRemoved(StatusBarNotification sbn) :当系统通知被删掉后出发回调;
以上是NotificationListenerService的主要方法,通过这些方法就可以在应用中操作系统通知,在NotificationListenerService中除了对通知的操作之外,还可以获取到通知的StatusBarNotification对象,通过该对象可以获取通知更详细的数据。
StatusBarNotification主要方法(成员变量):
getId():返回通知对应的id;
getNotification():返回通知对象;
getPackageName():返回通知对应的包名;
getPostTime():返回通知发起的时间;
getTag():返回通知的Tag,如果没有设置返回null;
getUserId():返回UserId,用于多用户场景;
isClearable():返回该通知是否可被清楚,FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT、FLAG_NO_CLEAR;
isOngoing():检查该通知的flag是否为FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT;
使用简介
正确使用NotificationListenerService需要注意三点:
(1). 新建一个类并继承自NotificationListenerService,override其中重要的两个方法;
- public class NotificationMonitor extends NotificationListenerService {
- @Override
- public void onNotificationPosted(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- Log.i("SevenNLS","Notification posted");
- }
- @Override
- public void onNotificationRemoved(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- Log.i("SevenNLS","Notification removed");
- }
- }
(2). 在AndroidManifest.xml中注册Service并声明相关权限;
- <service android:name=".NotificationMonitor"
- android:label="@string/service_name"
- android:permission="android.permission.BIND_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SERVICE">
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.service.notification.NotificationListenerService" />
- </intent-filter>
- </service>
完成以上两步之后,将程序编译并安装到手机上,但此时该程序是无法监听到新增通知和删除通知的,还需要在"Settings > Security > Notification access"中,勾选NotificationMonitor。此时如果系统收到新的通知或者通知被删除就会打印出相应的log了。
这里需要注意,如果手机上没有安装使用NotificationListenerService类的APP,Notification access是不会显示出来的。可以在源码/packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/SecuritySettings.java中看到,如果没有使用NotificationListenerService的APK,直接就不显示这一项了。
- mNotificationAccess = findPreference(KEY_NOTIFICATION_ACCESS);
- if (mNotificationAccess != null) {
- final int total = NotificationAccessSettings.getListenersCount(mPM);
- if (total == 0) {
- if (deviceAdminCategory != null) {
- deviceAdminCategory.removePreference(mNotificationAccess);
- }
- } else {
- final int n = getNumEnabledNotificationListeners();
- if (n == 0) {
- mNotificationAccess.setSummary(getResources().getString(
- R.string.manage_notification_access_summary_zero));
- } else {
- mNotificationAccess.setSummary(String.format(getResources().getQuantityString(
- R.plurals.manage_notification_access_summary_nonzero,
- n, n)));
- }
- }
- }
使用详解
通过前面的讲解(实际上就是对AndroidDeveloper的解释),已经可以正常使用NotificationListenerService了,但对于实际应用中,需要考虑的事情还比较多。比如:
1. 如何检测应用已开启Notification access监听功能?
如果检测到应用没有激活Notification access监听功能,需要提示用户开启;
2. 能不能主动跳转到Notification access监听页面?
如果能够根据第1步的判断自动跳转到对应的页面,那可以省掉很多操作;
3. 如何与NotificationListenerService交互?
涉及到与Service的交互,但又与普通的Service不同,这里后文解释;
4. NotificationListenerService使用过程中有哪些注意事项?
在使用NotificationListenerService过程中自己遇到了一些坑,后文会通过分析给出相应的解决方案;
程序运行截图
图 1 程序运行截图
示例介绍
NotificationListenerDemo主要用于获取系统当前通知信息,并可手动创建"可清除通知",逐条删除"可清除通知",一次性删除"可清除通知",以及显示系统当前活动的通知信息。实际上该示例回答了前面使用详解中提出的各项疑问,在实际使用过程中相信大部分人都会遇到,因此这里逐条展开与大家分享。
图 2 主界面
功能分析
1. 如何检测应用已开启Notification access监听功能?
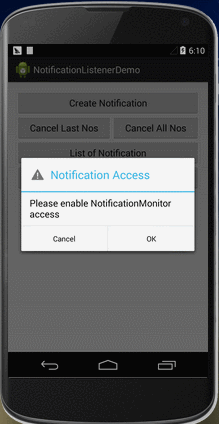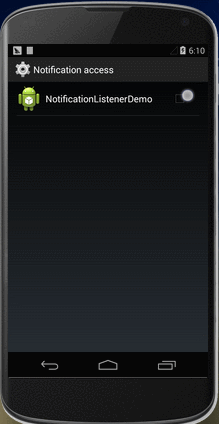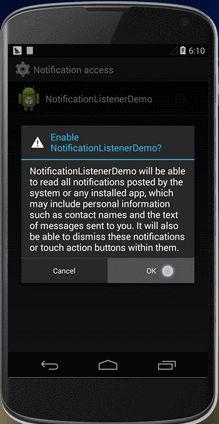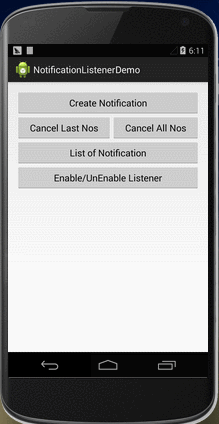
在程序启动时,执行Notification access的检测,查看是否访问Notification的权限。如果用户没有Enable Notification access,则弹出提示对话框,点击OK跳转到Notification access设置页面。图 3 首次启动 isEnable
使用NotificationListenerService的应用如果开启了Notification access,系统会将包名等相关信息写入SettingsProver数据库中,因此可以从数据库中获取相关信息并过滤,从而判断应用是否开启了Notification access,代码如下:
- private static final String ENABLED_NOTIFICATION_LISTENERS = "enabled_notification_listeners";
- private boolean isEnabled() {
- String pkgName = getPackageName();
- final String flat = Settings.Secure.getString(getContentResolver(),
- ENABLED_NOTIFICATION_LISTENERS);
- if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(flat)) {
- final String[] names = flat.split(":");
- for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
- final ComponentName cn = ComponentName.unflattenFromString(names[i]);
- if (cn != null) {
- if (TextUtils.equals(pkgName, cn.getPackageName())) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
2. 能不能主动跳转到Notification access监听页面?
通过查看可以知道,Notification access界面接收action为"android.settings.ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS"的intent启动,因此使用startActivity可以很容易的跳转到该页面,从而避免用户在Settings中查找。代码如下:
- private static final String ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS = "android.settings.ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS";
- private void openNotificationAccess() {
- startActivity(new Intent(ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS));
- }
3. 如何与NotificationListenerService交互?
因为NotificationListenerService中包含了四个重要的方法,分别是:onNotificationPosted、onNotificationRemoved、cancelNotification、cancelAllNotifications。通过这些方法我们才能实现诸如通知信息的获取以及删除等功能,虽然这些方法是public的,那是不是意味着我们只要拿到NotificationListenerService的对象就可以直接调用这些方法了呢?那如何拿到Service的对象呢?在之前的博文中,曾有提到与Service的交互( 具体可参考拙作《Android中程序与Service交互的方式——交互方式》),可以看到与Service的交互有很多种方法,但如果要拿到Service的对象,归根到底还是需要Binder。
也就是说得使用bindService的办法,将onServiceConnected回调中的IBinder对象转型成NotificationListenerService的对象。测试代码如下:
- //在MainActivity.java的onCreate方法中使用bindService帮顶NotificationMonitor服务
- bindService(new Intent(this,NotificationMonitor.class ), new ServiceConnection() {
- @Override
- public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) {
- }
- @Override
- public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName arg0, IBinder arg1) {
- NotificationMonitor.MyBinder localBinder = (MyBinder)arg1;
- NotificationMonitor mMonitor = localBinder.getService();
- }
- }, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
- //NotificationMonitor的onBind方法返回构造的Binder对象
- public class NotificationMonitor extends NotificationListenerService {
- private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
- public class MyBinder extends Binder{
- public NotificationMonitor getService(){
- return NotificationMonitor.this;
- }
- }
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
- return mBinder;
- }
- @Override
- public void onNotificationPosted(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- getActiveNotifications();
- cancelAllNotifications();
- }
- @Override
- public void onNotificationRemoved(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- }
- }
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- if (mWrapper == null) {
- mWrapper = new INotificationListenerWrapper();
- }
- return mWrapper;
- }
- private class INotificationListenerWrapper extends INotificationListener.Stub
而NotificationMonitor继承自NotificationListenerService,默认的onBind方法却是:
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- return super.onBind(intent);
- }
那应该如何使用NotificationListenerService中的方法呢?在拙作《Android中程序与Service交互的方式——交互方式》中,已经提供了很多的例子,这里仅以广播的方式为例。
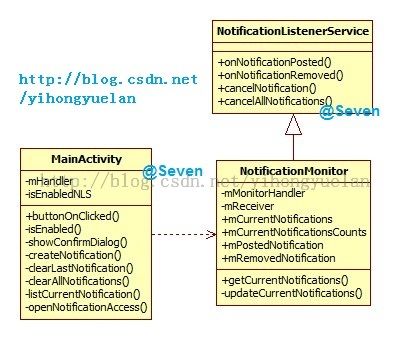
既然NotificationMonitor可以使用NotificationListenerService的方法,那通过NotificationMonitor把通知状态的改变以及数据获取到,并使用static数据进行存储,之后再在MainActivity中直接使用即可。在MainActivity中控制通知的单个删除和全部删除,则使用广播的方式发送给NotificationMonitor进行处理。MainActivity与NotificationMonitor的关系类图如下:
- public class NotificationMonitor extends NotificationListenerService {
- private static final String TAG = "SevenNLS";
- private static final String TAG_PRE = "[" + NotificationMonitor.class.getSimpleName() + "] ";
- private static final int EVENT_UPDATE_CURRENT_NOS = 0;
- public static final String ACTION_NLS_CONTROL = "com.seven.notificationlistenerdemo.NLSCONTROL";
- //用于存储当前所有的Notification的StatusBarNotification对象数组
- public static List<StatusBarNotification[]> mCurrentNotifications = new ArrayList<StatusBarNotification[]>();
- public static int mCurrentNotificationsCounts = 0;
- //收到新通知后将通知的StatusBarNotification对象赋值给mPostedNotification
- public static StatusBarNotification mPostedNotification;
- //删除一个通知后将通知的StatusBarNotification对象赋值给mRemovedNotification
- public static StatusBarNotification mRemovedNotification;
- private CancelNotificationReceiver mReceiver = new CancelNotificationReceiver();
- // String a;
- private Handler mMonitorHandler = new Handler() {
- @Override
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- switch (msg.what) {
- case EVENT_UPDATE_CURRENT_NOS:
- updateCurrentNotifications();
- break;
- default:
- break;
- }
- }
- };
- class CancelNotificationReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String action;
- if (intent != null && intent.getAction() != null) {
- action = intent.getAction();
- if (action.equals(ACTION_NLS_CONTROL)) {
- String command = intent.getStringExtra("command");
- if (TextUtils.equals(command, "cancel_last")) {
- if (mCurrentNotifications != null && mCurrentNotificationsCounts >= 1) {
- //每次删除通知最后一个
- StatusBarNotification sbnn = getCurrentNotifications()[mCurrentNotificationsCounts - 1];
- cancelNotification(sbnn.getPackageName(), sbnn.getTag(), sbnn.getId());
- }
- } else if (TextUtils.equals(command, "cancel_all")) {
- //删除所有通知
- cancelAllNotifications();
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- super.onCreate();
- logNLS("onCreate...");
- IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
- filter.addAction(ACTION_NLS_CONTROL);
- registerReceiver(mReceiver, filter);
- //在onCreate时第一次调用getActiveNotifications()
- mMonitorHandler.sendMessage(mMonitorHandler.obtainMessage(EVENT_UPDATE_CURRENT_NOS));
- }
- @Override
- public void onDestroy() {
- super.onDestroy();
- unregisterReceiver(mReceiver);
- }
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- // a.equals("b");
- logNLS("onBind...");
- return super.onBind(intent);
- }
- @Override
- public void onNotificationPosted(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- //当系统收到新的通知后,更新mCurrentNotifications列表
- updateCurrentNotifications();
- logNLS("onNotificationPosted...");
- logNLS("have " + mCurrentNotificationsCounts + " active notifications");
- mPostedNotification = sbn;
- //通过以下方式可以获取Notification的详细信息
- /*
- * Bundle extras = sbn.getNotification().extras; String
- * notificationTitle = extras.getString(Notification.EXTRA_TITLE);
- * Bitmap notificationLargeIcon = ((Bitmap)
- * extras.getParcelable(Notification.EXTRA_LARGE_ICON)); Bitmap
- * notificationSmallIcon = ((Bitmap)
- * extras.getParcelable(Notification.EXTRA_SMALL_ICON)); CharSequence
- * notificationText = extras.getCharSequence(Notification.EXTRA_TEXT);
- * CharSequence notificationSubText =
- * extras.getCharSequence(Notification.EXTRA_SUB_TEXT);
- * Log.i("SevenNLS", "notificationTitle:"+notificationTitle);
- * Log.i("SevenNLS", "notificationText:"+notificationText);
- * Log.i("SevenNLS", "notificationSubText:"+notificationSubText);
- * Log.i("SevenNLS",
- * "notificationLargeIcon is null:"+(notificationLargeIcon == null));
- * Log.i("SevenNLS",
- * "notificationSmallIcon is null:"+(notificationSmallIcon == null));
- */
- }
- @Override
- public void onNotificationRemoved(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- //当有通知被删除后,更新mCurrentNotifications列表
- updateCurrentNotifications();
- logNLS("removed...");
- logNLS("have " + mCurrentNotificationsCounts + " active notifications");
- mRemovedNotification = sbn;
- }
- private void updateCurrentNotifications() {
- try {
- StatusBarNotification[] activeNos = getActiveNotifications();
- if (mCurrentNotifications.size() == 0) {
- mCurrentNotifications.add(null);
- }
- mCurrentNotifications.set(0, activeNos);
- mCurrentNotificationsCounts = activeNos.length;
- } catch (Exception e) {
- logNLS("Should not be here!!");
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- //获取当前状态栏显示通知总数
- public static StatusBarNotification[] getCurrentNotifications() {
- if (mCurrentNotifications.size() == 0) {
- logNLS("mCurrentNotifications size is ZERO!!");
- return null;
- }
- return mCurrentNotifications.get(0);
- }
- private static void logNLS(Object object) {
- Log.i(TAG, TAG_PRE + object);
- }
- }
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- private static final String TAG = "SevenNLS";
- private static final String TAG_PRE = "["+MainActivity.class.getSimpleName()+"] ";
- private static final int EVENT_SHOW_CREATE_NOS = 0;
- private static final int EVENT_LIST_CURRENT_NOS = 1;
- private static final String ENABLED_NOTIFICATION_LISTENERS = "enabled_notification_listeners";
- private static final String ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS = "android.settings.ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS";
- private boolean isEnabledNLS = false;
- private TextView mTextView;
- private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
- @Override
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- switch (msg.what) {
- case EVENT_SHOW_CREATE_NOS:
- //显示创建的Notification对应的pkgName、Tag、Id
- showCreateNotification();
- break;
- case EVENT_LIST_CURRENT_NOS:
- //显示当前所有的Notification数量及其包名
- listCurrentNotification();
- break;
- default:
- break;
- }
- }
- };
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- mTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onResume() {
- super.onResume();
- //判断是否有开启Notification access
- isEnabledNLS = isEnabled();
- logNLS("isEnabledNLS = " + isEnabledNLS);
- if (!isEnabledNLS) {
- //如果没有开启则显示确认对话框
- showConfirmDialog();
- }
- }
- public void buttonOnClicked(View view) {
- mTextView.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
- switch (view.getId()) {
- case R.id.btnCreateNotify:
- logNLS("Create notifications...");
- //创建可清除的Notification
- createNotification(this);
- //显示当前状态栏中所有Notification数量及其包名
- mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(mHandler.obtainMessage(EVENT_SHOW_CREATE_NOS), 50);
- break;
- case R.id.btnClearLastNotify:
- logNLS("Clear Last notification...");
- //清除最后一个Notification
- clearLastNotification();
- //显示当前状态栏中所有Notification数量及其包名
- mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(mHandler.obtainMessage(EVENT_LIST_CURRENT_NOS), 50);
- break;
- case R.id.btnClearAllNotify:
- logNLS("Clear All notifications...");
- //清除所有"可被清除"的Notification
- clearAllNotifications();
- mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(mHandler.obtainMessage(EVENT_LIST_CURRENT_NOS), 50);
- break;
- case R.id.btnListNotify:
- logNLS("List notifications...");
- listCurrentNotification();
- break;
- case R.id.btnEnableUnEnableNotify:
- logNLS("Enable/UnEnable notification...");
- //打开Notification access启动/取消界面
- openNotificationAccess();
- break;
- default:
- break;
- }
- }
- //......省略
- }
4. NotificationListenerService使用过程中有哪些注意事项?
如果细心察看代码的童鞋,一定发现代码中有使用Handler,以及一些奇怪但又被注释掉的代码,比如"a.equals("b")"。从使用上来说,没有必要使用handler,那干嘛要多次一举?这里就给大家分享一下在写NotificationListenerDemo时遇到的一些坑。
①. NotificationMonitor的onCreate方法中使用handler来调用getActiveNotifications()方法
若直接在onCreate或者onBind方法中调用getActiveNotifications()方法是无法获取当前系统通知。主要是因为NotificationMonitor还未完成初始化,而根本原因则是INotificationListenerWrapper对象mWrapper还未初始化,此时使用getActiveNotifications()方法又会调用到mWrapper,因此无法返回正常数据。在NotificationListenerService中可以看到getActiveNotifications()的源码:
- public StatusBarNotification[] getActiveNotifications() {
- try {
- return getNotificationInterface().getActiveNotificationsFromListener(mWrapper);
- } catch (android.os.RemoteException ex) {
- Log.v(TAG, "Unable to contact notification manager", ex);
- }
- return null;
- }
②. 如果NotificationMonitor在onCreate或onBind方法中crash,则该service已经失效,需重启手机才能进行后续开发验证
如果在onCreate或者onBind方法中,出现异常导致NotificationMonitor发生crash,就算找到问题并将其改正,之后的验证还是无法继续进行的,也就是无法收到通知的新增和删除消息,onNotificationPosted和onNotificationRemoved方法不会被调用。
这也是我在onBind方法中故意注释导致空指针异常的代码,有兴趣的童鞋可以把注释去掉后尝试,去掉注释会导致NotificationListenerDemo异常停止,此时你再加上注释再次运行NotificationListenerDemo,虽然程序可以正常启动,但无法正常执行NotificationMonitor中的onNotificationPosted和onNotificationRemoved方法。这个涉及NotificationListenerService的原理,后面会另行分析。
③. MainActivity中onClick方法里使用handler操作
当点击删除通知时,系统通知相关状态还未更新,此时还没有回调到NotificationMonitor中,所以获取的数据就还是上一次的数据。为了能够获取到正确的Notification数据,可以使用handler并加上延时,这样再去获取Notification信息时,系统已经触发了NotificationMonitor回调,数据也有正常了。另外,50ms的延时几乎是感知不到的。
④. 为什么要使用ArrayList来保存StatusBarNotification数组对象
当新增或者删除通知时,会触发onNotificationPosted或onNotificationRemoved回调,在该方法中调用getActiveNotifications()方法用以获取当前系统通知信息。而getActiveNotifications()返回的是StatusBarNotification[]数组,因为这个数组是可变长的,也就是长度会随时变化,因此无法直接存储。使用ArrayList可以很好的解决这个问题,在ArrayList对象中添加一个StatusBarNotification[]对象,之后使用ArrayList.set(0,statusbar[])方法对数据进行更新即可。
总结
NotificationListenerService是Android 4.3 之后新增的接口服务,用于获取系统Notification信息,这在之前的Android版本是无法直接办到的。在Android 4.4中,增加了Notification.extra变量,使得获取Notification相关信息更加丰富,这些接口的开放更加利于三方应用的使用,但同时也会带来一些隐私问题。
本文针对NotificationListenerService的使用进行了详细分析,当然其中不乏有失偏颇的地方,本着互联网知识共享精神也将自己的一些记录发布出来,一来可做笔记,二来希望能够给苦苦寻觅的童鞋一些帮助。
概况
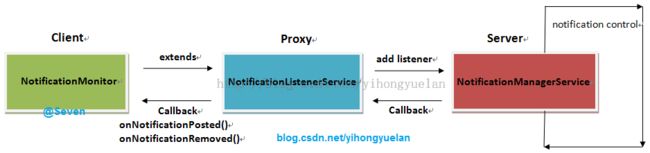
在上一篇文章《Android 4.4 KitKat NotificationManagerService使用详解与原理分析(一)__使用详解》中详细介绍了NotificationListenerService的使用方法,以及在使用过程中遇到的问题和规避方案。本文主要分析NotificationListenerService实现原理,以及详细分析在上一篇文章中提到的相关问题和产生的根本原因。在原理分析前,先看看NotificationListenerService涉及到的类以及基本作用,如图1所示:
图 1 NLS注册及回调过程
通过图1可以看到,整个通知状态获取分为三部分:
①. 监听器注册;新建一个类NotificationMonitor继承自NotificationListenerService。
②. 系统通知管理;系统通知管理由NotificationManagerService负责。
③. 通知状态回调;当系统通知状态改变之后,NotificationManagerService会通知NotificationListenerService,最后再由NotificationListenerService通知其所有子类。
在整个系统中,通知管理是由NotificationManagerService完成的,NotificationListenerService只是在通知改变时,会获得相应的通知消息,这些消息最终会回调到NotificationListenerService的所有子类中。
NotificationListenerService启动
NotificationListenerService虽然继承自Service,但系统中实际上启动的是其子类,为了表述方便,后文统一使用NotificationListenerService启动来指代。其子类的启动有三个途径,分别是:开机启动、接收PACKAGE相关广播(安装、卸载等)启动、SettingsProvider数据变更启动。
既然NotificationListenerService是一个service,那其子类启动方式自然就是bindService或者startService,在SourceCode/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/NotificationManagerService.java中可以找到,实际上NotificationListenerService的启动是通过bindServiceAsUser来实现的,而bindServiceAsUser与bindService作用一致。
开机启动
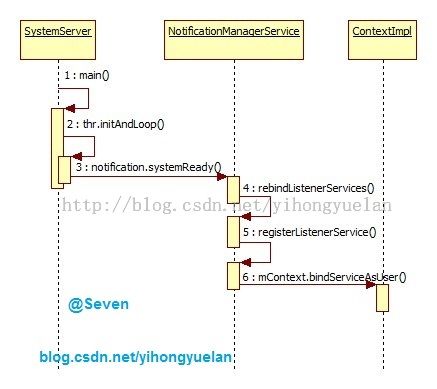
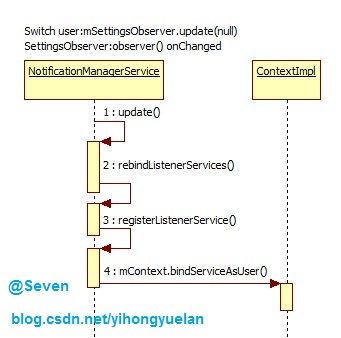
因为NotificationListenerService最终是在NotificationManagerService中启动的,因此当系统在开机第一次启动时,会进行NotificationManagerService初始化,之后会调用其SystemReady方法,继而调用rebindListenerServices以及registerListenerService(),最后使用bindServiceAsUser实现NotificationListenerService的启动。rebindListenerServices代码如下:
- void rebindListenerServices() {
- final int currentUser = ActivityManager.getCurrentUser();
- //获取系统中哪些应用开启了Notification access
- String flat = Settings.Secure.getStringForUser(
- mContext.getContentResolver(),
- Settings.Secure.ENABLED_NOTIFICATION_LISTENERS,
- currentUser);
- NotificationListenerInfo[] toRemove = new NotificationListenerInfo[mListeners.size()];
- final ArrayList<ComponentName> toAdd;
- synchronized (mNotificationList) {
- // unbind and remove all existing listeners
- toRemove = mListeners.toArray(toRemove);
- toAdd = new ArrayList<ComponentName>();
- final HashSet<ComponentName> newEnabled = new HashSet<ComponentName>();
- final HashSet<String> newPackages = new HashSet<String>();
- // decode the list of components
- if (flat != null) {
- String[] components = flat.split(ENABLED_NOTIFICATION_LISTENERS_SEPARATOR);
- for (int i=0; i<components.length; i++) {
- final ComponentName component
- = ComponentName.unflattenFromString(components[i]);
- if (component != null) {
- newEnabled.add(component);
- toAdd.add(component);
- newPackages.add(component.getPackageName());
- }
- }
- mEnabledListenersForCurrentUser = newEnabled;
- mEnabledListenerPackageNames = newPackages;
- }
- }
- //对所有NotificationListenerService全部unbindService操作
- for (NotificationListenerInfo info : toRemove) {
- final ComponentName component = info.component;
- final int oldUser = info.userid;
- Slog.v(TAG, "disabling notification listener for user " + oldUser + ": " + component);
- unregisterListenerService(component, info.userid);
- }
- //对所有NotificationListenerService进行bindService操作
- final int N = toAdd.size();
- for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
- final ComponentName component = toAdd.get(i);
- Slog.v(TAG, "enabling notification listener for user " + currentUser + ": "
- + component);
- registerListenerService(component, currentUser);
- }
- }
- private void registerListenerService(final ComponentName name, final int userid) {
- //... ...省略
- Intent intent = new Intent(NotificationListenerService.SERVICE_INTERFACE);
- intent.setComponent(name);
- intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_LABEL,
- R.string.notification_listener_binding_label);
- intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_INTENT, PendingIntent.getActivity(
- mContext, 0, new Intent(Settings.ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS), 0));
- try {
- if (DBG) Slog.v(TAG, "binding: " + intent);
- //使用bindService启动NotificationListenerService
- if (!mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent,
- new ServiceConnection() {
- INotificationListener mListener;
- @Override
- public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
- synchronized (mNotificationList) {
- mServicesBinding.remove(servicesBindingTag);
- try {
- mListener = INotificationListener.Stub.asInterface(service);
- NotificationListenerInfo info = new NotificationListenerInfo(
- mListener, name, userid, this);
- service.linkToDeath(info, 0);
- //service启动成功之后将相关信息添加到mListeners列表中,后续通过该列表触发回调
- mListeners.add(info);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- // already dead
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
- Slog.v(TAG, "notification listener connection lost: " + name);
- }
- },
- Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,
- new UserHandle(userid)))
- //... ...省略
- }
- }
图 2 NLS开机启动时序图
广播启动
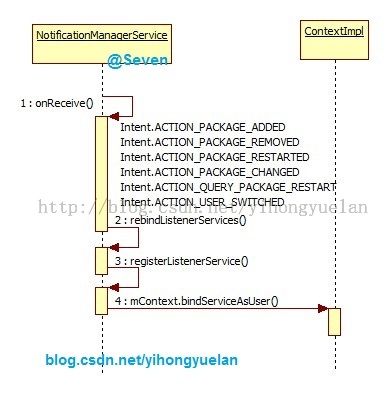
当系统安装或者卸载应用的时候,也会触发NotificationListenerService的启动。当一个使用NotificationListenerService的应用被卸载掉后,需要在Notification access界面清除相应的选项,或者当多用户切换时,也会更新NotificationListenerService的状态。在NotificationManagerService中监听了以下广播:
- Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED
- Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_REMOVED
- Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_RESTARTED
- Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_CHANGED
- Intent.ACTION_QUERY_PACKAGE_RESTART
- Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED
图 3 NLS广播启动
数据库变更启动
在NotificationManagerService中使用了ContentObserver监听SettingsProvider数据库变化,当Notification access有更新时,会更新NotificationListenerService的状态。例如,当用户进入Notification access界面,手动开启或关闭相关应用的Notification access权限时便会触发这种启动方式。当数据库中NotificationListenerService关联的信息改变后,会触发ContentObserver的onChange方法,继而调用update方法更新系统中NotificationListenerService的服务状态,最后调用到rebindListenerServices中。整个流程如下:
图 4 NLS数据库变更启动
NotificationListenerService启动小结
在系统中实际上运行的是NotificationListenerService的子类,这些子类的启动方式分为三种:开机启动时NotificationManagerService初始化回调;接收相关广播后执行;数据库变更后执行。这些启动方式归根到底还是bindService的操作。
NotificationListenerService调用流程
前面提到了NotificationListenerService的启动流程,当启动完成之后就是调用,整个调用流程分为两种情况,即:新增通知和删除通知。
新增通知
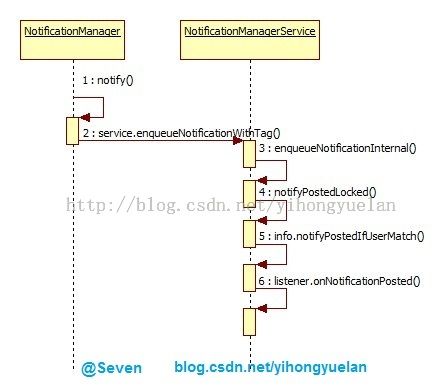
当系统收到新的通知消息时,会调用NotificationManager的notify方法用以发起系统通知,在notify方法中则调用关键方法enqueueNotificationWithTag:
- service.enqueueNotificationWithTag(......)
- private void notifyPostedLocked(NotificationRecord n) {
- final StatusBarNotification sbn = n.sbn.clone();
- //这里触发mListeners中所有的NotificationListenerInfo回调
- for (final NotificationListenerInfo info : mListeners) {
- mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- info.notifyPostedIfUserMatch(sbn);
- }});
- }
- }
- public void notifyPostedIfUserMatch(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- //... ...省略
- try {
- listener.onNotificationPosted(sbn);
- } catch (RemoteException ex) {
- Log.e(TAG, "unable to notify listener (posted): " + listener, ex);
- }
- }
上面的listener对象是NotificationListenerInfo类的全局变量,那是在哪里赋值的呢?还记得前面注册NotificationListenerService的时候bindServiceAsUser,其中new了一个ServiceConnection对象,并在其onServiceConnected方法中有如下代码:
- public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
- synchronized (mNotificationList) {
- mServicesBinding.remove(servicesBindingTag);
- try {
- //mListener就是NotificationListenerService子类的对象
- //service是INotificationListenerWrapper的对象,INotificationListenerWrapper
- //继承自INotificationListener.Stub,是NotificationListenerService的内部类
- mListener = INotificationListener.Stub.asInterface(service);
- //使用mListener对象生成对应的NotificationListenerInfo对象
- NotificationListenerInfo info = new NotificationListenerInfo(
- mListener, name, userid, this);
- service.linkToDeath(info, 0);
- mListeners.add(info);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- // already dead
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- if (mWrapper == null) {
- mWrapper = new INotificationListenerWrapper();
- }
- //这里返回的是INotificationListenerWrapper对象
- return mWrapper;
- }
- private class INotificationListenerWrapper extends INotificationListener.Stub {
- @Override
- public void onNotificationPosted(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- try {
- //onNotificationPosted是抽象方法之一
- NotificationListenerService.this.onNotificationPosted(sbn);
- } catch (Throwable t) {
- Log.w(TAG, "Error running onNotificationPosted", t);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void onNotificationRemoved(StatusBarNotification sbn) {
- try {
- //onNotificationRemoved是另一个抽象方法
- NotificationListenerService.this.onNotificationRemoved(sbn);
- } catch (Throwable t) {
- Log.w(TAG, "Error running onNotificationRemoved", t);
- }
- }
- }
通过以上代码可以知道,当在notifyPostedIfUserMatch执行listener.onNotificationPosted方法时,实际上会调用到NotificationListenerService.INotificationListenerWrapper的onNotificationPosted方法。
NotificationListenerService是一个Abstract类,其中的Abstract方法是onNotificationPosted和onNotificationRemoved。当触发NotificationListenerService.INotificationListenerWrapper的onNotificationPosted方法时,继续调用了NotificationListenerService.this.onNotificationPosted(sbn)。这样会继续调用所有NotificationListenerService子类中的onNotificationPosted方法,系统通知新增的消息便传到了所有NotificationListenerService中。
从整个流程来看,新增通知的发起点是NotificationManager,处理通知则是由NotificationManagerService完成,传输过程是通过NotificationListenerService,最后回调方法是各个继承自NotificationListenerService的子类。整个过程的调用时序图如下:
图 5 onNotificationPosted触发流程
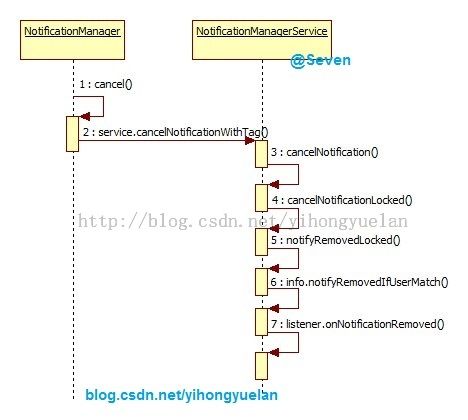
删除通知
与"新增通知"类似的流程是"删除通知",发起点在NotificationManager,之后经由NotificationManagerService处理和NotificationListenerService传递,最后到达各个继承自NotificationListenerService的子类中,只不过最后的处理方法变成了onNotificationRemoved。调用时序图下:
图 6 onNotificationRemoved触发流程
NotificationListenerService调用流程小结
简单来看,NotificationListenerService在系统通知的消息传递过程中,起到了代理的作用。继承自NotificationListenerService的类作为client端,真正的server端则是NotificationManagerService,由它负责整个Notification的控制与管理。NotificationManagerService将处理之后的结果通过NotificationListenerService返回给client端,最终各个client端通过onNotificationPosted和onNotificationRemoved方法拿到系统通知状态变更的相关信息。
NotificationListenerService重点分析
前文分析了整个NotificationListenerService的启动和调用,通过以上分析可以很清楚的了解NotificationListenerService的工作流程。在上一篇文章《Android 4.4 KitKat NotificationManagerService使用详解与原理分析(一)__使用详解》中,文末分析了在NotificationListenerService在使用过程中的遇到的一些问题,但并没有深究出现这些问题的根本原因,下文会对这些问题进行详细分析。
Notification access页面不存在
当手机上没有安装任何使用NotificationListenerService的应用时,系统默认不会显示"Notification access"选项。只有手机中安装了使用NotificationListenerService的应用,才可以在"Settings > Security > Notification access" 找到对应的设置页面。在SourceCode/packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/SecuritySettings.java中可以看到如下初始化代码:
- //... ...省略
- mNotificationAccess = findPreference(KEY_NOTIFICATION_ACCESS);
- if (mNotificationAccess != null) {
- final int total = NotificationAccessSettings.getListenersCount(mPM);
- if (total == 0) {
- if (deviceAdminCategory != null) {
- //如果系统中没有安装使用NLS的应用则删除显示
- deviceAdminCategory.removePreference(mNotificationAccess);
- }
- } else {
- //获取系统中有多少启动了Notification access的应用
- final int n = getNumEnabledNotificationListeners();
- //根据启用的数量显示不同的Summary
- if (n == 0) {
- mNotificationAccess.setSummary(getResources().getString(
- R.string.manage_notification_access_summary_zero));
- } else {
- mNotificationAccess.setSummary(String.format(getResources().getQuantityString(
- R.plurals.manage_notification_access_summary_nonzero,
- n, n)));
- }
- }
- }
- //... ...省略
getActiveNotifications()方法返回为null
有很多人在使用getActiveNotifications方法时返回为null,多数情况下是因为在onCreate或者在onBind中调用了getActiveNotifications方法。比如NotificaionMonitor extends NotificationListenerService:
- public class NotificationMonitor extends NotificationListenerService {
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- //getActiveNotifications();
- super.onCreate();
- }
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- getActiveNotifications();
- return super.onBind(intent);
- }
- }
找到NotificationListenerService中的getActiveNotifications方法实现,代码如下:
- public StatusBarNotification[] getActiveNotifications() {
- try {
- //getActiveNotifications成功执行的两个关键点:
- //1.getNotificationInterface方法返回正常
- //2.mWrapper对象不为null
- return getNotificationInterface().getActiveNotificationsFromListener(mWrapper);
- } catch (android.os.RemoteException ex) {
- Log.v(TAG, "Unable to contact notification manager", ex);
- }
- return null;
- }
- //通过查看可以知道,getNotificationInterface没有问题,如果为null会进行初始化
- private final INotificationManager getNotificationInterface() {
- if (mNoMan == null) {
- mNoMan = INotificationManager.Stub.asInterface(
- ServiceManager.getService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE));
- }
- return mNoMan;
- }
- //如果mWrapper为null则进行初始化
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- if (mWrapper == null) {
- mWrapper = new INotificationListenerWrapper();
- }
- return mWrapper;
- }
1. service的生命周期会先从onCraete->onBind逐步执行;
2. 此时调用getActiveNotifications方法会使用NotificationListenerService中的mWrapper对象;
3. mWrapper对象必须在NotificationMonitor完成super.onBind方法之后才会初始化;
综上所述,当在onCreate或者onBind方法中使用getActiveNotifications方法时,会导致mWrapper没有初始化,即mWrapper == null。解决方案可以在onCreate或者onBind方法中使用handler异步调用getActiveNotification方法,具体可参考《Android 4.4 KitKat NotificationManagerService使用详解与原理分析(一)__使用详解》。
NotificationListenerService失效
如果NotificationMonitor在onCreate或onBind方法中出现crash,则该NotificationMonitor已经失效。就算修改了NotificationMonitor的代码不会再crash,但NotificationMonitor还是不能收到onNotificationPosted和onNotificationRemoved回调,除非重启手机。
这个问题是google设计上的缺陷导致,出现NotificationListenerService失效的必要条件: 在NotificationMonitor的onCreate或者onBind中出现异常,导致service crash,也就是说service还没有完全启动的情况下出现了异常导致退出。
这里需要回到NotificationManagerService中,NotificationListenerService的注册方法registerListenerService中:
- private void registerListenerService(final ComponentName name, final int userid) {
- //servicesBindingTag可以理解为需要启动的service的标签
- final String servicesBindingTag = name.toString() + "/" + userid;
- //如果mServicesBinding中已经包含正在处理的service则直接return退出
- if (mServicesBinding.contains(servicesBindingTag)) {
- // stop registering this thing already! we're working on it
- return;
- }
- //将准备启动的service标签添加到mServicesBinding中
- mServicesBinding.add(servicesBindingTag);
- //... ...省略
- //使用bindServiceAsUser启动service
- Intent intent = new Intent(NotificationListenerService.SERVICE_INTERFACE);
- intent.setComponent(name);
- intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_LABEL,
- R.string.notification_listener_binding_label);
- intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_INTENT, PendingIntent.getActivity(
- mContext, 0, new Intent(Settings.ACTION_NOTIFICATION_LISTENER_SETTINGS), 0));
- try {
- if (DBG) Slog.v(TAG, "binding: " + intent);
- if (!mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent,
- new ServiceConnection() {
- INotificationListener mListener;
- @Override
- public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
- synchronized (mNotificationList) {
- //服务成功启动之后删除标签
- mServicesBinding.remove(servicesBindingTag);
- try {
- mListener = INotificationListener.Stub.asInterface(service);
- NotificationListenerInfo info = new NotificationListenerInfo(
- mListener, name, userid, this);
- service.linkToDeath(info, 0);
- mListeners.add(info);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- // already dead
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
- Slog.v(TAG, "notification listener connection lost: " + name);
- }
- },
- Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,
- new UserHandle(userid)))
- {
- //绑定服务失败后删除标签
- mServicesBinding.remove(servicesBindingTag);
- Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to bind listener service: " + intent);
- return;
- }
- } catch (SecurityException ex) {
- Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to bind listener service: " + intent, ex);
- return;
- }
- }
- }
当调用registerListenerService方法时,使用了一个mServicesBinding的ArrayList<String>用来记录当前正在启动的服务。在启动之前会判断当前service是否在mServicesBinding之中,如果是则表明正在执行bindServiceAsUser操作,直接退出,否则就继续执行bindServiceAsUser流程。调用bindServiceAsUser之前会在mServicesBinding中会添加标签,当连接成功之后也就是onServiceConnected返回后,以及绑定失败后会在mServicesBinding中删除标签。
google这样设计的目的可能是为了避免同一个service多次启动,因此在执行bindServiceAsUser之前就打上标签,当处理完成之后(onServiceConnected回调)就删掉这个标签,表明这个service 绑定完成。但是,如果执行bindServiceAsUser之后,NotificationMonitor在onCreate或者onBind的时候crash了,也就是NotificationMonitor还没有完成启动,因此就不会去调用onServiceConnected方法,并最终导致不会调用 mServicesBinding.remove(servicesBindingTag)方法,从而使得NotificationMonitor的标签被一致记录在mServicesBinding中。那么当下一次想再次注册该服务的时候,系统发现该服务已经在mServicesBinding中了,所以直接return,后面的bindServiceAsUser就不会被调用了。
虽然代码已经更新,但service无法正常启动,那么onNotificationPosted和onNotificationRemoved的回调自然就无法使用,此时的解决办法就只能重启手机,清空mServicesBinding的值。
总结
NotificationListenerService在系统通知获取的流程中,自身并没有启动,而是起到了一个代理的作用,每一个继承自NotificationListenerService的类,当系统通知变化后最终都会收到onNotificationPosted和onNotificationRemoved的回调。
bindService方法的返回与service是否成功启动无关,因此才会导致NotificationListenerService失效。
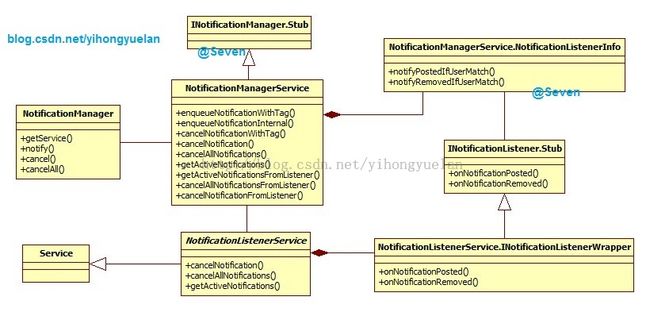
最后再看一下整个NotificationListenerService的关系类图:
图 7 NLS关系类图