学习OpenCV——Kalman滤波
背景:
卡尔曼滤波是一种高效率的递归滤波器(自回归滤波器), 它能够从一系列的不完全及包含噪声的测量中,估计动态系统的状态。卡尔曼滤波的一个典型实例是从一组有限的,包含噪声的,对物体位置的观察序列(可能有偏差)预测出物体的位置的坐标及速度。
这种滤波方法以它的发明者鲁道夫.E.卡尔曼(Rudolph E. Kalman)命名,但是根据文献可知实际上Peter Swerling在更早之前就提出了一种类似的算法。
斯坦利.施密特(Stanley Schmidt)首次实现了卡尔曼滤波器。卡尔曼在NASA埃姆斯研究中心访问时,发现他的方法对于解决阿波罗计划的轨道预测很有用,后来阿波罗飞船的导航电脑便使用了这种滤波器。 关于这种滤波器的论文由Swerling (1958)、Kalman (1960)与 Kalman and Bucy (1961)发表。
目前,卡尔曼滤波已经有很多不同的实现.卡尔曼最初提出的形式现在一般称为简单卡尔曼滤波器。除此以外,还有施密特扩展滤波器、信息滤波器以及很多Bierman, Thornton 开发的平方根滤波器的变种。也许最常见的卡尔曼滤波器是锁相环,它在收音机、计算机和几乎任何视频或通讯设备中广泛存在。
模型:
基本动态系统模型:
卡尔曼滤波建立在线性代数和隐马尔可夫模型(hidden Markov model)上。其基本动态系统可以用一个马尔可夫链表示,该马尔可夫链建立在一个被高斯噪声(即正态分布的噪声)干扰的线性算子上的。系统的状态可以用一个元素为实数的向量表示。 随着离散时间的每一个增加,这个线性算子就会作用在当前状态上,产生一个新的状态,并也会带入一些噪声,同时系统的一些已知的控制器的控制信息也会被加入。同时,另一个受噪声干扰的线性算子产生出这些隐含状态的可见输出。
模型图:
为了从一系列有噪声的观察数据中用卡尔曼滤波器估计出被观察过程的内部状态,我们必须把这个过程在卡尔曼滤波的框架下建立模型。也就是说对于每一步k,定义矩阵
例如:KalmanFilter KF(stateNum, measureNum, 0);
Fk : KF.transitionMatrix
Hk : KF.measurementMatrix
Qk : KF.processNoiseCov
Rk : KF.measurementNoiseCov
Pk : KF.errorCovPost
有时也需要定义Bk : KF.ontrolMatrix
如下。
尔曼滤波模型假设k时刻的真实状态是从(k − 1)时刻的状态演化而来,符合下式:
其中
- Fk 是作用在xk−1上的状态变换模型(/矩阵/矢量)。
- Bk 是作用在控制器向量uk上的输入-控制模型。
- wk 是过程噪声,并假定其符合均值为零,协方差矩阵为Qk的多元正态分布。
时刻k,对真实状态 xk的一个测量zk满足下式:
其中Hk是观测模型,它把真实状态空间映射成观测空间,vk 是观测噪声,其均值为零,协方差矩阵为Rk,且服从正态分布。
初始状态以及每一时刻的噪声{x0, w1, ..., wk, v1 ...vk} 都认为是互相独立的.
卡尔曼滤波器:
卡尔曼滤波是一种递归的估计,即只要获知上一时刻状态的估计值以及当前状态的观测值就可以计算出当前状态的估计值,因此不需要记录观测或者估计的历史信息。卡尔曼滤波器与大多数滤波器不同之处,在于它是一种纯粹的时域滤波器,它不需要像低通滤波器等频域滤波器那样,需要在频域设计再转换到时域实现。
卡尔曼滤波器的状态由以下两个变量表示:
- ,在时刻k 的状态的估计;
- ,误差相关矩阵,度量估计值的精确程度。
卡尔曼滤波器的操作包括两个阶段:预测与更新。在预测阶段,滤波器使用上一状态的估计,做出对当前状态的估计。在更新阶段,滤波器利用对当前状态的观测值优化在预测阶段获得的预测值,以获得一个更精确的新估计值。
预测 predict: Mat prediction = KF.predict();
- (预测状态)
- (预测估计协方差矩阵)
可参考:http://www.cs.unc.edu/~welch/media/pdf/kalman_intro.pdf
更新 updata: KF.correct(measurement);
- (测量余量,measurement residual)
- (测量余量协方差)
- (最优卡尔曼增益)
- (更新的状态估计)
- (更新的协方差估计)
使用上述公式计算仅在最优卡尔曼增益的时候有效。使用其他增益的话,公式要复杂一些,请参见推导。
不变量(Invariant)
如果模型准确,而且与 的值准确的反映了最初状态的分布,那么以下不变量就保持不变:所有估计的误差均值为零
且 协方差矩阵 准确的反映了估计的协方差:
请注意,其中表示的期望值,。
代码:
class Kalman:
class CV_EXPORTS_W KalmanFilter
{
public:
//! the default constructor
CV_WRAP KalmanFilter();
//! the full constructor taking the dimensionality of the state, of the measurement and of the control vector
CV_WRAP KalmanFilter(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams=0, int type=CV_32F);
//! re-initializes Kalman filter. The previous content is destroyed.
void init(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams=0, int type=CV_32F);
//! computes predicted state
CV_WRAP const Mat& predict(const Mat& control=Mat());
//! updates the predicted state from the measurement
CV_WRAP const Mat& correct(const Mat& measurement);
Mat statePre; //!< predicted state (x'(k)): x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
Mat statePost; //!< corrected state (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
Mat transitionMatrix; //!< state transition matrix (A)
Mat controlMatrix; //!< control matrix (B) (not used if there is no control)
Mat measurementMatrix; //!< measurement matrix (H)
Mat processNoiseCov; //!< process noise covariance matrix (Q)
Mat measurementNoiseCov;//!< measurement noise covariance matrix (R)
Mat errorCovPre; //!< priori error estimate covariance matrix (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)*/
Mat gain; //!< Kalman gain matrix (K(k)): K(k)=P'(k)*Ht*inv(H*P'(k)*Ht+R)
Mat errorCovPost; //!< posteriori error estimate covariance matrix (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
// temporary matrices
Mat temp1;
Mat temp2;
Mat temp3;
Mat temp4;
Mat temp5;
};
sample\kalman.cpp
1个1维点的运动跟踪,虽然这个点是在2维平面中运动,但由于它是在一个圆弧上运动,只有一个自由度,角度,所以还是1维的。还是一个匀速运动,建立匀速运动模型,设定状态变量x = [ x1, x2 ] = [ 角度,角速度 ]
#include "opencv2/video/tracking.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
static inline Point calcPoint(Point2f center, double R, double angle)
{
return center + Point2f((float)cos(angle), (float)-sin(angle))*(float)R;
}
void help()
{
printf( "\nExamle of c calls to OpenCV's Kalman filter.\n"
" Tracking of rotating point.\n"
" Rotation speed is constant.\n"
" Both state and measurements vectors are 1D (a point angle),\n"
" Measurement is the real point angle + gaussian noise.\n"
" The real and the estimated points are connected with yellow line segment,\n"
" the real and the measured points are connected with red line segment.\n"
" (if Kalman filter works correctly,\n"
" the yellow segment should be shorter than the red one).\n"
"\n"
" Pressing any key (except ESC) will reset the tracking with a different speed.\n"
" Pressing ESC will stop the program.\n"
);
}
int main(int, char**)
{
help();
Mat img(500, 500, CV_8UC3);
KalmanFilter KF(2, 1, 0);
Mat state(2, 1, CV_32F); /* (phi, delta_phi) */
Mat processNoise(2, 1, CV_32F);
Mat measurement = Mat::zeros(1, 1, CV_32F);
char code = (char)-1;
for(;;)
{
randn( state, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(0.1) );//随机生成一个矩阵,期望是0,标准差为0.1;
KF.transitionMatrix = *(Mat_<float>(2, 2) << 1, 1, 0, 1);//元素导入矩阵,按行;
//setIdentity: 缩放的单位对角矩阵;
//!< measurement matrix (H) 观测模型
setIdentity(KF.measurementMatrix);
//!< process noise covariance matrix (Q)
// wk 是过程噪声,并假定其符合均值为零,协方差矩阵为Qk(Q)的多元正态分布;
setIdentity(KF.processNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-5));
//!< measurement noise covariance matrix (R)
//vk 是观测噪声,其均值为零,协方差矩阵为Rk,且服从正态分布;
setIdentity(KF.measurementNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-1));
//!< priori error estimate covariance matrix (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)*/ A代表F: transitionMatrix
//预测估计协方差矩阵;
setIdentity(KF.errorCovPost, Scalar::all(1));
//!< corrected state (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
randn(KF.statePost, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(0.1));
for(;;)
{
Point2f center(img.cols*0.5f, img.rows*0.5f);
float R = img.cols/3.f;
double stateAngle = state.at<float>(0);
Point statePt = calcPoint(center, R, stateAngle);
Mat prediction = KF.predict();
double predictAngle = prediction.at<float>(0);
Point predictPt = calcPoint(center, R, predictAngle);
randn( measurement, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(KF.measurementNoiseCov.at<float>(0)));
// generate measurement
measurement += KF.measurementMatrix*state;
double measAngle = measurement.at<float>(0);
Point measPt = calcPoint(center, R, measAngle);
// plot points
#define drawCross( center, color, d ) \
line( img, Point( center.x - d, center.y - d ), \
Point( center.x + d, center.y + d ), color, 1, CV_AA, 0); \
line( img, Point( center.x + d, center.y - d ), \
Point( center.x - d, center.y + d ), color, 1, CV_AA, 0 )
img = Scalar::all(0);
drawCross( statePt, Scalar(255,255,255), 3 );
drawCross( measPt, Scalar(0,0,255), 3 );
drawCross( predictPt, Scalar(0,255,0), 3 );
//line( img, statePt, measPt, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, CV_AA, 0 );
//line( img, statePt, predictPt, Scalar(0,255,255), 3, CV_AA, 0 );
KF.correct(measurement);
randn( processNoise, Scalar(0), Scalar::all(sqrt(KF.processNoiseCov.at<float>(0, 0))));
state = KF.transitionMatrix*state + processNoise;
imshow( "Kalman", img );
code = (char)waitKey(100);
if( code > 0 )
break;
}
if( code == 27 || code == 'q' || code == 'Q' )
break;
}
return 0;
}

鼠标跟踪(详解):
1.初始化状态:
onst int stateNum=4;//状态数,包括(x,y,dx,dy)坐标及速度(每次移动的距离)
const int measureNum=2;//观测量,能看到的是坐标值,当然也可以自己计算速度,但没必要
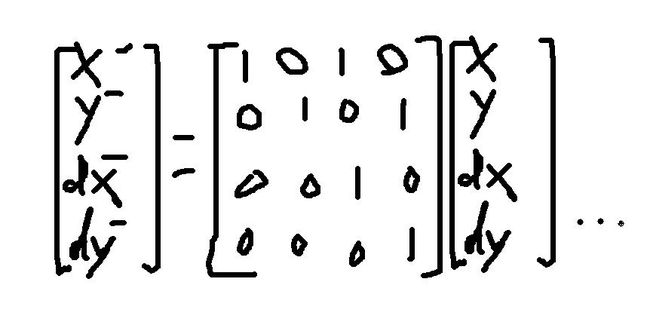
转移矩阵或者说增益矩阵的值好像有点莫名其妙
看下图就清楚了
X1=X+dx,依次类推
所以这个矩阵还是很容易却确定的,可以根据自己的实际情况定制转移矩阵
同样的方法,三维坐标的转移矩阵可以如下
float A[stateNum][stateNum] ={//transition matrix 1,0,0,1,0,0, 0,1,0,0,1,0, 0,0,1,0,0,1, 0,0,0,1,0,0, 0,0,0,0,1,0, 0,0,0,0,0,1 };
当然并不一定得是1和0
KalmanFilter KF(stateNum, measureNum, 0);
//KalmanFilter::KalmanFilter(intdynamParams, intmeasureParams, int controlParams=0, inttype=CV_32F)
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Mat state (stateNum, 1, CV_32FC1); // state(x,y,detaX,detaY)
Mat processNoise(stateNum, 1, CV_32F); // processNoise(x,y,detaX,detaY)
Mat measurement = Mat::zeros(measureNum, 1, CV_32F); //measurement(x,y)
需定义的参数矩阵:
Fk : KF.transitionMatrix
KF.transitionMatrix = *(Mat_<float>(2, 2) << 1, 0, 1, 0......);
Hk : KF.measurementMatrix:
setIdentity(KF.measurementMatrix);
Qk : KF.processNoiseCov
setIdentity(KF.processNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-5));
Rk : KF.measurementNoiseCov
setIdentity(KF.measurementNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-1));
Pk : KF.errorCovPost
setIdentity(KF.errorCovPost, Scalar::all(1));
注意:其中: KF.transitionMatrix :
(1,0,1,0,
0,1,0,1,
0,0,1,0,
0,0,0,1 );
2.预测predict,读出预测的位置
3.更新updata
3.1.更新观测矩阵:updata/generate measurement
- 对于鼠标跟踪:直接使用鼠标的实际位置更新,真实位置即为观测位置
- 对于自动更新:
randn( measurement, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(KF.measurementNoiseCov.at<float>(0))); // generate measurement measurement += KF.measurementMatrix*state;
3.2.更新KF:KF.correct(measurement);
分别显示前一状态的位置:Point statePt = Point( (int)KF.statePost.at<float>(0), (int)KF.statePost.at<float>(1));;
预测位置:Point predictPt = Point( (int)prediction.at<float>(0), (int)prediction.at<float>(1));
观测位置(真实位置):mousePosition(由setMouseCallback("Kalman", mouseEvent);得到,递归方式通过measurement计算得到)
#include <opencv/cv.h>
#include <opencv/highgui.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
const int winWidth = 800;
const int winHeight = 600;
Point mousePosition = Point(winWidth>>1, winHeight>>1);
//mouse call back
void mouseEvent(int event, int x, int y, int flags, void *param)
{
if(event==CV_EVENT_MOUSEMOVE)
{
mousePosition=Point(x,y);
}
}
int main()
{
//1.kalman filter setup
const int stateNum=4;
const int measureNum=2;
KalmanFilter KF(stateNum, measureNum, 0);
Mat state (stateNum, 1, CV_32FC1); //state(x,y,detaX,detaY)
Mat processNoise(stateNum, 1, CV_32F);
Mat measurement = Mat::zeros(measureNum, 1, CV_32F); //measurement(x,y)
randn( state, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(0.1) ); //随机生成一个矩阵,期望是0,标准差为0.1;
KF.transitionMatrix = *(Mat_<float>(4, 4) <<
1,0,1,0,
0,1,0,1,
0,0,1,0,
0,0,0,1 );//元素导入矩阵,按行;
//setIdentity: 缩放的单位对角矩阵;
//!< measurement matrix (H) 观测模型
setIdentity(KF.measurementMatrix);
//!< process noise covariance matrix (Q)
// wk 是过程噪声,并假定其符合均值为零,协方差矩阵为Qk(Q)的多元正态分布;
setIdentity(KF.processNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-5));
//!< measurement noise covariance matrix (R)
//vk 是观测噪声,其均值为零,协方差矩阵为Rk,且服从正态分布;
setIdentity(KF.measurementNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-1));
//!< priori error estimate covariance matrix (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)*/ A代表F: transitionMatrix
//预测估计协方差矩阵;
setIdentity(KF.errorCovPost, Scalar::all(1));
//!< corrected state (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
//initialize post state of kalman filter at random
randn(KF.statePost, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(0.1));
Mat showImg(winWidth, winHeight,CV_8UC3);
for(;;)
{
setMouseCallback("Kalman", mouseEvent);
showImg.setTo(0);
Point statePt = Point( (int)KF.statePost.at<float>(0), (int)KF.statePost.at<float>(1));
//2.kalman prediction
Mat prediction = KF.predict();
Point predictPt = Point( (int)prediction.at<float>(0), (int)prediction.at<float>(1));
//3.update measurement
measurement.at<float>(0)= (float)mousePosition.x;
measurement.at<float>(1) = (float)mousePosition.y;
//4.update
KF.correct(measurement);
//randn( processNoise, Scalar(0), Scalar::all(sqrt(KF.processNoiseCov.at<float>(0, 0))));
//state = KF.transitionMatrix*state + processNoise;
//draw
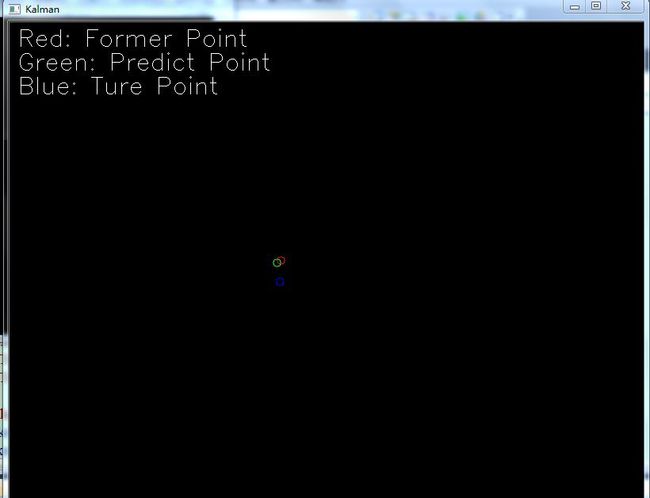
circle(showImg, statePt, 5, CV_RGB(255,0,0),1);//former point
circle(showImg, predictPt, 5, CV_RGB(0,255,0),1);//predict point
circle(showImg, mousePosition, 5, CV_RGB(0,0,255),1);//ture point
// CvFont font;//字体
// cvInitFont(&font, CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0, 1, 8);
putText(showImg, "Red: Former Point", cvPoint(10,30), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1 ,Scalar :: all(255));
putText(showImg, "Green: Predict Point", cvPoint(10,60), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1 ,Scalar :: all(255));
putText(showImg, "Blue: Ture Point", cvPoint(10,90), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1 ,Scalar :: all(255));
imshow( "Kalman", showImg );
int key = waitKey(3);
if (key == 27)
{
break;
}
}
}
主要资料:
1.维基百科:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kalman_filter(英文)
中文:http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%8D%A1%E5%B0%94%E6%9B%BC%E6%BB%A4%E6%B3%A2#.E5.8D.A1.E5.B0.94.E6.9B.BC.E6.BB.A4.E6.B3.A2.E5.99.A8
2.OpenCV文档:http://docs.opencv.org/modules/video/doc/motion_analysis_and_object_tracking.html?highlight=kalman#kalmanfilter
3.博客园kalman详解blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/feisky/archive/2009/12/04/1617287.html
4.CSDN kalman.cpp讲解yangxian:http://blog.csdn.net/yang_xian521/article/details/7050398
5.CSDN 鼠标跟踪:http://blog.csdn.net/onezeros/article/details/6318944
6.模型论文:http://www.cs.unc.edu/~welch/media/pdf/kalman_intro.pdf