Heap & Priority Queue
Heap & Priority Queue
Definition & Description:
In computer science/data structures, a priority queue is an abstract data type which is like a regular queue or stack data structure, but where additionally each element has a "priority" associated with it. In a priority queue, an element with high priority is served before an element with low priority. If two elements have the same priority, they are served according to their order in the queue
Similarly, in a multiuser environment, the operating system scheduler must decide which of several processes to run. Generally a process is only allowed to run for a fixed period of time. One algorithm uses a
queue. Jobs are initially placed at the end of the queue. The scheduler will repeatedly take the first job on the queue, run it until either it finishes or its time limit is up, and place it at the end of the queue if it does not finish. This strategy is generally not appropriate, because very short jobs will seem to take a long time because of the wait involved to run. Generally, it is important that short jobs finish as fast as possible, so these jobs should have preference over jobs that have already been running. Furthermore, some jobs that are not short are still very important and should also have preference.
This particular application seems to require a special kind of queue, known as a priority queue .
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
update: 2014.09.20 (补充对heap进行解释说明)
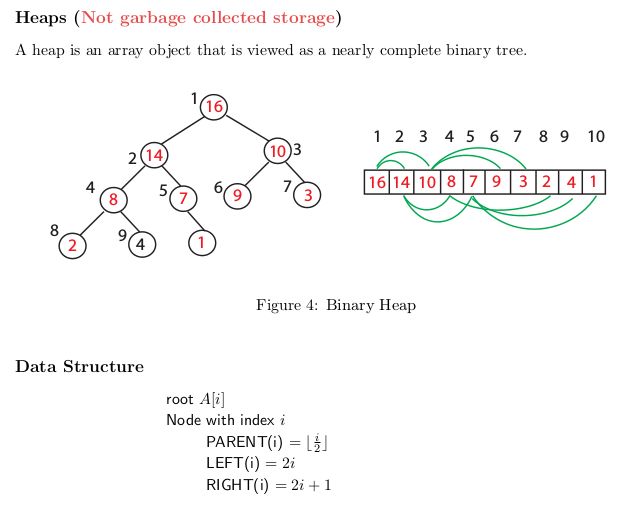
下面图示是一个最大堆.
Implementation:
Let's have a peak about what files we need to finish this work.
priority_queue.h
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : priority_queue.h e-mail : [email protected] code purpose : Just a header file for my implementation. What you should know is that you may call init_heap() when you want to create a priority queue. And then you could use build_heap() to create that queue with your source--@array. *********************************************************/ #ifndef _PRIORITY_QUEUE_H #define _PRIORITY_QUEUE_H #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define EMPTY_HEAP -1 #define NOEMPTY_HEAP 0 #define FULL_HEAP 1 #define NOFULL_HEAP 0 struct heap { int capacity; int size; /* ** ATTENTION! Just a little trick. */ int element[0]; }; struct heap* init_heap(int max_size); void destroy_heap(struct heap* p_heap); void insert_heap(struct heap* p_heap,int element); int delete_heap(struct heap* p_heap); void build_heap(struct heap* p_heap,int* array,int size); void precolate_down(struct heap* p_heap,int parent); int is_empty(struct heap* p_heap); int is_full(struct heap* p_heap); void print_heap(struct heap* p_heap); #endif
build_heap.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : build_heap.c e-mail : [email protected] code purpose : @p_heap : A pointer which point to our heap. @array : A pointer which point to our input-data which we want to fill heap with it. @size : The size of our array. *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" void build_heap(struct heap* p_heap,int* array,int size) { if(!p_heap || !array) { printf("In function: %s() p_heap: %p array: %p\n",__FUNCTION__,p_heap,array); return ; } p_heap->size = size; int index = 0; int tmp = 0; int foo = 0; int min = 0; int parent = 0; int right_child = 0; int left_child = 0; for(index = 0; index < size ;index++) { p_heap->element[index+1] = array[index]; } for(parent = size/2; parent > 0; parent--) { precolate_down(p_heap,parent); } }
delete_heap.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : delete_heap.c e-mail : [email protected] *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" int delete_heap(struct heap* p_heap) { if(!p_heap) { printf("malloc failed in function %s()!\n",__FUNCTION__); return -1; } /* ** You have to know that heap data get start from ** element[1] which is just for simplicty to implement ** heap in array. */ int min_element = p_heap->element[1]; int last_element = p_heap->element[p_heap->size--]; int me = 0; int child = 0; for(me = 1;me*2 < p_heap->size; me = child) { child = me*2; /* ** Make sure that child index into the smaller one ** between the right child and the left child. */ if(child != p_heap->size && p_heap->element[child+1] < p_heap->element[child]) { child++; } if(last_element > p_heap->element[child]) { p_heap->element[me] = p_heap->element[child]; } else { break; } } p_heap->element[me] = last_element; return min_element; }
destroy_heap.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : destroy_heap.c e-mail : [email protected] code description: **NEVER** forget to call this function to free out memory which p_heap point to. *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" void destroy_heap(struct heap* p_heap) { if(!p_heap) { printf("malloc failed in function %s()!\n",__FUNCTION__); return ; } free(p_heap); }
init_heap.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : init_heap.c e-mail : [email protected] code purpose : @max_size : what's the size of the heap that you want to create it ? This function would return a pointer which point to the heap that you created. *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" struct heap* init_heap(int max_size) { if(max_size < 0) { return NULL; } struct heap* p_heap = NULL; p_heap = (struct heap*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(max_size+1) + sizeof(struct heap)); if(!p_heap) { printf("malloc failed in function %s()!\n",__FUNCTION__); return NULL; } p_heap->capacity = max_size; p_heap->size = 0; return p_heap; }
insert_heap.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : insert_heap.c e-mail : [email protected] code purpose : Just call this function and insert @element into heap that @p_heap point to. *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" void insert_heap(struct heap* p_heap,int element) { if(!p_heap) { printf("p_heap is NULL in function %s\n",__FUNCTION__); return ; } int child = 0; /* ** Percolate up */ for(child = ++p_heap->size; p_heap->element[child/2] > element; child/=2) { p_heap->element[child] = p_heap->element[child/2]; } p_heap->element[child] = element; }
is_empty.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : is_empty.c e-mail : [email protected] *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" int is_empty(struct heap* p_heap) { if(!p_heap) { printf("p_heap is NULL in function %s()\n",__FUNCTION__); return -1; } if(!p_heap->size) { return EMPTY_HEAP; } return NOEMPTY_HEAP; }
is_full.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : is_full.c e-mail : [email protected] *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" int is_full(struct heap* p_heap) { if(!p_heap) { printf("p_heap is NULL in function %s()\n",__FUNCTION__); return -1; } if(p_heap->size >= p_heap->capacity) { return FULL_HEAP; } return NOFULL_HEAP; }
precolate_down.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : precolate_down.c e-mail : [email protected] code purpose : This is a implementation of precolate_down() which use recursion. *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" void precolate_down(struct heap* p_heap,int parent) { /* ** If we got the last parent, precolate_down() end. */ if(2*parent > p_heap->size) { return; } int tmp = 0; int foo = 0; int min = 0; int right_child = 0; int left_child = 0; tmp = p_heap->element[parent]; foo = p_heap->element[parent]; left_child = p_heap->element[2*parent]; /* ** If we got the last parent and the size of ** heap is even. This means that the child of the ** last parent is just only one.Here is the method ** to process this situation. */ if(p_heap->size %2 == 0 && 2*parent == p_heap->size) { if(foo > min) { tmp = p_heap->element[parent]; p_heap->element[parent] = p_heap->element[2*parent]; p_heap->element[2*parent] = tmp; } return ; } /* ** If parent have two child. */ right_child = p_heap->element[2*parent+1]; min = left_child < right_child ? left_child : right_child; if(foo > min) { if(right_child > left_child) { tmp = p_heap->element[parent]; p_heap->element[parent] = p_heap->element[2*parent]; p_heap->element[2*parent] = tmp; precolate_down(p_heap,2*parent); } else { tmp = p_heap->element[parent]; p_heap->element[parent] = p_heap->element[2*parent+1]; p_heap->element[2*parent+1] = tmp; precolate_down(p_heap,2*parent+1); } } }
print_heap.c
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : print_heap.c e-mail : [email protected] code description: Just print out the current heap that @p_heap point to. *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" void print_heap(struct heap* p_heap) { if(!p_heap) { printf("You passed NULL in function %s()\n",__FUNCTION__); return ; } printf("The capacity of heap : %d\n",p_heap->capacity); printf("The size of heap:%d\n",p_heap->size); int index = 0; int tmp = 1; for(index = 0,tmp = 2;index < p_heap->size;index++) { printf("%d ",p_heap->element[index+1]); if(index == 0) { printf("\n"); } else if(index == tmp) { tmp += 1<<tmp; printf("\n"); } } printf("\n"); }
测试用程序:
priority_queue_test.c
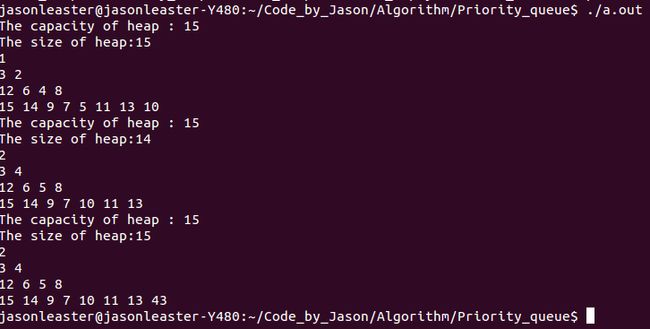
/********************************************************* code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.19 code file : priority_queue_test.c e-mail : [email protected] code description: This code would help us to test our implementation of heap. *********************************************************/ #include "priority_queue.h" int main() { int array[] = {10,12,1,14,6,5,8,15,3,9,7,4,11,13,2}; int size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]); struct heap* p_heap = NULL; p_heap = init_heap(size); if(!p_heap) { printf("Inintialize failed!\n"); return 0; } build_heap(p_heap,array,size); print_heap(p_heap); delete_heap(p_heap); print_heap(p_heap); insert_heap(p_heap,43); print_heap(p_heap); destroy_heap(p_heap); return 0; }
测试结果:
update :2015.01.12
使用Python实现Heap
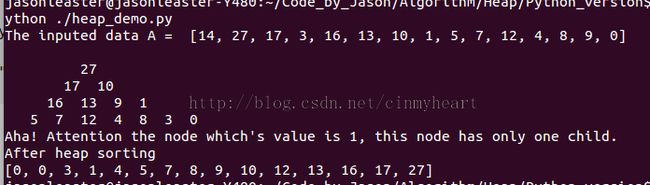
"""************************************************** Code writer : EOF Code date : 2015.01.10 Code file : heap_demo.py e-mail : [email protected] Code purpose: There is a implementation of ADT-Heap which is in Python. If you find something error with my code, please touch me by e-mail. Thank you. *****************************************************""" import sys """ These function are used for searching the index of parent, left child and right child """ def parent(i): return i/2 def left(i): return i*2 def right(i): return (i*2 + 1) """ We store the size of heap as the first element of Heap. """ def heap_size(A) : return A[0] def init_input(A) : size = len(A) A = [size] + A return A def max_heapify(A, i) : l = left(i) r = right(i) if l < heap_size(A) and A[l] > A[i] : largest = l else : largest = i if r < heap_size(A) and A[r] > A[largest] : largest = r if largest != i : tmp = A[i] A[i] = A[largest] A[largest] = tmp max_heapify(A,largest) return A def build_max_heap(A) : hs = heap_size(A) for i in range(hs/2,0,-1) : A = max_heapify(A,i) return A def show_heap(A) : depth = 0 depth_up_bound = 0 tmp = heap_size(A) while tmp > 0: depth_up_bound += 1 tmp >>= 1 for i in range(1,heap_size(A)+1) : if i == (1<<depth) : blank = depth_up_bound - depth sys.stdout.write('\n' + 2*(blank)*' ') depth += 1 sys.stdout.write(" %s " % A[i]) print "" def heap_sort(A) : for i in range(len(A)-1,0,-1) : tmp = A[1] A[1] = A[i] A[i] = tmp """ heap size minus 1, Attention that we store the value of the heap size into the A[0] """ A[0] -= 1 max_heapify(A,1) return A #----up this line is implementation of funcs. Below this is testing code--- A = [27,17,3,16,13,10,1,5,7,12,4,8,9,0] A = init_input(A) print "The inputed data A = ", A Sorted_A = build_max_heap(A) show_heap(Sorted_A) print "Aha! Attention the node which's value is 1," + \ " this node has only one child." print "After heap sorting" print heap_sort(A)