STL之priority_queue
一、概述
priority_queue,首先它是一个queue,即只允许在低端加入元素,并从顶端取出元素,除此之外别无其他存取元素的途径(故priority_queue不提供遍历功能,也不提供迭代器);再次它具有priority,即queue中的元素具有一定的priority:其内的元素自动依照元素的权值排列,权值最高者(也就是数值最高),排在最前面。
注:在queue并非是依照严格的权值递减的顺序排列,而是每次保持顶端(对头)元素为queue中权值最高的元素(其内部采用heap来实现(默认是max heap))。
二、实现
由于priority_queue完全以底部容器为根据,在加上heap处理规则,所以其实现较简单,且缺省情况下以vector为底部容器。
联系适配器(adapter)的定义:具有这种【修改某物接口,形成另一种风貌】之性质者,称为adapter。因为,STL priority_queue被归类为:container adapter 。
其SGI(Silicon Graphics Computer Systems, Inc.) STL中的priority_queue的源码如下:
template<class T, class Sequeue = vector<T>, class Compare = less<typename Sequeue::value_type> >
class priority_queue
{
public:
typedef typename Sequeue::value_type value_type;
typedef typename Sequeue::size_type size_type;
typedef typename Sequeue::reference reference;
typedef typename Sequeue::const_reference const_reference;
protected:
Sequeue c; //底层容器
Compare comp; //元素大小比较标准
public:
priority_queue(): c() { }
explicit priority_queue(const Compare& x) : c(), comp(x) {}
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const Compare& x)
:c(first, last), comp(x){make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) //使用默认的comp比较标准
:c(first, last){make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
bool empty() const {return c.empty(); }
size_type size() const {return c.size(); }
const_reference top() const {return c.front(); }
void push(const value_type& x)
{
__STL_TRY
{
c.push_back(x); //先加入容器(vector)
push_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); //再利用heap对容器排序
}
__STL_UNWIND(c.clear());
}
void pop()
{
———STL_TRY
{
pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); //先退出heap(排序)
c.pop_back(); //再从容器中删除
}
__STL_UNWIND(c.clear());
}
};
注:
class Compare = less<typename Sequeue::value_type>中的less对应大顶堆,即用parent与holeIndex值比较,若小于则percolate up:调整洞号,向上提升值父节点。---见《STL源码剖析》P175。
三、测试实例
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class myComparison
{
bool reverse;
public:
myComparison(const bool& revParam = false)
{
reverse = revParam;
}
bool operator()(const int& lhs, const int& rhs) const
{
if(reverse)
return (lhs > rhs);
else
return (lhs < rhs);
}
};
int main()
{
int myInts[] = {10, 60, 50 ,20};
priority_queue<int> first;
priority_queue<int> second(myInts, myInts+4);
cout << "second size: " << second.size() << endl;
cout << "second top: " << second.top() << endl;
second.push(100);
cout << "second top: " << second.top() << endl;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > third(myInts, myInts+4);
cout << "third size: " << third.size() << endl;
cout << "third top: " << third.top() << endl;
third.push(100);
cout << "third top: " << third.top() << endl;
//using myComparison
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, myComparison > fourth;
typedef priority_queue<int, vector<int>, myComparison> myPq_type;
myPq_type fifth(myComparison() );
myPq_type sixth(myInts, myInts+4, myComparison(true) );
cout << "sixth top: " << sixth.top() << endl;
sixth.pop();
cout << "sixth top: " << sixth.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
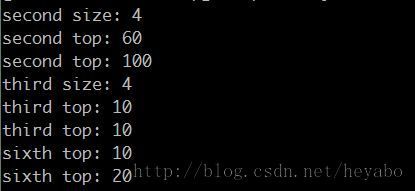
输出结果:
References
<<STL 源码剖析>>
class tmplate std::priority_queue