实现Android下的FPS实时显示工具
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ariesjzj/article/details/10428435
FPS是图形性能的主要指标之一,Android中的一些应用有显示FPS的功能,如Bsplayer,Skype,Antutu等,但绝大多数应用并不提供显示FPS的功能。而且应用提供的往往是应用本身的刷新率,并不等于最终用户所看到的刷新率,因为屏幕上往往不止一个应用参与显示。我们知道Android中每个应用都会绘制自己的Surface,完了都丢给Surfaceflinger,Surfaceflinger统一对它们进行composition,然后swap framebuffer输出到屏幕。前文介绍了Android中的so注入和hook技巧(http://blog.csdn.net/ariesjzj/article/details/9900105),示例了如何动态hook系统中的Surfaceflinger中的eglSwapBuffers函数。那么很自然的,我们就可以通过它来计算当前的FPS,并实时显示在屏幕上。
ARM下有FPS实时显示工具-FPS meter,不过要收费。本文中我们自己做一个功能类似的免费工具,而且x86和ARM平台通用。整个应用分为几个部分,首先是用于so注入的native程序和要注入的动态链接库。这部分是前文(http://blog.csdn.net/ariesjzj/article/details/9900105)中主要涉及的内容,不再累述。基本思想是在要注入的so中定义自己的eglSwapBuffers函数,然后在初始化时将之替换got表中老的eglSwapBuffers函数地址。这样,当Surfaceflinger需要刷新屏幕时,就会先调用我们定义的eglSwapBuffers函数,在这个函数被调用时,它会记录和统计调用次数,并写入一个专用的pipe文件,然后调用系统自己的eglSwapBuffers。在应用端我们需要以下几个部分:一个Activity用于显示界面与用户交互,一个Service用于主要工作,即从pipe读取FPS信息并且实时显示在屏幕上,最后是一个native的程序,用于在service启动时完成so的注入。
大体流程如下:
Activity启动时根据平台ABI将相应版本的用于注入的native程序和要注入的so拷贝到应用私有目录:
File file_inject = new File(APP_PATH + "inject");
File file_lib = new File(APP_PATH + "libfpsshow.so");
if (!file_inject.exists() || !file_lib.exists()) {
String sysabi = getSystemProp("ro.product.cpu.abi");
Log.e(TAG, "System ABI is: " + sysabi + "\n");
if (sysabi.startsWith("armeabi")) {
copyFile("inject_arm", APP_PATH + "inject");
copyFile("libfpsshow_arm.so", APP_PATH + "libfpsshow.so");
} else if (sysabi.startsWith("x86")) {
copyFile("inject", APP_PATH + "inject");
copyFile("libfpsshow.so", APP_PATH + "libfpsshow.so");
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "ABI not supported\n");
Toast.makeText(this, "ABI not supported", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "Already copied\n");
}然后等待用户启动service:
case R.id.buttonStart: Log.d(TAG, "starting service"); startService(new Intent(this, FPSService.class)); break; case R.id.buttonStop: Log.d(TAG, "stopping service"); stopService(new Intent(this, FPSService.class)); break;Service启动时的onCreate()函数,做一坨初始化工作,包括创建pipe,显示悬浮文字,执行注入等:
// Create the pipe file for receiving data
createPipe();
// Create floating textview to display FPS
createLayout();
// Inject and hook
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("chmod 775 " + APP_PATH + "inject");
list.add("chmod 666 " + APP_PATH + "pipe");
list.add("chmod 775 " + APP_PATH + "libfpsshow.so");
list.add(APP_PATH + "inject");
// Execute as root
if (execute(list)) {
Log.e(TAG, "OK\n");
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "Execute abnormally, please make sure it's rooted.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.e(TAG, "Error\n");
this.stopSelf();
}其中的执行注入和hook程序是要root权限的,所以要通过:
public final boolean execute(ArrayList<String> commands) {
...
Process suProcess = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("su");
DataOutputStream os = new DataOutputStream(suProcess.getOutputStream());
for (String currCommand : commands) {
os.writeBytes(currCommand + "\n");
os.flush();
}
os.writeBytes("exit\n");
os.flush();
int suProcessRetval = suProcess.waitFor();
...
}加悬浮文字,其实就是加个Layout:
windowManager = (WindowManager) getApplicationContext().getSystemService("window");
layoutParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
layoutParams.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT;
layoutParams.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE | WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
layoutParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
layoutParams.gravity = Gravity.TOP | Gravity.CENTER;
layoutParams.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
layoutParams.height = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
layoutParams.x = 0;
layoutParams.y = 0;
// myLayout is the customized layout which contains textview
myLayout = new MyLayout(this);
windowManager.addView(myLayout, layoutParams);
Service启动时onStartCommand()会被调用,其中会启动线程:
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.v(TAG, "onStartCommand");
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Started", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
handleCommand(intent);
myhandler.postDelayed(myTasks, 1000);
return Service.START_STICKY;
}
线程每一秒执行一次run()函数,该函数从pipe读Surfaceflinger传来的FPS,然后显示在屏幕上。
private Runnable myTasks = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int fps = readFps();
Log.e(TAG, "Service FPS = " + fps + "\n");
myLayout.setFPS(fps);
// Do other customized computation.
...
myLayout.setFPSAvg(fps_avg);
myhandler.postDelayed(myTasks, 1000);
}
};
实现的时候还有些细节需要考虑,比如当启动多个应用后,后台非关键Service会被Android杀掉。为了解决这个问题,可以仿照Android官方例子中ApiDemo中的ForegroundService例子将Service设为前台进程,这样就不容易被杀了。另外在屏幕显示FPS的话,如果一秒更新一次,那显示FPS本身也会影响FPS(尽管只有一帧),如果觉得有影响可以把它关掉,让FPS只输出到log。
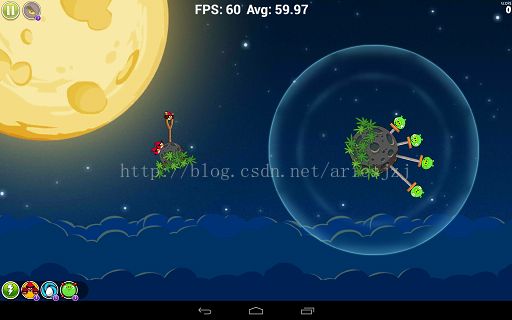
效果截图: