struts2中的jar文件说明
struts2-codebehind-plugin.jar
1.用途:使struts2配置文件更简单。
2.下载:附件
3.如何使用:直接放在lib下。
4.如何修改struts.xml:
使用前:
- <package name="xxn" extends="struts-default" >
- <action name="user" class="test">
- <result name="input">/user-input.jsp</result>
- <result name="list">/user-list.jsp</result>
- <result name="show">/user-show.jsp</result>
- <result name="register">/user-register.jsp</result>
- </action>
- </package>
<package name="xxn" extends="struts-default" > <action name="user" class="test"> <result name="input">/user-input.jsp</result> <result name="list">/user-list.jsp</result> <result name="show">/user-show.jsp</result> <result name="register">/user-register.jsp</result> </action> </package>
使用后:
- <package name="xxn" extends="struts-default" >
- <action name="user" class="test">
- <result type="redirect-action">user</result>
- </action>
- </package>
<package name="xxn" extends="struts-default" > <action name="user" class="test"> <result type="redirect-action">user</result> </action> </package>
5.说明:使用这个插件后,你只要配置<result type="redirect-action">user</result>,他就会自动的跳转到相应的页面。对应方式是:例如http://localhost/test/user!input.action ,则自动跳转到user-input.jsp,也就是说程序自动跳转到action名-方法名.jsp
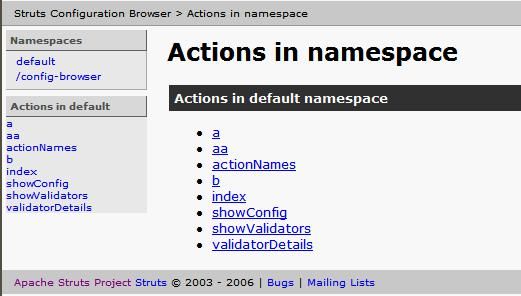
Config Browser Plugin
Config Browser Plugin — Struts2运行期间可通过此插件查看Struts2的配置情况。
又是一个很不错的插件哦,使用方法也很简单.
在你下载的struts\lib目录下应该可以找到该插件struts2-config-browser-plugin
然后把该jar复制到你的工程目录下:WEB-INF/lib下
然后,启动你的项目
输入:http://localhost:8008/你的发布工程名/config-browser/index.action
OK,就这么简单,然后你就可以看到如下的统计:
struts2-convention-plugin
零配置并不是没有配置,而是通过约定大于配置的方式,大量通过约定来调度页面的跳转而使得配置大大减少。所以,首先应该了解下convention-plugin的约定:
1. 默认所有的结果页面都存储在WEB-INF/content下,你可以通过设置struts.convention.result.path这个属性的值来改变到其他路径。如:
1. <constant name="struts.convention.result.path" value="/WEB-INF/page" />
则将路径配置到了WEB-INF/page 下。
2. 默认包路径包含action,actions,struts,struts2的所有包都会被struts作为含有Action类的路径来搜索。你可以通过设置struts.convention.package.locators属性来修改这个配置。如:
<constant name="struts.convention.package.locators" value="web,action" />
则定义了在项目中,包路径包含web和action的将被视为Action存在的路径来进行搜索。
Com.ustb.web.*/com.ustb.action.*都将被视为含有Action的包路径而被搜索。
3. 接着,Convention从前一步找到的package以及其子package中寻找 com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action 的实现以及以Action结尾的类:
1. com.example.actions.MainAction
2. com.example.actions.products.Display (implements com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action)
3. com.example.struts.company.details.ShowCompanyDetailsAction
4. 命名空间。从定义的.package.locators标示开始到包结束的部分,就是命名空间。举个例子:
Com.ustb.web.user.userAction的命名空间是:”/user”。Com.ustb.web.user.detail.UserAction的命名空间是:”/user/detail”
5. Convention通过如下规则确定URL的具体资源部分:去掉类名的Action部分。然后将将每个分部的首字母转为小写,用’-’分割,你可以设置struts.convention.action.name.separator 如:
<constant name="struts.convention.action.name.separator" value="-" />
还是举个例子:
UserAction->user UserDetailAction ->user-detail。结合上面的。对于com.ustb.web.user.detail.UserDetailAction,映射的 url就是/WEB-INF/content/user/detail/user-detail.jsp
6. struts支持.jsp .html .htm .vm格式的文件。
下面是actiong和结果模版的映射关系:
URL Result
File that could match Result Type
/hello success /WEB-INF/content/hello.jsp Dispatcher
/hello success /WEB-INF/content/hello-success.htm Dispatcher
/hello success /WEB-INF/content/hello.ftl FreeMarker
/hello-world input /WEB-INF/content/hello-world-input.vm Velocity
/test1/test2/hello error /WEB-INF/content/test/test2/hello-error.html Dispatcher
以上的内容来自struts2的文档http://struts.apache.org/2.1.6/docs/convention-plugin.html
当然,简单的通过默认的方式来进行配置不能完全满足实际项目的需要。所幸,convention的零配置是非常灵活的。
通过@Action注释
对如下例子:
1. package com.example.web;
2.
3. import com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action;
4. import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
5.
6. public class HelloAction extends ActionSupport {
7. @Action("action1")
8. public String method1() {
9. return SUCCESS;
10. }
11.
12. @Action("/user/action2")
13. public String method2() {
14. return SUCCESS;
15. }
16. }
方法名 默认调用路径 默认映射路径
method1 /hello!method1.action . /WEB-INF/content/hello.jsp
method2 /hello!method2.action. /WEB-INF/content/hello.jsp
通过@Action注释后
方法名 @Action注释后调用路径 @Action注释 后映射路径
method1 /action1!method1.action. /WEB-INF/content/action1.jsp
method1 /user/action2!method2.action /WEB-INF/content/user/action2.jsp
通过@Actions注释
1. package com.example.web;
2.
3. import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
4. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Action;
5. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Actions;
6.
7. public class HelloAction extends ActionSupport {
8. @Actions({
9. @Action("/different/url"),
10. @Action("/another/url")
11. })
12. public String method1() {
13. return “error”;
14. }
我们可以通过:/different/url!method1.action 或 /another/url!method1.action 来调用method1 方法。
对应的映射路径分别是/WEB-INF/content/different/url-error.jsp; /WEB-INF/content/another/url-error.jsp
可能误导了大家,一个方法被@Action注释后,只是多了一种调用方式,而不是说覆盖了原来的调用方式。比如对于如下例子:
1. package com.example.web;
2.
3. import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
4. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Action;
5. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Actions;
6.
7. public class HelloAction extends ActionSupport {
8. @Action("/another/url")
9. public String method1() {
10. return “error”;
11. }
我们调用method1方法可以通过两种方式:
1 /hello!method1.action 映射 url:/WEB-INF/content/hello-error.jsp
2 /another/url!method1.action 映射 url:/WEB-INF/content/another/url-error.jsp
可见,两种方式均可对method1方法进行调用,唯一的区别就是,两种调用的映射是不一样的,所以,想跳转到不同的界面,这是一个非常好的选择。
通过@Namespace 注释
1. package com.example.web;
2.
3. import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
4. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Action;
5. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Actions;
6. @Namespace("/other")
7. public class HelloWorld extends ActionSupport {
8.
9. public String method1() {
10. return “error”;
11. }
12. @Action("url")
13. public String method2() {
14. return “error”;
15. }
16.
17. @Action("/different/url")
18. public String method3() {
19. return “error”;
20. }
21. }
通过 /other/hello-world!method1.action 访问method1 方法。
通过 /other/url!method2.action 访问method2 方法
通过 /different /url!method3.action 访问method3 方法
与@Action 注释不同的是,该注释覆盖了默认的namespace(这里是’/’),此时再用hello!method1.action 已经不能访问method1 了.
@Results和@Result
1 全局的(global)。
全局results可以被action类中所有的action分享,这种results在action类上使用注解进行声明。
1. package com.example.actions;
2.
3. import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
4. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Action;
5. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Actions;
6. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Result;
7. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Results;
8.
9. @Results({
10. @Result(name="failure", location="/WEB-INF/fail.jsp")
11. })
12. public class HelloWorld extends ActionSupport {
13. public String method1() {
14. return “failure”;
15. }
16. @Action("/different/url")
17. public String method2() {
18. return “failure”;
19. }
20.
21. }
当我们访问 /hello -world !method1.action 时,返回 /WEB-INF/fail.jsp
当我们访问 /hello -world !method2.action 时,返回 /WEB-INF/fail.jsp
当我们访问 /different/url!method2.action 时,返回 /WEB-INF/fail.jsp
2 本地的(local)。
本地results只能在action方法上进行声明。
1. package com.example.actions;
2.
3. import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
4. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Action;
5. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Actions;
6. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Result;
7. import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Results;
8.
9. public class HelloWorld extends ActionSupport {
10. @Action(value="/other/bar",results={@Result(name = "error", location = "http://www.baidu.com%22,type=%22redirect/")})
11. public String method1() {
12. return “error”;
13. }
14. }
当我们调用 /hello -world !method1.action 时,返回 /WEB-INF/content/hello-error.jsp
当我们调用 /other/bar!method1.action 时,返回 http://www.baidu.com/
struts2-embeddedjsp-plugin
通常JSP页面来自于文件系统。利用这个插件,你可以将jsp页面部署到jar包中。当你写一个插件时,很可能希望这样。
struts2-gxp-plugin
Google XML Pages
- 支持多种语言(包括Java&JavaScript; C++开发中)。
- 支持运行期重新编译。
- 编译时类型检查和部分标记验证。
- 类型自动识别,减少了XSS漏洞的机会
- 易于使用的国际化支持
- 方便的参数传递/模块化系统
- 非常轻量的运行系统