CUDA系列学习(四)Parallel Task类型 与 Memory Allocation
本文为CUDA系列学习第四讲,首先介绍了Parallel communication patterns的几种形式(map, gather, scatter, stencil, transpose), 然后复习了cuda memory model并从high level上分析怎样写出高效代码,最后学习了流程控制(control flow)以及其中一个重要部分——原子操作。参考资料:udacity cs344.
(一). Parallel communication Patterns
在上一章CUDA系列学习(二)CUDA memory & variables中我们介绍了memory和variable的不同类型,本章中根据不同的memory映射方式,我们将task分为以下几种类型:Map, Gather, Scatter, Stencil, transpose.
1.1 Map, Gather, Scatter
- Map: one input - one output
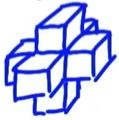
- Gather: several input - one output
e.g image blur by average - Scatter: one input - several output
e.g add a value to its neighbors
(因为每个thread 将结果scatter到各个memory,所以叫scatter)
图为Map, Gather & Scatter示意图:
1.2 Stencil, Transpose
stencil: 对input中的每一个位置,
stencil input:该点的neighborhood
stencil output:该点value
e.g image blur by average
这样也可以看出,stencil和gather很像,其实stencil是gather的一种,只不过stencil要求input必须是neighborhood而且对input的每一个元素都要操作
图示:transpose
input:matrix M
output: M^T
图示:
Exercise
Q:
看这个quiz图,给每个蓝线画着的句子标注map/gather/scatter/stencil/transpose:

A:四个位置分别选AECB。
这里我最后一个选错成B&D, 为什么不选D呢?看stencil的定义:如果是average,也应该对每一个位置都要进行average,而题目中有if(i%2)这个condition。
那么对于不同的Parallel communication Patterns需要关注哪些点呢?
1. threads怎样高效访问memory?- 怎样重用数据?
2. threads怎样相互交互部分结果?(通过sharing memory)这样安全吗?
我们将在下一节中首先回顾讲过的memory model,然后结合具体问题分析阐述how to program。
(二). Programming model and Memroy model
第一讲和第三讲中我们讲过SM与grid, block, thead的关系:各个grid, block的thread组织(gridDim,blockDim,grid shape, block shape)可以不同,分别用于执行不同kernel。
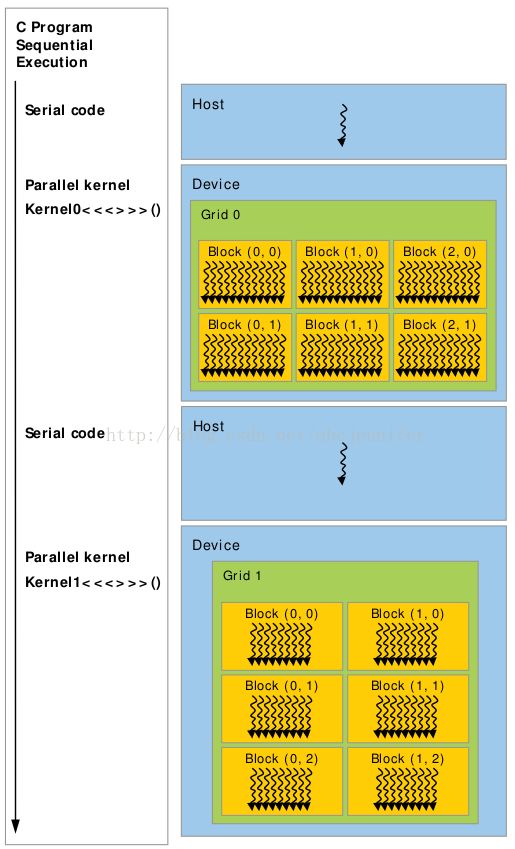
如我们第一章所讲,不同GPU有不同数量的硬件SM(streaming Multiprocessors),GPU负责将这些block分配到SMs,所有SM独立,并行地跑。
2.1 Memory model
第二讲中我们讲了memroy的几种形式,这里我们先来回顾一下memory model.
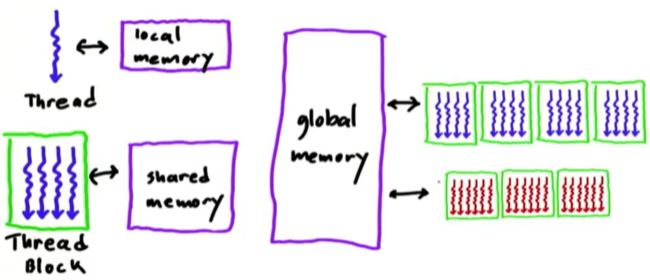
每个thread都可以访问:
1. 该thread独占的local memory
2. block内threads共享的shared memory
3. GPU中所有threads(包括不同SM的所有threads)共享的global memory
下面复习一下,做两个quiz。
Ans:选择A,B,D
解读:根据定义,一个block只能run在一个SM;SM中不同blocks的threads不能cooperate
Ans: 都不选~~~
解读:block执行时间及顺序不可控;block分配到哪个SM是GPU做的事情,并非programmer能指定的;
2.2 Memory in Program
How to write Efficient Programs from high level
maximize arithmetic intensity
arithmetic intensity = calculation/memory
即要maximize calculation per thread 并 minimize memory per thread(其实目的是minimize memory access的时间)
方法:经常访问的数据放在可快速访问的memory(GPU中不同memory在硬件层的介绍参考第二章),对于刚才讲的local, shared and global memory的访问速度, 有
local > shared >> global >> CPU memory
所以,比如我想经常访问一个global memory,那可以在kernel中先将该global memory variable赋值给一个shared memory variable, 然后频繁访问那个shared memory variable.minimize memory access stride
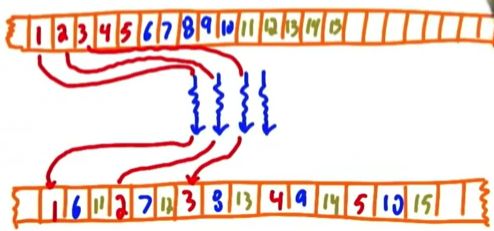
如coalesce memory access图所示:

如果GPU的threads访问相邻memory,我们称为coalesced,如果threads间访问memory有固定步长(蹦着走),我们称stripped,完全没规律的memory访问称为random。访问速度,有
coalesced > strided > randomavoid thread divergence
这个我们在前两讲中有过相应说明。
Exercise:
给下面这段代码中5,6,7,8行的几句话执行速度排序(1最快,4最慢):
1 __global__ void f(float* x, float* y, float* z){
2 float s,t,u;
3 __shared__ float a,b,c;
4 ...
5 s = *x;
6 t = s;
7 a = b;
8 *y = *z;
9 }Ans: 5,6,7,8行执行速度为:3,1,2,4。
下面一节我们来看具体programming问题中的流程控制与同步。
(三). Control flow and synchronisation
3.1 program 运行顺序
在讲流程控制之前我们首先看一个例子,用来测试不同block的运行顺序。
Demo code:
#include <stdio.h>
#define Num_block 16
#define Num_thread 1
__global__ void print(){
printf(“Num: %d\n”,blockIdx.x);
}
int main(){
//launch the kernel
print<<<Num_block, Num_thread>>>();
cudaDeviceSynchronize();// what is the function of this sentence? - force the printf()s to flush, 不然运行时显示不出来
return 0;
}编译命令:
nvcc -arch=sm_21 -I ~/NVIDIA_GPU_Computing_SDK/C/common/inc print.cu
运行两次结果:
可见程序执行每一次的结果都不同,也就是不同block之间的执行顺序是不可控的,正如刚才quiz的ans。那么如果我们希望同步各个threads呢?
3.2 同步机制
第二章中我们在一个例子中引入并使用了同步函数syncthreads(), 即设置一个barrier,使所有threads运行到同步函数的时候stop and wait, 直到所有threads运行到此处,那么问题来了。
Exercise:
考虑一个程序,将每个位置i的元素移到i-1的位置,需要多少个syncthreads()?
e.g kernel中声明如下:
…
int idx = threadIdx.x;
__shared__ int array[128];
array[idx] = idx;
if (idx<127){
array[idx + 1] = array[idx];
}
…Ans: 3个~
…
int idx = threadIdx.x;
__shared__ int array[128];
array[idx] = idx;
__syncthreads(); //如果不加将导致array还没赋值就被操作
if (idx<127){
int tmp = array[idx];
__syncthreads();//如不加导致先读后写,数据相关
array[idx] = tmp;
__syncthreads(); //如不加不能确保下面的程序访问到正确数据
}
…
Quiz: 看下面这个程序会不会出现collision,哪里会出现collision?
1__global__ void f(){
2 __shared__ int s[1024];
3 int i = threadIdx.x;
4 __syncthreads();
5 s[i] = s[i-1];
6 __syncthreads();
7 if(i%2) s[i] = s[i-1];
8 __syncthreads();
9 s[i] = (s[i-1]+s[i+1])/2;
10 printf(“%d\n”,s[i]);
11 }Ans: Collision在
1. 第5行,如上题,应为int tmp = s[i-1]; __syncthread(); s[i] = tmp;
2. 第9行,同理
PS: 第7行是没问题的,模拟一下就知道
3.3 Atomic Memory Operation
这一节中我们将要接触到原子操作。
首先考虑一个问题:用1000000个threads给一个长为10个元素的array做加法,希望每个thread加100000,这个代码大家先写写看,很简单,依照我们之前的方法有下面的code:
注:这里的gputimer.h请去我的资源页面自行下载。
#include <stdio.h>
#include "gputimer.h"
using namespace Gadgetron;
#define NUM_THREADS 1000000
#define ARRAY_SIZE 10
#define BLOCK_WIDTH 1000
void print_array(int *array, int size)
{
printf("{ ");
for (int i = 0; i<size; i++) { printf("%d ", array[i]); }
printf("}\n");
}
__global__ void increment_naive(int *g)
{
// which thread is this?
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// each thread to increment consecutive elements, wrapping at ARRAY_SIZE
i = i % ARRAY_SIZE;
g[i] = g[i] + 1;
}
__global__ void increment_atomic(int *g)
{
// which thread is this?
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// each thread to increment consecutive elements, wrapping at ARRAY_SIZE
i = i % ARRAY_SIZE;
atomicAdd(&g[i], 1);
}
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
GPUTimer timer;
printf("%d total threads in %d blocks writing into %d array elements\n",
NUM_THREADS, NUM_THREADS / BLOCK_WIDTH, ARRAY_SIZE);
// declare and allocate host memory
int h_array[ARRAY_SIZE];
const int ARRAY_BYTES = ARRAY_SIZE * sizeof(int);
// declare, allocate, and zero out GPU memory
int * d_array;
cudaMalloc((void **) &d_array, ARRAY_BYTES);
cudaMemset((void *) d_array, 0, ARRAY_BYTES);
// launch the kernel - comment out one of these
timer.start();
//increment_atomic<<<NUM_THREADS/BLOCK_WIDTH, BLOCK_WIDTH>>>(d_array);
increment_naive<<<NUM_THREADS/BLOCK_WIDTH, BLOCK_WIDTH>>>(d_array);
timer.stop();
// copy back the array of sums from GPU and print
cudaMemcpy(h_array, d_array, ARRAY_BYTES, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
print_array(h_array, ARRAY_SIZE);
// free GPU memory allocation and exit
cudaFree(d_array);
return 0;
}
可见结果里每个元素都是648/647,不符合预期100000。这是为什么呢?
看我们的kernel部分代码,每次执行g[i] = g[i] + 1, 一个read-modify-write操作,这样会导致许多线程读到g[i]的value,然后慢的线程将快的线程写结果覆盖掉了。如何解决呢?我们引入原子操作(atomic operation), 更改上面的kernel部分为:
__global__ void increment_atomic(int *g)
{
// which thread is this?
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// each thread to increment consecutive elements, wrapping at ARRAY_SIZE
i = i % ARRAY_SIZE;
atomicAdd(&g[i], 1);
}可见,结果正确。那么原子操作atomicAdd用了怎样的机制呢?——原子操作用了GPU built-in的特殊硬件,用以保证原子操作(同一时刻只能有一个thread做read-modify-write操作)
这里来看一下原子操作的limitations:
1. only certain operations, data type(功能有限)
2. still no ordering constraints(还是无序执行)
3. serializes access to memory(所以慢)
(四). 总结
本节课介绍了以下内容:
communication patterns
- map
- gather
- scatter
- stencil
- transpose
gpu hardware & programming model
- SMs, threads, blocks ordering
- synchronization
- Memory model - local, global, shared memory
efficient GPU programming
- coalesced memory access
- faster memory for common used variable
OK~ 第三课就结束了,过两天我把exercise上上来~ 敬请关注~.~