FFmpeg源代码简单分析:avformat_write_header()
=====================================================
FFmpeg的库函数源代码分析文章列表:
【架构图】
FFmpeg源代码结构图 - 解码
FFmpeg源代码结构图 - 编码
【通用】
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:av_register_all()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avcodec_register_all()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:内存的分配和释放(av_malloc()、av_free()等)
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:常见结构体的初始化和销毁(AVFormatContext,AVFrame等)
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avio_open2()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:av_find_decoder()和av_find_encoder()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avcodec_open2()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avcodec_close()
【解码】
图解FFMPEG打开媒体的函数avformat_open_input
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avformat_open_input()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avformat_find_stream_info()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:av_read_frame()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avcodec_decode_video2()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avformat_close_input()
【编码】
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avformat_alloc_output_context2()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avformat_write_header()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:avcodec_encode_video()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:av_write_frame()
FFmpeg 源代码简单分析:av_write_trailer()
【其它】
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:日志输出系统(av_log()等)
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:结构体成员管理系统-AVClass
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:结构体成员管理系统-AVOption
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:libswscale的sws_getContext()
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:libswscale的sws_scale()
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:libavdevice的avdevice_register_all()
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:libavdevice的gdigrab
【脚本】
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:makefile
FFmpeg源代码简单分析:configure
【H.264】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:概述
=====================================================
打算写两篇文章简单分析FFmpeg的写文件用到的3个函数:avformat_write_header(),av_write_frame()以及av_write_trailer()。其中av_write_frame()用于写视频数据,avformat_write_header()用于写视频文件头,而av_write_trailer()用于写视频文件尾。
本文首先分析avformat_write_header()。PS:
需要注意的是,尽管这3个函数功能是配套的,但是它们的前缀却不一样,写文件头Header的函数前缀是“avformat_”,其他两个函数前缀是“av_”(不太明白其中的原因)。
avformat_write_header()的声明位于libavformat\avformat.h,如下所示。
/** * Allocate the stream private data and write the stream header to * an output media file. * * @param s Media file handle, must be allocated with avformat_alloc_context(). * Its oformat field must be set to the desired output format; * Its pb field must be set to an already opened AVIOContext. * @param options An AVDictionary filled with AVFormatContext and muxer-private options. * On return this parameter will be destroyed and replaced with a dict containing * options that were not found. May be NULL. * * @return 0 on success, negative AVERROR on failure. * * @see av_opt_find, av_dict_set, avio_open, av_oformat_next. */ int avformat_write_header(AVFormatContext *s, AVDictionary **options);简单解释一下它的参数的含义:
s:用于输出的AVFormatContext。函数正常执行后返回值等于0。
options:额外的选项,目前没有深入研究过,一般为NULL。
该函数最典型的例子可以参考:
最简单的基于FFMPEG的视频编码器(YUV编码为H.264)
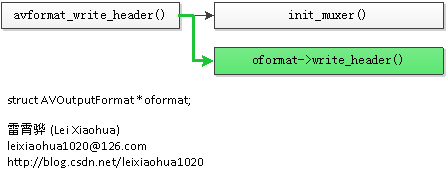
函数调用关系图
avformat_write_header()的调用关系如下图所示。
avformat_write_header()
avformat_write_header()的定义位于libavformat\mux.c,如下所示。int avformat_write_header(AVFormatContext *s, AVDictionary **options)
{
int ret = 0;
if (ret = init_muxer(s, options))
return ret;
if (s->oformat->write_header) {
ret = s->oformat->write_header(s);
if (ret >= 0 && s->pb && s->pb->error < 0)
ret = s->pb->error;
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (s->flush_packets && s->pb && s->pb->error >= 0 && s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_FLUSH_PACKETS)
avio_flush(s->pb);
}
if ((ret = init_pts(s)) < 0)
return ret;
if (s->avoid_negative_ts < 0) {
av_assert2(s->avoid_negative_ts == AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_AUTO);
if (s->oformat->flags & (AVFMT_TS_NEGATIVE | AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS)) {
s->avoid_negative_ts = 0;
} else
s->avoid_negative_ts = AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_MAKE_NON_NEGATIVE;
}
return 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,avformat_write_header()完成了以下工作:
(1)调用init_muxer()初始化复用器下面看一下这两个函数。
(2)调用AVOutputFormat的write_header()
init_muxer()
init_muxer()用于初始化复用器,它的定义如下所示。static int init_muxer(AVFormatContext *s, AVDictionary **options)
{
int ret = 0, i;
AVStream *st;
AVDictionary *tmp = NULL;
AVCodecContext *codec = NULL;
AVOutputFormat *of = s->oformat;
AVDictionaryEntry *e;
if (options)
av_dict_copy(&tmp, *options, 0);
if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict(s, &tmp)) < 0)
goto fail;
if (s->priv_data && s->oformat->priv_class && *(const AVClass**)s->priv_data==s->oformat->priv_class &&
(ret = av_opt_set_dict2(s->priv_data, &tmp, AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN)) < 0)
goto fail;
#if FF_API_LAVF_BITEXACT
if (s->nb_streams && s->streams[0]->codec->flags & CODEC_FLAG_BITEXACT)
s->flags |= AVFMT_FLAG_BITEXACT;
#endif
// some sanity checks
if (s->nb_streams == 0 && !(of->flags & AVFMT_NOSTREAMS)) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "No streams to mux were specified\n");
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto fail;
}
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
st = s->streams[i];
codec = st->codec;
#if FF_API_LAVF_CODEC_TB
FF_DISABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
if (!st->time_base.num && codec->time_base.num) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Using AVStream.codec.time_base as a "
"timebase hint to the muxer is deprecated. Set "
"AVStream.time_base instead.\n");
avpriv_set_pts_info(st, 64, codec->time_base.num, codec->time_base.den);
}
FF_ENABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
#endif
if (!st->time_base.num) {
/* fall back on the default timebase values */
if (codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO && codec->sample_rate)
avpriv_set_pts_info(st, 64, 1, codec->sample_rate);
else
avpriv_set_pts_info(st, 33, 1, 90000);
}
switch (codec->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
if (codec->sample_rate <= 0) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "sample rate not set\n");
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto fail;
}
if (!codec->block_align)
codec->block_align = codec->channels *
av_get_bits_per_sample(codec->codec_id) >> 3;
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
if ((codec->width <= 0 || codec->height <= 0) &&
!(of->flags & AVFMT_NODIMENSIONS)) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "dimensions not set\n");
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto fail;
}
if (av_cmp_q(st->sample_aspect_ratio, codec->sample_aspect_ratio)
&& FFABS(av_q2d(st->sample_aspect_ratio) - av_q2d(codec->sample_aspect_ratio)) > 0.004*av_q2d(st->sample_aspect_ratio)
) {
if (st->sample_aspect_ratio.num != 0 &&
st->sample_aspect_ratio.den != 0 &&
codec->sample_aspect_ratio.num != 0 &&
codec->sample_aspect_ratio.den != 0) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Aspect ratio mismatch between muxer "
"(%d/%d) and encoder layer (%d/%d)\n",
st->sample_aspect_ratio.num, st->sample_aspect_ratio.den,
codec->sample_aspect_ratio.num,
codec->sample_aspect_ratio.den);
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto fail;
}
}
break;
}
if (of->codec_tag) {
if ( codec->codec_tag
&& codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_RAWVIDEO
&& ( av_codec_get_tag(of->codec_tag, codec->codec_id) == 0
|| av_codec_get_tag(of->codec_tag, codec->codec_id) == MKTAG('r', 'a', 'w', ' '))
&& !validate_codec_tag(s, st)) {
// the current rawvideo encoding system ends up setting
// the wrong codec_tag for avi/mov, we override it here
codec->codec_tag = 0;
}
if (codec->codec_tag) {
if (!validate_codec_tag(s, st)) {
char tagbuf[32], tagbuf2[32];
av_get_codec_tag_string(tagbuf, sizeof(tagbuf), codec->codec_tag);
av_get_codec_tag_string(tagbuf2, sizeof(tagbuf2), av_codec_get_tag(s->oformat->codec_tag, codec->codec_id));
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Tag %s/0x%08x incompatible with output codec id '%d' (%s)\n",
tagbuf, codec->codec_tag, codec->codec_id, tagbuf2);
ret = AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
goto fail;
}
} else
codec->codec_tag = av_codec_get_tag(of->codec_tag, codec->codec_id);
}
if (of->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER &&
!(codec->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER))
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Codec for stream %d does not use global headers "
"but container format requires global headers\n", i);
if (codec->codec_type != AVMEDIA_TYPE_ATTACHMENT)
s->internal->nb_interleaved_streams++;
}
if (!s->priv_data && of->priv_data_size > 0) {
s->priv_data = av_mallocz(of->priv_data_size);
if (!s->priv_data) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
if (of->priv_class) {
*(const AVClass **)s->priv_data = of->priv_class;
av_opt_set_defaults(s->priv_data);
if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict2(s->priv_data, &tmp, AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN)) < 0)
goto fail;
}
}
/* set muxer identification string */
if (!(s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_BITEXACT)) {
av_dict_set(&s->metadata, "encoder", LIBAVFORMAT_IDENT, 0);
} else {
av_dict_set(&s->metadata, "encoder", NULL, 0);
}
for (e = NULL; e = av_dict_get(s->metadata, "encoder-", e, AV_DICT_IGNORE_SUFFIX); ) {
av_dict_set(&s->metadata, e->key, NULL, 0);
}
if (options) {
av_dict_free(options);
*options = tmp;
}
return 0;
fail:
av_dict_free(&tmp);
return ret;
}
init_muxer()代码很长,但是它所做的工作比较简单,可以概括成两个字:检查。函数的流程可以概括成以下几步:
(1)将传入的AVDictionary形式的选项设置到AVFormatContext
(2)遍历AVFormatContext中的每个AVStream,并作如下检查:a)AVStream的time_base是否正确设置。如果发现AVStream的time_base没有设置,则会调用avpriv_set_pts_info()进行设置。b)对于音频,检查采样率设置是否正确;对于视频,检查宽、高、宽高比。c)其他一些检查,不再详述。
AVOutputFormat->write_header()
avformat_write_header()中最关键的地方就是调用了AVOutputFormat的write_header()。write_header()是AVOutputFormat中的一个函数指针,指向写文件头的函数。不同的AVOutputFormat有不同的write_header()的实现方法。在这里我们举例子看一下FLV封装格式对应的AVOutputFormat,它的定义位于libavformat\flvenc.c,如下所示。AVOutputFormat ff_flv_muxer = {
.name = "flv",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("FLV (Flash Video)"),
.mime_type = "video/x-flv",
.extensions = "flv",
.priv_data_size = sizeof(FLVContext),
.audio_codec = CONFIG_LIBMP3LAME ? AV_CODEC_ID_MP3 : AV_CODEC_ID_ADPCM_SWF,
.video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_FLV1,
.write_header = flv_write_header,
.write_packet = flv_write_packet,
.write_trailer = flv_write_trailer,
.codec_tag = (const AVCodecTag* const []) {
flv_video_codec_ids, flv_audio_codec_ids, 0
},
.flags = AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER | AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS |
AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT,
};
从ff_flv_muxer的定义中可以看出,write_header()指向的函数为flv_write_header()。我们继续看一下flv_write_header()函数。flv_write_header()的定义同样位于libavformat\flvenc.c,如下所示。
static int flv_write_header(AVFormatContext *s)
{
int i;
AVIOContext *pb = s->pb;
FLVContext *flv = s->priv_data;
int64_t data_size;
//设置参数
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
AVCodecContext *enc = s->streams[i]->codec;
FLVStreamContext *sc;
switch (enc->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
if (s->streams[i]->avg_frame_rate.den &&
s->streams[i]->avg_frame_rate.num) {
//设置帧率,从AVStream拷贝过来
flv->framerate = av_q2d(s->streams[i]->avg_frame_rate);
}
if (flv->video_enc) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"at most one video stream is supported in flv\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
//视频编码的AVCodecContext
flv->video_enc = enc;
if (enc->codec_tag == 0) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Video codec '%s' for stream %d is not compatible with FLV\n",
avcodec_get_name(enc->codec_id), i);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4 ||
enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H263) {
int error = s->strict_std_compliance > FF_COMPLIANCE_UNOFFICIAL;
av_log(s, error ? AV_LOG_ERROR : AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Codec %s is not supported in the official FLV specification,\n", avcodec_get_name(enc->codec_id));
if (error) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"use vstrict=-1 / -strict -1 to use it anyway.\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
} else if (enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_VP6) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Muxing VP6 in flv will produce flipped video on playback.\n");
}
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
if (flv->audio_enc) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"at most one audio stream is supported in flv\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
//音频编码的AVCodecContext
flv->audio_enc = enc;
if (get_audio_flags(s, enc) < 0)
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
if (enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_PCM_S16BE)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"16-bit big-endian audio in flv is valid but most likely unplayable (hardware dependent); use s16le\n");
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA:
if (enc->codec_id != AV_CODEC_ID_TEXT && enc->codec_id != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Data codec '%s' for stream %d is not compatible with FLV\n",
avcodec_get_name(enc->codec_id), i);
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
flv->data_enc = enc;
break;
default:
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Codec type '%s' for stream %d is not compatible with FLV\n",
av_get_media_type_string(enc->codec_type), i);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
avpriv_set_pts_info(s->streams[i], 32, 1, 1000); /* 32 bit pts in ms */
sc = av_mallocz(sizeof(FLVStreamContext));
if (!sc)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
s->streams[i]->priv_data = sc;
sc->last_ts = -1;
}
flv->delay = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
//开始写入
//Signature
avio_write(pb, "FLV", 3);
//Version
avio_w8(pb, 1);
//“!!”意思是把非0转换成1
//Flags
avio_w8(pb, FLV_HEADER_FLAG_HASAUDIO * !!flv->audio_enc +
FLV_HEADER_FLAG_HASVIDEO * !!flv->video_enc);
//Header size
avio_wb32(pb, 9);
//Header结束
//Previous Tag Size
avio_wb32(pb, 0);
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++)
if (s->streams[i]->codec->codec_tag == 5) {
avio_w8(pb, 8); // message type
avio_wb24(pb, 0); // include flags
avio_wb24(pb, 0); // time stamp
avio_wb32(pb, 0); // reserved
avio_wb32(pb, 11); // size
flv->reserved = 5;
}
write_metadata(s, 0);
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
AVCodecContext *enc = s->streams[i]->codec;
if (enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC || enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 || enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4) {
int64_t pos;
avio_w8(pb, enc->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO ?
FLV_TAG_TYPE_VIDEO : FLV_TAG_TYPE_AUDIO);
avio_wb24(pb, 0); // size patched later
avio_wb24(pb, 0); // ts
avio_w8(pb, 0); // ts ext
avio_wb24(pb, 0); // streamid
pos = avio_tell(pb);
if (enc->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC) {
avio_w8(pb, get_audio_flags(s, enc));
avio_w8(pb, 0); // AAC sequence header
avio_write(pb, enc->extradata, enc->extradata_size);
} else {
avio_w8(pb, enc->codec_tag | FLV_FRAME_KEY); // flags
avio_w8(pb, 0); // AVC sequence header
avio_wb24(pb, 0); // composition time
ff_isom_write_avcc(pb, enc->extradata, enc->extradata_size);
}
data_size = avio_tell(pb) - pos;
avio_seek(pb, -data_size - 10, SEEK_CUR);
avio_wb24(pb, data_size);
avio_skip(pb, data_size + 10 - 3);
avio_wb32(pb, data_size + 11); // previous tag size
}
}
return 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,flv_write_header()完成了FLV文件头的写入工作。该函数的工作可以大体分为以下两部分:
(1)给FLVContext设置参数写文件头的代码很短,如下所示。
(2)写文件头,以及相关的Tag
avio_write(pb, "FLV", 3);
avio_w8(pb, 1);
avio_w8(pb, FLV_HEADER_FLAG_HASAUDIO * !!flv->audio_enc +
FLV_HEADER_FLAG_HASVIDEO * !!flv->video_enc);
avio_wb32(pb, 9);可以参考下图中FLV文件头的定义比对一下上面的代码。
雷霄骅
[email protected]
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020