SCEA_Messaging
SCEA_Messaging
JMS provides a highly flexible and scalable solution for building loosely coupled applications in the enterprise environment.
Messages: A message is a unit of data that is sent from one process to another. The data in the message can range from simple text to a more complex data structure. The only restriction is that the object must be serializable.
Message-Oriented Middleware: MOM is middleware that is used for messaging.
Communication Modes: synchronous(ex: credit card authorization) / asynchronous(ex: e-mail)
| Scenario |
Solution |
| Need to implement a messaging system in which a response is not immediately required. |
Asynchronous |
| Need a high-volume transaction processing capability for sending messages. |
Asynchronous |
| Want a messaging system that uses your system hardware in an efficient manner. |
Asynchronous |
| Use a credit card authorization/ user login authentication system to send a message in which the response to the message is required before the transaction can be completed. |
Synchronous |
Message Models: publish/subscribe(pub/sub), in which messages are published on a one or more-to-many basis. Point-to-point(PTP), in which messages are sent on a one-to-one basis.
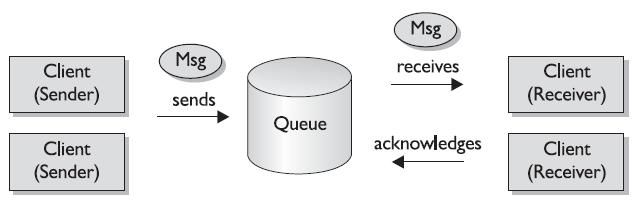
Point-to-Point(PTP) model
A message is delivered to a destination, known as a queue. Messages in a queue are processed on a first-in, first-out(FIFO) basis.
Publish/subscribe(pub/sub) model
JMS Interfaces
| JMS Common Interfaces |
Pub-sub Interfaces |
PTP Interfaces |
| Destination |
Topic |
Queue |
| ConnectionFactory |
TopicConnectionFactory |
QueueConnectionFactory |
| Connection |
TopicConnection |
QueueConnection |
| Session |
TopicSession |
QueueSession |
| MessageProducer |
TopicPublisher |
QueueSender |
| MessageConsumer |
TopicSubscriber |
QueueReceiver, QueueBrowser |
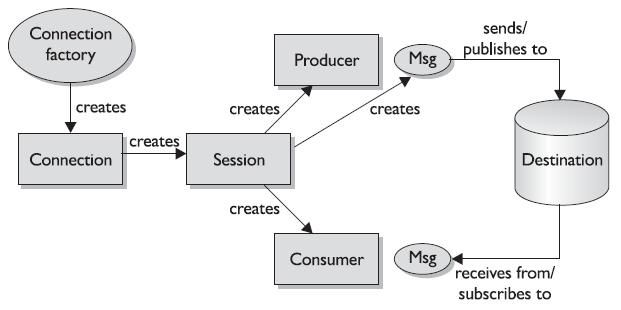
JMS component relationships
Questions:
1. Which of the following are characteristics of publish/subscribe message model?
A. Always use a URL to identify publishers.
B. Subject-based addressing.
C. Location-independent publishers.
D. Only synchronous communication between publishers and subscribers is possible.
B,C
2. Which of the following are valid methods for a TopicSubscriber?
A. receive()
B. receiveNoWait()
C. receiveWait()
D. receiveSync()
A,B
3. What are the types of messaging models supported in JMS?
A. Point-to-point
B. Send/receive
C. Transmit/receive
D. Publish/subscribe
A,D
4. What is a message digest?
A. A digital fingerprint value that is computed from a message, file, or byte stream
B. A shortened summary of a message
C. The subject line of a message
D. A processing function of the mail server
A
5.Which of the following scenarios are not suitable for publish/subscribe messaging model?
A. It is used to receive news stories.
B. It is used for receiving sales forecasts.
C. It is used for sending stock prices to traders on the trading floor.
D. It is used to authorize a user ID and password.
D
6.What deliver modes are available in JMS?
A. PERSISTENT
B. NON_PERSISTENT
C. PERMANENT
D. DURABLE
A,B
Note: When creating a MessageProducer, you can also specify the default delivery mode(setDeliveryMode). This can be either NON_PERSISTENT, which has a lower overhead because the message is not logged, or PERSISTENT, which requires the message to be logged, typically to a database.
7. Which of the following are valid message acknowledgment types?
A. AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE
B. CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE
C. DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE
D. NO_ACKNOWLEDGE
A,B,C
8. Which of the following are not valid message body formats?
A. MapMessage
B. ObjectMessage
C. TextMessage
D. StringMessage
D
Message Body Format: ByteMessage, MapMessage, ObjectMessage, StreamMessage, TextMessage
9. Which of the following are not valid JMS objects?
A. MessageProducer
B. MessageConsumer
C. MessageViewer
D. MessageSelector
C
10. Which of the following would not be used in a client application performing point-to-point messaging?
A. Topic
B. InitialContext
C. Queue
D. Session
A
11. Which of the following are advantages of asynchronous messaging architectures?
A. Better use of bandwidth
B. Supports load balancing
C. Provides sender with instant response
D. Scalability
A,B,D
12. Which of the following statements are true for asynchronous messaging?
A. It decouples senders and receivers.
B. It can increase performance.
C. It is better suited to smaller message sizes.
D. It only works with blocking calls.
A,B,C
13. Which method must be called to receive messages asynchronously?
A. The receive method
B. The processMessage method
C. The readMessage method
D. The onMessage method
D
14. Which of the following are not features of asynchronous messaging?
A. As the volume of traffic increases, it is better able to handle the spike in demand.
B. A message must be acknowledged before the producer can send another.
C. It is less affected by failures at the hardware, software, and network levels.
D. When capacities are exceeded, information is not lost; instead, it is delayed.
B
15.Which method must be called to receive messages synchronously?
A. The receive method
B. The processMessage method
C. The readMessage method
D. The onMessage method
A
16. Which of the following cases are better suited to synchronous messaging?
A. Electronic mail
B. Credit card authorization
C. Electronic processing of tax returns
D. Validation of data entered
B,D
17.Which of the following are features of synchronous messaging?
A. Both parties must be active to participate.
B. Messages must be acknowledged before proceeding.
C. It decouples senders and receivers.
D. It does not work with blocking calls.
A,B
18. Which of the following are not features of synchronous messaging?
A. Both parties must be active to participate.
B. It is unaffected by increases in traffic volume.
C. Message must be acknowledged before proceeding to the next.
D. Message is queued until it is ready for processing.
B,D
19. Which of the following scenarios are not suitable for publish/subscribe messaging model?
A. Sending an instant message
B. Sending an order to another system
C. Sending news stories to interested parties
D. Sending a transaction to another system
A,B,D
20. What method must be implemented to receive messages in a message-driven bean (MDB)?
A. The receive method
B. The onMessage method
C. The readMessage method
D. The processMessage method
B