1087. All Roads Lead to Rome (30)
Indeed there are many different tourist routes from our city to Rome. You are supposed to find your clients the route with the least cost while gaining the most happiness.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 2 positive integers N (2<=N<=200), the number of cities, and K, the total number of routes between pairs of cities; followed by the name of the starting city. The next N-1 lines each gives the name of a city and an integer that represents the happiness one can gain from that city, except the starting city. Then K lines follow, each describes a route between two cities in the format "City1 City2 Cost". Here the name of a city is a string of 3 capital English letters, and the destination is always ROM which represents Rome.
Output Specification:
For each test case, we are supposed to find the route with the least cost. If such a route is not unique, the one with the maximum happiness will be recommended. If such a route is still not unique, then we output the one with the maximum average happiness -- it is guaranteed by the judge that such a solution exists and is unique.
Hence in the first line of output, you must print 4 numbers: the number of different routes with the least cost, the cost, the happiness, and the average happiness (take the integer part only) of the recommended route. Then in the next line, you are supposed to print the route in the format "City1->City2->...->ROM".
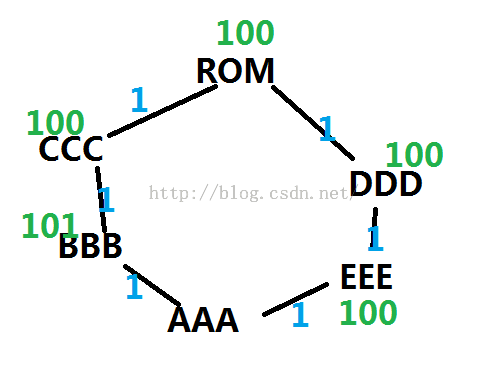
Sample Input:6 7 HZH ROM 100 PKN 40 GDN 55 PRS 95 BLN 80 ROM GDN 1 BLN ROM 1 HZH PKN 1 PRS ROM 2 BLN HZH 2 PKN GDN 1 HZH PRS 1Sample Output:
3 3 195 97 HZH->PRS->ROM

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int happy[202];
int cost[202][202];
struct record{
int citys;//表示从起点开始经过的城市数目
int parent;//表示上一个节点
int average;//表示平均的开心数
int happy_all;//表示此条路径的开心总数
record() :citys(0), parent(-1), average(-1) {}
};
bool mark[202];
int dist[202];
int happy_sum[202];
vector<record*>vec[202];
map<string, int>S2I;//字符串转化为数字
map<int, string>I2S;//数字转化为字符串
void dij(int s, int t,int city_num){
mark[s] = true;
dist[s] = 0;
happy_sum[s] = happy[s];
int newP = s;
record *rec_s = new record();
rec_s->citys = 1;
rec_s->parent = -1;
rec_s->happy_all = happy[s];
rec_s->average = rec_s->happy_all / rec_s->citys;
vec[s].push_back(rec_s);
while (!mark[t]){
for (int i = 0; i < city_num; ++i){
if (cost[newP][i] == -1 || cost[newP][i] == 0 || mark[i])continue;
else if (dist[i] == -1 || dist[i] > dist[newP] + cost[newP][i]){
//如果有更小距离的,那么把vec清空,并且根据newP节点的所有路径构建record
dist[i] = dist[newP] + cost[newP][i];
vec[i].clear();
//happy_sum[i] = happy_sum[newP] + happy[i];
for (int j = 0; j < vec[newP].size(); j++){
record *rec = new record();
rec->citys = vec[newP][j]->citys + 1;
rec->parent = newP;
rec->happy_all = vec[newP][j]->happy_all + happy[i];
//rec->average = happy_sum[i] / (rec->citys - 1);
rec->average = rec->happy_all / (rec->citys - 1);
vec[i].push_back(rec);
}
}
else if (dist[i] == dist[newP] + cost[newP][i]){
//如果最短距离相同,则构造record添加到vec中
for (int j = 0; j < vec[newP].size(); j++){
record *rec = new record();
rec->citys = vec[newP][j]->citys + 1;
rec->parent = newP;
rec->happy_all = vec[newP][j]->happy_all + happy[i];
rec->average = rec->happy_all / (rec->citys - 1);
vec[i].push_back(rec);
}
}
}
int min = 0x7fffffff;
for (int i = 0; i < city_num; ++i){
if (mark[i] || dist[i] == -1)continue;
if (dist[i] < min){
min = dist[i];
newP = i;
}
}
mark[newP] = true;
}//while
}
void printPath(int start_city, int end_city, int max_idx){
//打印路径
if (end_city != start_city){
int parent = vec[end_city][max_idx]->parent;
int parent_max = 0;
int max = 0;
int happy_max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vec[parent].size(); ++i){
if (vec[parent][i]->happy_all > happy_max || (vec[parent][i]->happy_all == happy_max && vec[parent][i]->average > max)){
parent_max = i;
max = vec[parent][i]->average;
happy_max = vec[parent][i]->happy_all;
}
}
printPath(start_city, parent, parent_max);
cout << I2S[parent] << "->";
}
}
int main(){
freopen("F://Temp/input.txt", "r", stdin);
int city_num, road_num;
for (int i = 0; i < 202; i++){
happy[i] = 0;
dist[i] = -1;
mark[i] = false;
happy_sum[i] = 0;
vec[i].clear();
for (int j = 0; j < 202; ++j)
cost[i][j] = -1;
cost[i][i] = 0;
}
S2I.clear();
I2S.clear();
string start_city_str;
int start_city;
cin >> city_num >> road_num >> start_city_str;
int idx = 0;
if (S2I.find(start_city_str) == S2I.end()){
S2I[start_city_str] = idx;
I2S[idx] = start_city_str;
start_city = idx;
idx++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < city_num - 1; ++i){
string str_input;
int happy_input;
cin >> str_input >> happy_input;
if (S2I.find(str_input) == S2I.end()){
S2I[str_input] = idx;
I2S[idx] = str_input;
happy[idx] = happy_input;
idx++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < road_num; ++i){
string str_start, str_end;
int cost_input;
cin >> str_start >> str_end >> cost_input;
cost[S2I[str_start]][S2I[str_end]] = cost[S2I[str_end]][S2I[str_start]] = cost_input;
}
int end_city = S2I["ROM"];
dij(start_city,end_city,city_num);
int max_idx = 0;
int max = 0;
int happy_max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vec[end_city].size(); ++i){
if (vec[end_city][i]->happy_all > happy_max || (vec[end_city][i]->happy_all == happy_max && vec[end_city][i]->average > max)){
//这里的判断条件一定要写对,详见附图,因为有happy总数不一样,而平均happy数一样的情况
//我第一次写的是vec[end_city][i]->happy_all > happy_max && vec[end_city][i]->average > max出错了
max_idx = i;
max = vec[end_city][i]->average;
happy_max = vec[end_city][i]->happy_all;
}
}
cout << vec[end_city].size() << " " << dist[end_city] << " " << happy_max << " " << max << endl;
printPath(start_city, end_city, max_idx);
cout << "ROM" << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
//每个城市结点
struct Edge
{
int cost;
int next;
};
struct Node
{
int value;
string str;
vector<Edge> next;
int distant, happy; // 第i个结点距离起始城市的最小距离和最大happy
int rNums; // 到第i个结点的最短路径的条数
int pNums; // 到第i个结点最大幸福经历的最少结数
bool visit;
int parent; //最大幸福的前一个结点,
Node():distant(INT_MAX), happy(0), rNums(INT_MAX), pNums(0), visit(false), parent(-1)
{
next.clear();
}
};
const int N = 201;
map<string, int> mp; //城市名字到结点编号的映射
Node node[N]; //
int seq[N];
int main(void)
{
int n, k;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
string startS;
cin >> startS;
mp[startS] = 0;
node[0].value = 0;
node[0].distant = 0;
node[0].rNums = 0;
node[0].pNums = 1;
node[0].str = startS;
string city;
int value;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
cin >> city >> value;
mp[city] = i;
node[i].value = value;
node[i].str = city;
}
string city1, city2;
int c1, c2;
Edge edge;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
cin >> city1 >> city2 >> edge.cost;
c1 = mp[city1];
c2 = mp[city2];
edge.next = c2;
node[c1].next.push_back(edge);
edge.next = c1;
node[c2].next.push_back(edge);
}
city = "ROM";
int romIndex = mp[city];
while (true)
{
int minIndex = -1, minDistant = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (node[i].visit == false && node[i].distant < minDistant)
{
minIndex = i;
minDistant = node[i].distant;
}
}
if (minIndex == -1)
break;
node[minIndex].visit = true;
if (minIndex == romIndex)
break;
for (vector<Edge>::iterator iter = node[minIndex].next.begin(); iter != node[minIndex].next.end(); ++iter)
{
if (node[iter->next].visit == true)
continue;
else
{
if (node[minIndex].distant + iter -> cost < node[iter -> next].distant)
{
node[iter -> next].distant = node[minIndex].distant + iter -> cost;
node[iter -> next].parent = minIndex;
node[iter -> next].happy = node[minIndex].happy + node[iter -> next].value;
node[iter -> next].pNums = node[minIndex].pNums;
node[iter -> next].rNums = node[minIndex].rNums + 1;
}
else if (node[minIndex].distant + iter -> cost == node[iter -> next].distant)
{
node[iter -> next].pNums += node[minIndex].pNums;
if ((node[iter -> next].happy < node[minIndex].happy + node[iter -> next].value))
{
node[iter -> next].happy = node[minIndex].happy + node[iter -> next].value;
node[iter -> next].rNums = node[minIndex].rNums + 1;
node[iter -> next].parent = minIndex;
}
}
}
}
}
printf("%d %d %d %d\n", node[romIndex].pNums, node[romIndex].distant, node[romIndex].happy, node[romIndex].happy / node[romIndex].rNums);
int index = 0;
while (romIndex != -1)
{
seq[index++] = romIndex;
romIndex = node[romIndex].parent;
}
--index;
cout << node[seq[index]].str;
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
printf("->");
cout << node[seq[i]].str;
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}