Dijkstra算法求最短路径(java)
任务描述:在一个无向图中,获取起始节点到所有其他节点的最短路径描述
Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的最短路径路由算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
Dijkstra一般的表述通常有两种方式,一种用永久和临时标号方式,一种是用OPEN, CLOSE表方式
用OPEN,CLOSE表的方式,其采用的是贪心法的算法策略,大概过程如下:
1.声明两个集合,open和close,open用于存储未遍历的节点,close用来存储已遍历的节点
2.初始阶段,将初始节点放入close,其他所有节点放入open
3.以初始节点为中心向外一层层遍历,获取离指定节点最近的子节点放入close并从新计算路径,直至close包含所有子节点
代码实例如下:
Node对象用于封装节点信息,包括名字和子节点
MapBuilder用于初始化数据源,返回图的起始节点
Dijkstra对象用于计算起始节点到所有其他节点的最短路径
Main用于测试Dijkstra对象
打印输出如下:
D:A->D
E:A->F->E
F:A->F
G:A->C->G
B:A->B
C:A->C
H:A->B->H
Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的最短路径路由算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
Dijkstra一般的表述通常有两种方式,一种用永久和临时标号方式,一种是用OPEN, CLOSE表方式
用OPEN,CLOSE表的方式,其采用的是贪心法的算法策略,大概过程如下:
1.声明两个集合,open和close,open用于存储未遍历的节点,close用来存储已遍历的节点
2.初始阶段,将初始节点放入close,其他所有节点放入open
3.以初始节点为中心向外一层层遍历,获取离指定节点最近的子节点放入close并从新计算路径,直至close包含所有子节点
代码实例如下:
Node对象用于封装节点信息,包括名字和子节点
public class Node {
private String name;
private Map<Node,Integer> child=new HashMap<Node,Integer>();
public Node(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Map<Node, Integer> getChild() {
return child;
}
public void setChild(Map<Node, Integer> child) {
this.child = child;
}
}
MapBuilder用于初始化数据源,返回图的起始节点
public class MapBuilder {
public Node build(Set<Node> open, Set<Node> close){
Node nodeA=new Node("A");
Node nodeB=new Node("B");
Node nodeC=new Node("C");
Node nodeD=new Node("D");
Node nodeE=new Node("E");
Node nodeF=new Node("F");
Node nodeG=new Node("G");
Node nodeH=new Node("H");
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeB, 1);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeC, 1);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeD, 4);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeG, 5);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeF, 2);
nodeB.getChild().put(nodeA, 1);
nodeB.getChild().put(nodeF, 2);
nodeB.getChild().put(nodeH, 4);
nodeC.getChild().put(nodeA, 1);
nodeC.getChild().put(nodeG, 3);
nodeD.getChild().put(nodeA, 4);
nodeD.getChild().put(nodeE, 1);
nodeE.getChild().put(nodeD, 1);
nodeE.getChild().put(nodeF, 1);
nodeF.getChild().put(nodeE, 1);
nodeF.getChild().put(nodeB, 2);
nodeF.getChild().put(nodeA, 2);
nodeG.getChild().put(nodeC, 3);
nodeG.getChild().put(nodeA, 5);
nodeG.getChild().put(nodeH, 1);
nodeH.getChild().put(nodeB, 4);
nodeH.getChild().put(nodeG, 1);
open.add(nodeB);
open.add(nodeC);
open.add(nodeD);
open.add(nodeE);
open.add(nodeF);
open.add(nodeG);
open.add(nodeH);
close.add(nodeA);
return nodeA;
}
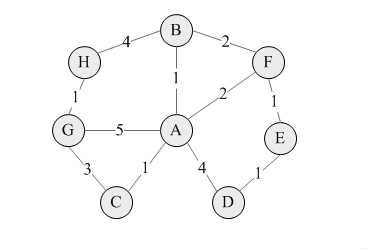
}图的结构如下图所示:

Dijkstra对象用于计算起始节点到所有其他节点的最短路径
public class Dijkstra {
Set<Node> open=new HashSet<Node>();
Set<Node> close=new HashSet<Node>();
Map<String,Integer> path=new HashMap<String,Integer>();//封装路径距离
Map<String,String> pathInfo=new HashMap<String,String>();//封装路径信息
public Node init(){
//初始路径,因没有A->E这条路径,所以path(E)设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE
path.put("B", 1);
pathInfo.put("B", "A->B");
path.put("C", 1);
pathInfo.put("C", "A->C");
path.put("D", 4);
pathInfo.put("D", "A->D");
path.put("E", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
pathInfo.put("E", "A");
path.put("F", 2);
pathInfo.put("F", "A->F");
path.put("G", 5);
pathInfo.put("G", "A->G");
path.put("H", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
pathInfo.put("H", "A");
//将初始节点放入close,其他节点放入open
Node start=new MapBuilder().build(open,close);
return start;
}
public void computePath(Node start){
Node nearest=getShortestPath(start);//取距离start节点最近的子节点,放入close
if(nearest==null){
return;
}
close.add(nearest);
open.remove(nearest);
Map<Node,Integer> childs=nearest.getChild();
for(Node child:childs.keySet()){
if(open.contains(child)){//如果子节点在open中
Integer newCompute=path.get(nearest.getName())+childs.get(child);
if(path.get(child.getName())>newCompute){//之前设置的距离大于新计算出来的距离
path.put(child.getName(), newCompute);
pathInfo.put(child.getName(), pathInfo.get(nearest.getName())+"->"+child.getName());
}
}
}
computePath(start);//重复执行自己,确保所有子节点被遍历
computePath(nearest);//向外一层层递归,直至所有顶点被遍历
}
public void printPathInfo(){
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> pathInfos=pathInfo.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String, String> pathInfo:pathInfos){
System.out.println(pathInfo.getKey()+":"+pathInfo.getValue());
}
}
/**
* 获取与node最近的子节点
*/
private Node getShortestPath(Node node){
Node res=null;
int minDis=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Map<Node,Integer> childs=node.getChild();
for(Node child:childs.keySet()){
if(open.contains(child)){
int distance=childs.get(child);
if(distance<minDis){
minDis=distance;
res=child;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
Main用于测试Dijkstra对象
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dijkstra test=new Dijkstra();
Node start=test.init();
test.computePath(start);
test.printPathInfo();
}
}
打印输出如下:
D:A->D
E:A->F->E
F:A->F
G:A->C->G
B:A->B
C:A->C
H:A->B->H