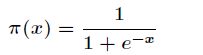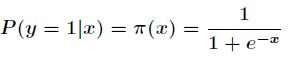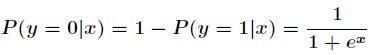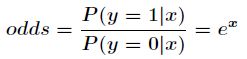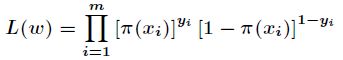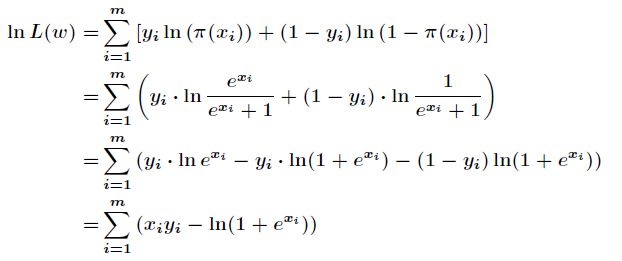Logistic回归与梯度下降法
Logistic回归为概率型非线性回归模型,是研究二分类观察结果![]() 与一些影响因素
与一些影响因素![]() 之间关系的一种
之间关系的一种
多变量分析方法。通常的问题是,研究某些因素条件下某个结果是否发生,比如医学中根据病人的一些症状来判断它是
否患有某种病。
在讲解Logistic回归理论之前,我们先从LR分类器说起。LR分类器,即Logistic Regression Classifier。
在分类情形下,经过学习后的LR分类器是一组权值![]() ,当测试样本的数据输入时,这组权值与测试数
,当测试样本的数据输入时,这组权值与测试数
据按照线性加和得到
这里![]() 是每个样本的
是每个样本的![]() 个特征。之后按照Sigmoid函数(又称为Logistic函数)的形式求出
个特征。之后按照Sigmoid函数(又称为Logistic函数)的形式求出
由于Sigmoid函数的定义域为![]() ,值域为
,值域为![]() ,因此最基本的LR分类器适合对两类目标进行分类。
,因此最基本的LR分类器适合对两类目标进行分类。
所以Logistic回归最关键的问题就是研究如何求得![]() 这组权值。此问题用极大似然估计来做。
这组权值。此问题用极大似然估计来做。
下面正式地来讲Logistic回归模型。
考虑具有![]() 个独立变量的向量
个独立变量的向量![]() ,设条件慨率
,设条件慨率![]() 为根据观测量相对于某事件
为根据观测量相对于某事件![]() 发生
发生
的概率。那么Logistic回归模型可以表示为
其中![]() ,那么在
,那么在![]() 条件下
条件下![]() 不发生的概率为
不发生的概率为
所以事件发生与不发生的概率之比为
这个比值称为事件的发生比(the odds of experiencing an event),简记为odds。
可以看出Logistic回归都是围绕一个Logistic函数来展开的。接下来就讲如何用极大似然估计求分类器的参数。
假设有![]() 个观测样本,观测值分别为
个观测样本,观测值分别为![]() ,设
,设![]() 为给定条件下得到
为给定条件下得到![]() 的概率,
的概率,
同样地,![]() 的概率为
的概率为![]() ,所以得到一个观测值的概率为
,所以得到一个观测值的概率为![]() 。
。
因为各个观测样本之间相互独立,那么它们的联合分布为各边缘分布的乘积。得到似然函数为
然后我们的目标是求出使这一似然函数的值最大的参数估计,最大似然估计就是求出参数![]() ,使
,使
得![]() 取得最大值,对函数
取得最大值,对函数![]() 取对数得到
取对数得到
现在求向量![]() ,使得
,使得![]() 最大,其中
最大,其中![]() 。
。
这里介绍一种方法,叫做梯度下降法(求局部极小值),当然相对还有梯度上升法(求局部极大值)。
对上述的似然函数求偏导后得到
由于是求局部极大值,所以根据梯度上升法,有
根据上述公式,只需初始化向量![]() 全为零,或者随机值,迭代到指定精度为止。
全为零,或者随机值,迭代到指定精度为止。
现在就来用C++编程实现Logistic回归的梯度上升算法。首先要对训练数据进行处理,假设训练数据如下
训练数据:TrainData.txt
1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 1 0 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 1 2 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 2 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 2 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 2 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 0 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 1 0 2 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 2 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 2 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 0
上面训练数据中,每一行代表一组训练数据,每组有7个数组,第1个数字代表ID,可以忽略之,2~6代表这组训
练数据的特征输入,第7个数字代表输出,为0或者1。每个数据之间用一个空格隔开。
首先我们来研究如何一行一行读取文本,在C++中,读取文本的一行用getline()函数。
getline()函数表示读取文本的一行,返回的是读取的字节数,如果读取失败则返回-1。用法如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string filename = "data.in";
ifstream file(filename.c_str());
char s[1024];
if(file.is_open())
{
while(file.getline(s,1024))
{
int x,y,z;
sscanf(s,"%d %d %d",&x,&y,&z);
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<z<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
拿到每一行后,可以把它们提取出来,进行系统输入。 Logistic回归的梯度上升算法实现如下
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#define Type double
#define Vector vector
using namespace std;
struct Data
{
Vector<Type> x;
Type y;
};
void PreProcessData(Vector<Data>& data, string path)
{
string filename = path;
ifstream file(filename.c_str());
char s[1024];
if(file.is_open())
{
while(file.getline(s, 1024))
{
Data tmp;
Type x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7;
sscanf(s,"%lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf", &x1, &x2, &x3, &x4, &x5, &x6, &x7);
tmp.x.push_back(1);
tmp.x.push_back(x2);
tmp.x.push_back(x3);
tmp.x.push_back(x4);
tmp.x.push_back(x5);
tmp.x.push_back(x6);
tmp.y = x7;
data.push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
void Init(Vector<Data> &data, Vector<Type> &w)
{
w.clear();
data.clear();
PreProcessData(data, "TrainData.txt");
for(int i = 0; i < data[0].x.size(); i++)
w.push_back(0);
}
Type WX(const Data& data, const Vector<Type>& w)
{
Type ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < w.size(); i++)
ans += w[i] * data.x[i];
return ans;
}
Type Sigmoid(const Data& data, const Vector<Type>& w)
{
Type x = WX(data, w);
Type ans = exp(x) / (1 + exp(x));
return ans;
}
Type Lw(const Vector<Data>& data, Vector<Type> w)
{
Type ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
{
Type x = WX(data[i], w);
ans += data[i].y * x - log(1 + exp(x));
}
return ans;
}
void Gradient(const Vector<Data>& data, Vector<Type> &w, Type alpha)
{
for(int i = 0; i < w.size(); i++)
{
Type tmp = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < data.size(); j++)
tmp += alpha * data[j].x[i] * (data[j].y - Sigmoid(data[j], w));
w[i] += tmp;
}
}
void Display(int cnt, Type objLw, Type newLw, Vector<Type> w)
{
cout<<"第"<<cnt<<"次迭代: ojLw = "<<objLw<<" 两次迭代的目标差为: "<<(newLw - objLw)<<endl;
cout<<"参数w为: ";
for(int i = 0; i < w.size(); i++)
cout<<w[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
void Logistic(const Vector<Data>& data, Vector<Type> &w)
{
int cnt = 0;
Type alpha = 0.1;
Type delta = 0.00001;
Type objLw = Lw(data, w);
Gradient(data, w, alpha);
Type newLw = Lw(data, w);
while(fabs(newLw - objLw) > delta)
{
objLw = newLw;
Gradient(data, w, alpha);
newLw = Lw(data, w);
cnt++;
Display(cnt,objLw,newLw, w);
}
}
void Separator(Vector<Type> w)
{
Vector<Data> data;
PreProcessData(data, "TestData.txt");
cout<<"预测分类结果:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
{
Type p0 = 0;
Type p1 = 0;
Type x = WX(data[i], w);
p1 = exp(x) / (1 + exp(x));
p0 = 1 - p1;
cout<<"实例: ";
for(int j = 0; j < data[i].x.size(); j++)
cout<<data[i].x[j]<<" ";
cout<<"所属类别为:";
if(p1 >= p0) cout<<1<<endl;
else cout<<0<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Vector<Type> w;
Vector<Data> data;
Init(data, w);
Logistic(data, w);
Separator(w);
return 0;
}
测试数据:TestData.txt
10009 1 0 0 1 0 1 10025 0 0 1 2 0 0 20035 0 0 1 0 0 1 20053 1 0 0 0 0 0 30627 1 0 1 2 0 0 30648 2 0 0 0 1 0