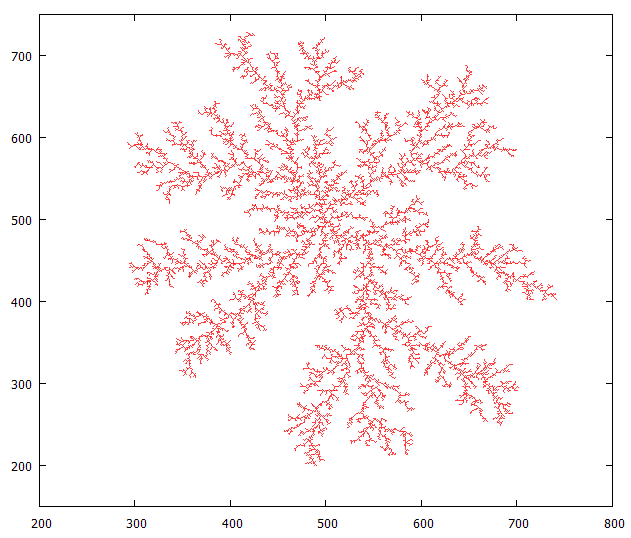
DLA (扩散限制凝聚)模型的计算机模拟
几年前写的一个小程序,最近找到了。程序写的比较简单,也没做什么优化。对正在学习计算物理的同学可能会有点帮助。
下面关于DLA模型的介绍来自百度百科。
Diffusion-limited Aggregation(DLA)扩散限制凝聚,是由Witten和Sander于1981年共同提出来的,其基本思想是:首先置一初始粒子作为种子,在远离种子的任意位置随机产生一个粒子使其做无规行走,直至与种子接触,成为集团的一部分;然后再随机产生一个粒子,重复上述过程,这样就可以得到足够大的DLA团簇(cluster)。
创始人之一Sander曾经总结过DLA 的研究意义:
- 模型用极其简单的算法抓住了广泛的自然现象的关键成分却没有明确的物理机制;
- .通过简单的运动学和动力学过程就可以产生具有标度不变性的自相似的分形结构,从而建立分形理论和实验观察之间的桥梁,在一定程度上揭示出实际体系中分形生长的机理;
- 界面具有复杂的形状和不稳定性的性质,生长过程是一个远离平衡的动力学过程,但集团的结构却有稳定且确定的分形维数。
我的程序想法很简单。用个大数组保存凝聚的微粒。
const int WIDTH = 1000; const int HEIGHT = 1000; static char s_Grid[WIDTH][HEIGHT]; static int s_YRange; static int s_XRange; static int s_YCenter; static int s_XCenter; static int s_XLow; static int s_YLow; static int s_XHigh; static int s_YHigh;
先在中心位置放个微粒,作为起始条件。程序中就是将数组的相应位置置1。
void DLA_Init(void)
{
int x, y;
s_XCenter = WIDTH / 2;
s_YCenter = HEIGHT / 2;
for(y = 0; y < HEIGHT; y++)
{
for(x = 0; x < WIDTH; x++)
{
s_Grid[y][x] = 0;
}
}
s_Grid[s_YCenter][s_XCenter] = 1;
cout << s_XCenter << " " << s_YCenter << endl;
//cout << "#XCenter = " << s_XCenter << endl;
//cout << "#YCenter = " << s_YCenter << endl;
}
然后随机的产生一些微粒,让微粒做随机游动。当一个微粒游动到其他微粒附近时就停止移动了。就这样一个微粒一个微粒的进行。
walk() 函数用来产生游走。
isAdjacent() 函数用来判断是否临近其他微粒。
这两个函数的实现都比较简单。唯一需要说明的是我采用的是周期性边界条件。也就是说微粒从一边游走出边界会从对面的边界处回来。
static inline void walk(int *pX, int *pY)
{
int w;
w = rand() % 8;
//cout << "w = " << w << endl;
switch (w)
{
case 0: // Right
(*pX) ++;
break;
case 1: // Left
(*pX) --;
break;
case 2: // Down
(*pY) ++;
break;
case 3: // Up
(*pY) --;
break;
case 4: // Right Down
(*pX) ++;
(*pY) ++;
break;
case 5: // Right Up
(*pX) ++;
(*pY) --;
break;
case 6: // Left Down
(*pX) --;
(*pY) ++;
break;
case 7: // Left Up
(*pX) --;
(*pY) --;
break;
default:
break;
}
//cout << "X = " << *pX << " ,Y = " << *pY << endl;
if(*pX > s_XHigh) *pX = s_XLow;
if(*pY > s_YHigh) *pY = s_YLow;
if(*pX < s_XLow) *pX = s_XHigh;
if(*pY < s_YLow) *pY = s_YHigh;
//cout << "X = " << *pX << " ,Y = " << *pY << endl;
return;
}
static inline bool isAdjacent(int x, int y)
{
//***
//* *
//***
//临近位置包括8个点
int xx, yy;
xx = x + 1;
if(xx > s_XHigh) xx = s_XLow;
if( s_Grid[y][xx] == 1) return true;// Right
yy = y + 1;
if(yy > s_YHigh) yy = s_YLow;
if( s_Grid[yy][xx] == 1) return true; // Right Down
if( s_Grid[yy][x] == 1) return true; // Down
yy = y - 1;
if(yy < s_YLow) yy = s_YHigh;
if( s_Grid[yy][xx] == 1) return true; //Right Up
if( s_Grid[yy][x] == 1) return true; // Up
xx = x - 1;
if(xx < s_XLow) xx = s_XHigh;
if( s_Grid[yy][xx] == 1) return true; //Left Uo
if( s_Grid[y][xx] == 1) return true; // Left
yy = y + 1;
if(yy > s_YHigh) yy = s_YLow;
if( s_Grid[yy][xx] == 1) return true; // Left Down
return false;
}
void DLA_Gen(int *pX, int *pY)
{
//int i = 0; do
{
*pX = rand() % s_XRange + s_XLow;
*pY = rand() % s_YRange + s_YLow;
}
while(s_Grid[*pY][*pX] == 1);
//*pX = s_XLow;
//*pY = s_YLow;// 这个位置是肯定不会有粒子的
// cout << "X = " << *pX << " ,Y = " << *pY << endl;
while(isAdjacent(*pX, *pY) == false )
{
walk(pX, pY);
}
s_Grid[*pY][*pX] = 1;
return;
}
另外一个需要特别说明的问题是微粒游走的边界的大小。刚开始平面上微粒很少,如果我们让新加入的微粒在全平面上游走的话,新的微粒与原来的微粒相碰的机会很少。游走的步数会非常的长,整个程序的运行时间会长到让我们难以接受。所以我这里采用了个小技巧,就是让开始时的微粒的运动范围限制在个较小的区域。随着微粒数的增多,逐步的增加微粒的活动范围。利用这个技巧程序的运行速度快了很多。
void setRange(int xRange, int yRange)
{
s_XRange = xRange;
s_YRange = yRange;
s_XLow = s_XCenter - xRange / 2;
s_YLow = s_YCenter - yRange / 2;
s_XHigh = s_XCenter + xRange / 2 - 1;
s_YHigh = s_YCenter + yRange / 2 - 1;
}
最后贴出主函数来:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int i;
int x, y;
//cerr << "#Hello world!" << endl;
srand(time(0));
//srand(0);
DLA_Init();
cerr << "stage 1" << endl;
setRange(200, 200);
for(i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
DLA_Gen(&x, &y);
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
cerr << "stage 2" << endl;
setRange(400, 400);
for(i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
DLA_Gen(&x, &y);
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
cerr << "stage 3" << endl;
setRange(600, 600);
for(i = 0; i < 5000; i++)
{
DLA_Gen(&x, &y);
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
cerr << "stage 4" << endl;
setRange(700, 700);
for(i = 0; i < 5000; i++)
{
DLA_Gen(&x, &y);
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
cerr << "stage 5" << endl;
setRange(900, 900);
for(i = 0; i < 5000; i++)
{
DLA_Gen(&x, &y);
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
cerr << "finished" << endl;
return 0;
}
将运算结果存入文本文件。然后用数据绘图软件(gnuplot、matlab等都可以)将数据画出来。下面的图形使用 gnuplot 绘制的。