中断之中断向量表IDT的初始化
中断的初始化是在哪里完成的呢?是在start_kernel()中:
512 trap_init(); 535 /* init some links before init_ISA_irqs() */ 536 early_irq_init(); 537 init_IRQ(); //最终调用native_init_IRQ,由它来完成主要工作。
中断向量表的初始化分为两个部分:
(1)对0~19号和0x80号系统保留中断向量的初始化,在trap_init中完成
(2)对其它中断向量的初始化,在init_IRQ中完成。
我们首先来看对系统保留中断向量的初始化,这部分的初始化工作实在trap_init中完成的:
void __init trap_init(void)
{
int i;
#ifdef CONFIG_EISA
void __iomem *p = early_ioremap(0x0FFFD9, 4);
if (readl(p) == 'E' + ('I'<<8) + ('S'<<16) + ('A'<<24))
EISA_bus = 1;
early_iounmap(p, 4);
#endif
set_intr_gate(0, ÷_error);
set_intr_gate_ist(2, &nmi, NMI_STACK);
/* int4 can be called from all */
set_system_intr_gate(4, &overflow);
set_intr_gate(5, &bounds);
set_intr_gate(6, &invalid_op);
set_intr_gate(7, &device_not_available);
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_32
set_task_gate(8, GDT_ENTRY_DOUBLEFAULT_TSS);
#else
set_intr_gate_ist(8, &double_fault, DOUBLEFAULT_STACK);
#endif
set_intr_gate(9, &coprocessor_segment_overrun);
set_intr_gate(10, &invalid_TSS);
set_intr_gate(11, &segment_not_present);
set_intr_gate_ist(12, &stack_segment, STACKFAULT_STACK);
set_intr_gate(13, &general_protection);
set_intr_gate(15, &spurious_interrupt_bug);
set_intr_gate(16, &coprocessor_error);
set_intr_gate(17, &alignment_check);
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_MCE
set_intr_gate_ist(18, &machine_check, MCE_STACK);
#endif
set_intr_gate(19, &simd_coprocessor_error);
/* Reserve all the builtin and the syscall vector: */
for (i = 0; i < FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR; i++)
set_bit(i, used_vectors);
#ifdef CONFIG_IA32_EMULATION
set_system_intr_gate(IA32_SYSCALL_VECTOR, ia32_syscall);
set_bit(IA32_SYSCALL_VECTOR, used_vectors);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_32
set_system_trap_gate(SYSCALL_VECTOR, &system_call);
set_bit(SYSCALL_VECTOR, used_vectors);
#endif
/*
* Should be a barrier for any external CPU state:
*/
cpu_init();
x86_init.irqs.trap_init(); //这个是什么意思呢?好像跟虚拟机有关,我们不用关注。
}
程序中首先设置中断向量表的头19个陷阱门,这些中断向量表都是CPU保留用于异常处理的。
接着,有这样的操作:
/* Reserve all the builtin and the syscall vector: */ for (i = 0; i < FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR; i++) set_bit(i, used_vectors);系统设置了一个位图used_vectors,来表示每个中断向量表的使用情况,FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR = 20,可以看到,这里是将前20(0~19)个向量表项对应的位图设置为1,表示已经被占用了。
紧接着:
set_system_trap_gate(SYSCALL_VECTOR, &system_call);初始化系统调用向量。SYS_CALL_VECTOR = 0x80。这里有一个这样的问题,为什么用的是set_system_trap_gate,而不是像2.4那样用set_system_gate呢?我们可以将系统调用看成是trap,因为它同样要陷入内核空间,可以这样理解,当陷入陷阱时,EIP指向的是下一条指令,而当故障(fault)发生时,EIP指向当前指令,当异常发生时,EIP的指向是不固定的,因此想想系统调用后EIP的变化,它必然是属于陷阱范畴的。
接下来,看这样一个操作cpu_init()
/* * cpu_init() initializes state that is per-CPU. Some data is already * initialized (naturally) in the bootstrap process, such as the GDT * and IDT. We reload them nevertheless, this function acts as a * 'CPU state barrier', nothing should get across. * A lot of state is already set up in PDA init for 64 bit */ void __cpuinit cpu_init(void) { int cpu = smp_processor_id(); struct task_struct *curr = current; struct tss_struct *t = &per_cpu(init_tss, cpu); struct thread_struct *thread = &curr->thread; if (cpumask_test_and_set_cpu(cpu, cpu_initialized_mask)) { //test a bit and return its old value;测试cpumask是否已经被设置了。 printk(KERN_WARNING "CPU#%d already initialized!\n", cpu); for (;;) local_irq_enable(); //实际上就是执行开中断指令:sti } printk(KERN_INFO "Initializing CPU#%d\n", cpu); if (cpu_has_vme || cpu_has_tsc || cpu_has_de) clear_in_cr4(X86_CR4_VME|X86_CR4_PVI|X86_CR4_TSD|X86_CR4_DE); load_idt(&idt_descr); //下文详述 switch_to_new_gdt(cpu); /* * Set up and load the per-CPU TSS and LDT */ atomic_inc(&init_mm.mm_count); curr->active_mm = &init_mm; BUG_ON(curr->mm); enter_lazy_tlb(&init_mm, curr); load_sp0(t, thread); set_tss_desc(cpu, t); load_TR_desc(); load_LDT(&init_mm.context); t->x86_tss.io_bitmap_base = offsetof(struct tss_struct, io_bitmap); #ifdef CONFIG_DOUBLEFAULT /* Set up doublefault TSS pointer in the GDT */ __set_tss_desc(cpu, GDT_ENTRY_DOUBLEFAULT_TSS, &doublefault_tss); #endif clear_all_debug_regs(); dbg_restore_debug_regs(); fpu_init(); xsave_init(); }我们来看一下load_idt()操作,这是一个宏定义:
#define load_idt(dtr) native_load_idt(dtr)在展开宏之前,先来看一下idt_descr结构:
struct desc_ptr idt_descr = { NR_VECTORS * 16 - 1, (unsigned long) idt_table }; //desc_ptr结构体如下: struct desc_ptr { unsigned short size; unsigned long address; } __attribute__((packed)) ; //idt_table如下: extern gate_desc idt_table[]; //接着看gate_desc: typedef struct desc_struct gate_desc; //好了,我们终于来到了终极目标,desc_struct: /* * FIXME: Accessing the desc_struct through its fields is more elegant, * and should be the one valid thing to do. However, a lot of open code * still touches the a and b accessors, and doing this allow us to do it * incrementally. We keep the signature as a struct, rather than an union, * so we can get rid of it transparently in the future -- glommer */ /* 8 byte segment descriptor */ struct desc_struct { union { struct { unsigned int a; unsigned int b; }; struct { u16 limit0; u16 base0; unsigned base1: 8, type: 4, s: 1, dpl: 2, p: 1; unsigned limit: 4, avl: 1, l: 1, d: 1, g: 1, base2: 8; }; }; } __attribute__((packed));这样可以看到,idt_desc实际上是以idt_table为起始地址,拥有NR_VECTOR*16-1个8个字节长的描述符,而这个描述符结构包含了任务门、中断门、陷阱门和调用门,这几种门的基本结构是相同的,只是相关的字段的设置不同而已,可以参考《情景分析》中相关内容理解。
接下来,看下面一个函数switch_new_gdt():
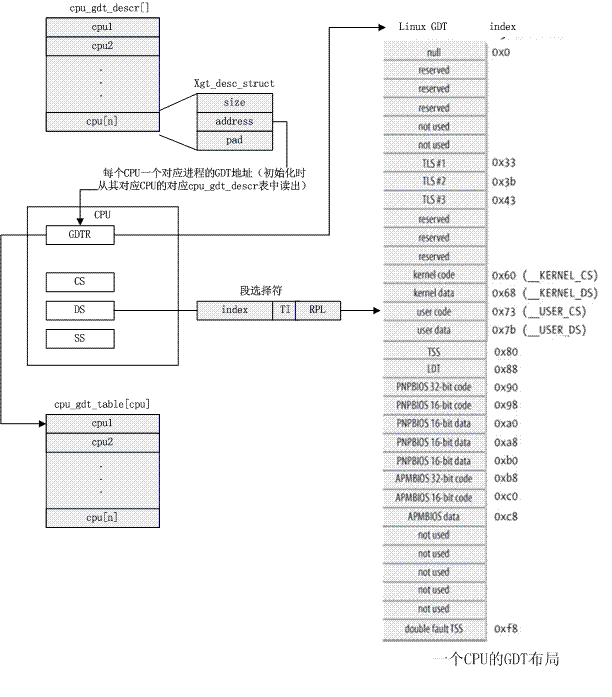
/* * Current gdt points %fs at the "master" per-cpu area: after this, * it's on the real one. */ void switch_to_new_gdt(int cpu) { struct desc_ptr gdt_descr; gdt_descr.address = (long)get_cpu_gdt_table(cpu); //指向给定cpu的gdt (有个问题,难倒每个CPU都有一个GDT么?) gdt_descr.size = GDT_SIZE - 1; //gdb_desc为32项 load_gdt(&gdt_descr); //执行lgdt指令将gdb_descr的地址加载到相应的寄存器中。 //#define load_gdt(dtr) native_load_gdt(dtr) //static inline void native_load_gdt(const struct desc_ptr *dtr) //{ // asm volatile("lgdt %0"::"m" (*dtr)); //} /* Reload the per-cpu base */ load_percpu_segment(cpu); }这样看来,应该是每个CPU对应一个GDT的。
我们好像忘了很重要的东西:
(1)set_intr_gate
/* * This needs to use 'idt_table' rather than 'idt', and * thus use the _nonmapped_ version of the IDT, as the * Pentium F0 0F bugfix can have resulted in the mapped * IDT being write-protected. */ static inline void set_intr_gate(unsigned int n, void *addr) { BUG_ON((unsigned)n > 0xFF); _set_gate(n, GATE_INTERRUPT, addr, 0, 0, __KERNEL_CS); //设置中断门 }
(2)set_system_intr_gate/* * This routine sets up an interrupt gate at directory privilege level 3. */ static inline void set_system_intr_gate(unsigned int n, void *addr) { BUG_ON((unsigned)n > 0xFF); _set_gate(n, GATE_INTERRUPT, addr, 0x3, 0, __KERNEL_CS); //设置中断门 }(3)set_task_gate
static inline void set_task_gate(unsigned int n, unsigned int gdt_entry) { BUG_ON((unsigned)n > 0xFF); _set_gate(n, GATE_TASK, (void *)0, 0, 0, (gdt_entry<<3)); //设置任务门 }
(4)set_system_trap_gate
static inline void set_system_trap_gate(unsigned int n, void *addr) { BUG_ON((unsigned)n > 0xFF); _set_gate(n, GATE_TRAP, addr, 0x3, 0, __KERNEL_CS); //设置陷阱门 }
我们观察一下这几个函数,都是调用_set_gate,区别在于第二个和第四个参数。第二个参数对应于中断门或陷阱门格式中的D标志位加上类型位段;第四个参数对应于DPL。下面,我们来看一下_set_gate函数:
static inline void _set_gate(int gate, unsigned type, void *addr, unsigned dpl, unsigned ist, unsigned seg) { gate_desc s; pack_gate(&s, type, (unsigned long)addr, dpl, ist, seg); //根据门的类型、入口地址等信息,组装一个64位的门描述符,保存在a,b中 /* * does not need to be atomic because it is only done once at * setup time */ write_idt_entry(idt_table, gate, &s); //将a,b写入idt。 }
其第一个操作pack_gate():static inline void pack_gate(gate_desc *gate, unsigned char type, unsigned long base, unsigned dpl, unsigned flags, unsigned short seg) { gate->a = (seg << 16) | (base & 0xffff); //设置门的低32位 gate->b = (base & 0xffff0000) | (((0x80 | type | (dpl << 5)) & 0xff) << 8); //设置门的高32位 }而wirte_idt_entry():#define write_idt_entry(dt, entry, g) native_write_idt_entry(dt, entry, g)
static inline void native_write_idt_entry(gate_desc *idt, int entry, const gate_desc *gate) { memcpy(&idt[entry], gate, sizeof(*gate)); }
以上我们在trap_init()中设置了一些为CPU保留专用的IDT表项以及系统调用所用的陷阱门。
下面,就进入init_IRQ()设置大量用于外设的通用中断门了:
void __init init_IRQ(void)
{
int i;
/*
* We probably need a better place for this, but it works for
* now ...
*/
x86_add_irq_domains();
/*
* On cpu 0, Assign IRQ0_VECTOR..IRQ15_VECTOR's to IRQ 0..15.
* If these IRQ's are handled by legacy interrupt-controllers like PIC,
* then this configuration will likely be static after the boot. If
* these IRQ's are handled by more mordern controllers like IO-APIC,
* then this vector space can be freed and re-used dynamically as the
* irq's migrate etc.
*/
for (i = 0; i < legacy_pic->nr_legacy_irqs; i++) //对于单CPU结构,
per_cpu(vector_irq, 0)[IRQ0_VECTOR + i] = i;
x86_init.irqs.intr_init();
}
我们来看这个函数的最后一个操作:
首先,我们得知道x86_init.irqs.intr_init是什么东西。
/* * The platform setup functions are preset with the default functions * for standard PC hardware. */ struct x86_init_ops x86_init __initdata = { .resources = { .probe_roms = probe_roms, .reserve_resources = reserve_standard_io_resources, .memory_setup = default_machine_specific_memory_setup, }, .mpparse = { .mpc_record = x86_init_uint_noop, .setup_ioapic_ids = x86_init_noop, .mpc_apic_id = default_mpc_apic_id, .smp_read_mpc_oem = default_smp_read_mpc_oem, .mpc_oem_bus_info = default_mpc_oem_bus_info, .find_smp_config = default_find_smp_config, .get_smp_config = default_get_smp_config, }, .irqs = { .pre_vector_init = init_ISA_irqs, .intr_init = native_init_IRQ, .trap_init = x86_init_noop, }, 。。。。。。。 。。。。。。。 };原来在init_IRQ的最后一行调用的是native_init_IRQ函数!
void __init native_init_IRQ(void) { int i; /* Execute any quirks before the call gates are initialised: */ x86_init.irqs.pre_vector_init(); //调用 init_ISA_irqs ,我们将在“中断队列初始化”的博文中详述 apic_intr_init(); //不关心 /* * Cover the whole vector space, no vector can escape * us. (some of these will be overridden and become * 'special' SMP interrupts) */ for (i = FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR; i < NR_VECTORS; i++) { //设置20~255号中断 /* IA32_SYSCALL_VECTOR could be used in trap_init already. */ if (!test_bit(i, used_vectors)) //要除去0x80中断 set_intr_gate(i, interrupt[i-FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR]); } if (!acpi_ioapic && !of_ioapic) setup_irq(2, &irq2); #ifdef CONFIG_X86_32 /* * External FPU? Set up irq13 if so, for * original braindamaged IBM FERR coupling. */ if (boot_cpu_data.hard_math && !cpu_has_fpu) setup_irq(FPU_IRQ, &fpu_irq); irq_ctx_init(smp_processor_id()); #endif }
现在,我们需要看一下好好看一下interrupt数组,它保存的是每个中断服务程序的入口地址,它的定义是在entry_32.S中,一下代码的解释参考
http://blog.csdn.net/jinhongzhou/article/details/6015551:
.section .init.rodata,"a" //定义一个段,.init.rodata表示该段可以被读写操作,"a"表示需要为该段分配内存 ENTRY(interrupt) //定义数据段的入口为interrupt .text //是告诉连接器,这部分数据是程序代码 .p2align 5 //advances the location counter until it a multiple of 32. If the location counter is already a multiple of 32, no change is needed. //按32字节对齐 ///.p2align指定下一行代码的对齐方式,第1参数表示按2的多少次幂字节对齐,第2参数表示对齐是跨越的位置用什么数据来填充,第3字节表示最多允许跨越多少字节。 .p2align CONFIG_X86_L1_CACHE_SHIFT //如果上一行.p2align 5没有执行,那么执行这一条:按2的CONFIG_X86_L1_CACHE_SHIFT次幂的字节对齐,其中CONFIG_X86_L1_CACHE_SHIFT是在内核配置中设定的 ENTRY(irq_entries_start) //代码段的入口定义为irq_entries_start RING0_INT_FRAME //宏展开:.macro RING0_INT_FRAME //# can't unwind into user space anyway CFI_STARTPROC simple #define CFI_STARTPROC .cfi_startproc //用在每个函数的开始,用于初始化一些内部数据结构 CFI_SIGNAL_FRAME //#define CFI_SIGNAL_FRAME .cfi_signal_frame;作用和上面一句类似 CFI_DEF_CFA esp, 3*4 #define CFI_DEF_CFA .cfi_def_cfa //定义计算CFA的规则 /*CFI_OFFSET cs, -2*4;*/ CFI_OFFSET eip, -3*4 //#define CFI_OFFSET .cfi_offset //xx reg ,offset reg中的值保存在offset中,offset是CFA的 .endm vector=FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR //#define FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR 0x20 在irq_verctors.h中,定义了0~31号内部中断 .rept (NR_VECTORS-FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR+6)/7 //.rept表示循环,#define NR_VECTORS 256,为256-32+6=230;230/7=32 .balign 32 //按32字节对齐 .rept 7 //加上前面的那个rept,则需要循环32*7=224次,这有点类似于两个for循环,在每次进行内循环时都要进行32字节的对齐操作 .if vector < NR_VECTORS //vector=0x20;NR_VECCTORS=256; .if vector <> FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET -4 //#define CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET .cfi_adjust_cfa_offset //xx offset 修改计算CFA的规则,修改前面一个offset。达到按4字节对齐 .endif 1: pushl $(~vector+0x80) /* Note: always in signed byte range */ ???? CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 //4字节对齐 .if ((vector-FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR)%7) <> 6 //当vector=41,48 等等时,if为假,则不jmp到标号2执行,而这样的情况总共有32次:我不知道为什么?? jmp 2f //数字定义的标号为临时标号,可以任意重复定义,例如:"2f"代表正向第一次出现的标号"2:",3b代表反向第一次出现的标号"3:" .endif .previous //.previous使汇编器返回到该自定义段之前的段进行汇编,则回到上面的数据段 .long 1b //在数据段中执行标号1的操作 .text //回到代码段 vector=vector+1 //vector增加1 .endif .endr 2: jmp common_interrupt .endr //结束224次循环 END(irq_entries_start) //结束代码段 .previous //返回数据段,结束数据段的interrupt END(interrupt) .previous //返回定义数据段之前定义的那个段
如果你没有兴趣仔细研读这段代码,那么记着下面的解释就行了:数组中每个元素的初始值是标号1的地址。因此访问数组中的元素时,都会跳到标号1处,执行相应的指令。
也就是,在除了0~19号和0x80号中断外,其余的所有中断在进入其自己的中断服务程序之前,必须是先条转执行common_interrupt的,而在“中断队列初始化”的博文中,我将详细讲述有关common_interrupt的知识。
现在,我们已经把中断向量表IDT初始化完毕了。