在Linux下对TCP/IP协议栈的分析的代码验证
在Linux下对TCP/IP协议栈的分析的代码验证
1. Linux 环境下验证下列程序。
/* portscan.c 此为端口扫描程序, 需要指定所要搜索的 IP 地址范围和一个用以
记录扫描结果的日志文件 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/signal.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define N 15
char server[20];
int port[N] ={
20,21,23,25,80,81,88,8083,8080,8001,8888,3128,3124,3000,1080}; /*
欲搜的端口号 */
int status=-1;
char serverName[20];
u_char p1,p2,p3,p4;
int sockfd=-1;
struct timeval timeout={2,0};
fd_set mask;
FILE *f=NULL;
int err;
int errlen;
u_long startIP,endIP,k;
void terminate(int sig) /* 异常中止处理子程程序 */
{
p1=(u_char)( (k>>24) & 0xFF); p2=(u_char)( (k>>16) & 0xFF);
p3=(u_char)( (k>>8 ) & 0xFF);
p4=(u_char)( k & 0xFF);
fprintf(f,"%d.%d.%d.%d killed.\n",p1,p2,p3,p4);
fclose(f);
if(sockfd>0) close(sockfd);
exit(0);
}
void findProxy(u_long addr)
{
int i;
struct sockaddr_in host;
/*若连上了主机,则看其所有有可能提供proxy服务的端口 */
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
host.sin_family=AF_INET;
host.sin_addr.s_addr=htonl(addr);
host.sin_port=htons(port[i]);
if ( (sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0))<0 )
{
fprintf(f," Error open socket\n");
exit(-1);
}
status=connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)& host,sizeof(host));
timeout.tv_sec=1;
timeout.tv_usec=0; /* 设置超时限制 */
FD_ZERO( & mask);
FD_SET(sockfd,& mask);
status=select(sockfd+1,(fd_set *)0,& mask, (fd_set *)0,& timeout);
switch(status)
{
case -1:
fprintf(f,"select error\n");
fclose(f);
close(sockfd);
exit(-1);
case 0: /* 如果连接超时 */
close(sockfd);
return;
default: /* 如果连接成功 */
if( FD_ISSET(sockfd,& mask) )
{
err=1;
errlen=1;
getsockopt(sockfd,SOL_SOCKET,SO_ERROR,(char*)&err,&errlen);
if(err==0)
fprintf(f,"%s\t%d\n",serverName,port[i]);
}
}
close(sockfd);
fflush(f);
}
}
main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int i;
if(argc!=4)
{
printf("Usage: %s startIP endIP logFile\n",argv[0]);
exit(-1);
}
startIP=ntohl(inet_addr(argv[1])); /* 搜索的IP范围 */
endIP=ntohl(inet_addr(argv[2]));
if(startIP>endIP)
{
k=startIP;
startIP=endIP;
endIP=k;
}
f=fopen(argv[3],"a"); /* 打开日志文件 */
if(f==NULL)
{
printf("error open log file: %s\n",argv[3]);
exit(-1);
}
fprintf(f,"%s--------->%s\n",argv[1],argv[2]);
fflush(f);
printf("Searching proxy...\n");
printf("%s----------->%s\n",argv[1],argv[2]);
printf("\tport:\n");
for( i=0;i<N;i++)
{
printf("\t%d ",port[i]);
switch(port[i])
{
case 21:
printf("(ftp)\n");
break;
case 23:
printf("(telnet)\n");
break;
default:
printf("\n");
}
}
signal(SIGTERM,terminate); /* 设置异常中止处理 */
switch(fork())
{
case 0: /* 如果是子进程则继续执行 */
break;
case -1: /* 出错 */
printf("fork() error\n");
exit(-1);
default: /* 如果是父进程则结束该进程 */
fclose(f);
exit(0);
}
setpgid(0, getpgrp());
i=open("/dev/tty",O_RDWR); /* 切断与控制台的联系 */
if(i>=0)
{
ioctl(i,TIOCNOTTY,0);
close(i);
}
else {
fprintf(f,"TTY eacape error\n");
fflush(f);
}
for(k=startIP;k<=endIP;k++)
{
if( (k % 256)==0)
continue; /* localhost */
if( (k % 256)==255)
continue; /* broadcast */
p1=(u_char)( (k>>24) & 0xFF);
p2=(u_char)( (k>>16) & 0xFF);
p3=(u_char)( (k>>8 ) & 0xFF);
p4=(u_char)( k & 0xFF);
sprintf(serverName,"%d.%d.%d.%d",p1,p2,p3,p4);
findProxy(k);
}
fprintf(f,"All done\n");
fclose(f);
}
运行结果:
2、sniffer 软件的使用
运行结果:
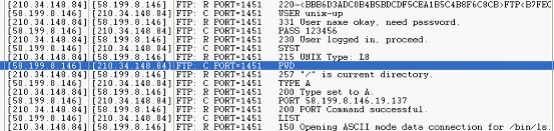
//初始化ftp连接时截获的信息
//连接时进行的三次握手
//断开时进行的四次握手