广告牌技术教程:球体广告牌
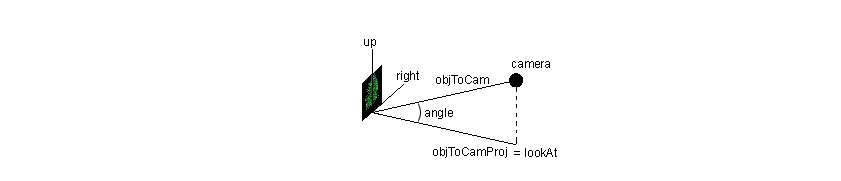
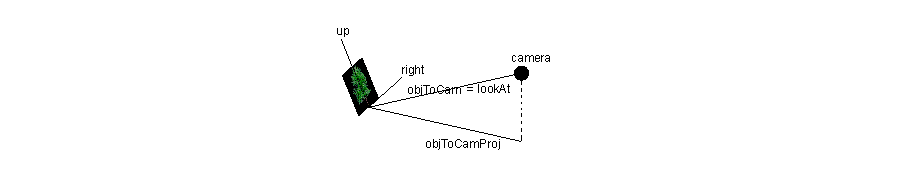
The spherical version is a simple extension to the cylindrical case. After the object is rotated using the cylindrical approach, all that is left to do is to tilt the object until it truly faces the camera.
球体版本的广告牌是圆柱体广告牌的一个简单扩展。在使用圆柱广告牌技术将物体旋转之后,所剩下的工作就是使物体倾斜以达到真正面对照相机的效果。
The axis of rotation is the right vector. As for the angle, a cosine can be obtained by the inner product between objToCamProj and objToCam.
旋转轴是右向量。至于这个角度嘛,可以用objTocamProj向量和objToCam向量的内积来求出角度的cosine值。
As in the previous billboards a function can be defined to setup the billboard. The code is as follows:
正如先前的广告牌那样,可以定义一个函数来生成广告牌。代码如下:
void billboardSphericalBegin(float camX, float camY, float camZ,float objPosX, float objPosY, float objPosZ) {
float lookAt[3],objToCamProj[3], objToCam[3], upAux[3];
float modelview[16],angleCosine;
glPushMatrix();
// objToCamProj is the vector in world coordinates from the
// local origin to the camera projected in the XZ plane
objToCamProj[0] = camX - objPosX ;
objToCamProj[1] = 0;
objToCamProj[2] = camZ - objPosZ ;
// This is the original lookAt vector for the object
// in world coordinates
lookAt[0] = 0;
lookAt[1] = 0;
lookAt[2] = 1;
// normalize both vectors to get the cosine directly afterwards
mathsNormalize(objToCamProj);
// easy fix to determine wether the angle is negative or positive
// for positive angles upAux will be a vector pointing in the
// positive y direction, otherwise upAux will point downwards
// effectively reversing the rotation.
mathsCrossProduct(upAux,lookAt,objToCamProj);
// compute the angle
angleCosine = mathsInnerProduct(lookAt,objToCamProj);
// perform the rotation. The if statement is used for stability reasons
// if the lookAt and objToCamProj vectors are too close together then
// |angleCosine| could be bigger than 1 due to lack of precision
if ((angleCosine < 0.99990) && (angleCosine > -0.9999))
glRotatef(acos(angleCosine)*180/3.14,upAux[0], upAux[1], upAux[2]);
// so far it is just like the cylindrical billboard. The code for the
// second rotation comes now
// The second part tilts the object so that it faces the camera
// objToCam is the vector in world coordinates from
// the local origin to the camera
objToCam[0] = camX - objPosX;
objToCam[1] = camY - objPosY;
objToCam[2] = camZ - objPosZ;
// Normalize to get the cosine afterwards
mathsNormalize(objToCam);
// Compute the angle between objToCamProj and objToCam,
//i.e. compute the required angle for the lookup vector
angleCosine = mathsInnerProduct(objToCamProj,objToCam);
// Tilt the object. The test is done to prevent instability
// when objToCam and objToCamProj have a very small
// angle between them
if ((angleCosine < 0.99990) && (angleCosine > -0.9999))
if (objToCam[1] < 0)
glRotatef(acos(angleCosine)*180/3.14,1,0,0);
else
glRotatef(acos(angleCosine)*180/3.14,-1,0,0);
}
The function billboardEnd() should be called after rendering the object as shown in the following example.
函数billboardEnd()应该在渲染完物体后被调用,正如我们再先前的那个例子中做的。
billboardCylindricalBegin(cx,cy,cz,ox,oy,oz);
drawObject();
billboardEnd();