[置顶] 二维中的OBB相交测试
1. 背景知识
OBB全称oriented bounding box,比AABB(axis-aligned bounding box)多了一个方向性。
求交核心思想:向量点积的投影意义,unitX为(1,0)单位向量, A.dot( unitX ) 结果值为为A点的x分量,表示意义是A点在x轴上的投影。
1)一维求交
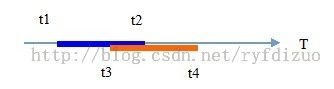
如图1,线段[t1, t2]和线段[t3, t4]相交 当且仅当 两个线段在T轴上是投影区间相交,即
t3 < t4 && t1 < t2 && !(t3 >= t2 || t1 >= t4)2)二维AABB相交 如图2,蓝色OBB在X轴投影区间为[x1, x3],在Y轴投影区间为[y1, y3];橙色矩形在X轴投影为[x2, x4],在Y轴投影区间为[y2, y4]。二维的OBB求交通过投影,转化为两个一维的求交运算。 蓝色、红色矩形相交当且仅当它们在X、Y轴上的投影区间同时相交。即
!(x2 >= x3 || x1 >= x4) && !(y2 >= y3 || y1 >= y4)3)二维OBB求交
如图3,蓝色、橙色为任意朝向包围矩形。我们选橙色矩形相邻两条正交边为投影轴S和T轴,且橙色矩阵在S轴上投影区间为[s1, s2],在T轴上投影区间为[t1, t2];蓝色矩形在S轴投影区间为[s3, s4],在T轴上投影为[t3, t4]。与AABB求交思路类似,OBB橙色矩形和蓝色矩形相交则一定得出他们在坐标系S-T轴上的投影区间分别相交,但不是充分必要件:
左图中,首先将蓝色、橙色矩形分别投影在橙色矩阵确定的S、T轴上,投影区间都相交,但是目测两个矩形其实并没有相交;再次将蓝色、橙色矩形分别投影到在蓝色矩形确定的S、T轴上,结果二者在S轴上的投影区间并不相交,从而得出蓝色、橙色矩形其实并不相交。
因此,OBB相交测试中需要投影到橙色的坐标系上做投影测试,如果通过则投影到蓝色矩形坐标系上做测试,只有两次都相交才可以。代码实际执行时,第一次相交测试已经能过滤至少50%的case,只有剩余的50%再次执行第二次相交测试。
2. 代码
google obb求交,第一个资料就是flipcode的教程:http://www.flipcode.com/archives/2D_OBB_Intersection.shtml
我实际测试发现flip code上的obb代码并不能正确运行。
下面是我修改后的程序: 2dobb.h
class Vector2
{
public:
typedef float data_type;
Vector2() {
m_Data[0] = m_Data[1] = 0.0f;
}
Vector2(const Vector2& other) {
m_Data[0] = other.m_Data[0];
m_Data[1] = other.m_Data[1];
}
Vector2(data_type x, data_type y) {
m_Data[0] = x;
m_Data[1] = y;
}
double dot(const Vector2& other) const {
return other.m_Data[0] * m_Data[0] + other.m_Data[1] * m_Data[1];
}
double squaredLength() const {
return sqrtf(m_Data[0]*m_Data[0] + m_Data[1]*m_Data[1]);
}
Vector2& operator/(data_type factor) {
m_Data[0] /= factor;
m_Data[1] /= factor;
return *this;
}
Vector2& operator/=(data_type factor) {
m_Data[0] /= factor;
m_Data[1] /= factor;
return *this;
}
Vector2& operator*(data_type factor) {
m_Data[0] *= factor;
m_Data[1] *= factor;
return *this;
}
Vector2& operator*=(data_type factor) {
m_Data[0] *= factor;
m_Data[1] *= factor;
return *this;
}
Vector2& operator+=(const Vector2& other) {
m_Data[0] += other.m_Data[0];
m_Data[1] += other.m_Data[1];
return *this;
}
Vector2& operator=(const Vector2& other) {
if (this==&other) {
return *this;
}
m_Data[0] = other.m_Data[0];
m_Data[1] = other.m_Data[1];
return *this;
}
operator const data_type* () const {
return &(m_Data[0]);
}
const data_type* data() const {
return &(m_Data[0]);
}
friend static Vector2 operator-(const Vector2& first, const Vector2& second) {
data_type x = first.m_Data[0] - second.m_Data[0];
data_type y = first.m_Data[1] - second.m_Data[1];
return Vector2(x, y);
}
friend static Vector2 operator+(const Vector2& first, const Vector2& second) {
data_type x = first.m_Data[0] + second.m_Data[0];
data_type y = first.m_Data[1] + second.m_Data[1];
return Vector2(x, y);
}
private:
data_type m_Data[2];
};
class OBB2D {
private:
/** Corners of the box, where 0 is the lower left. */
Vector2 corner[4];
/** Two edges of the box extended away from corner[0]. */
Vector2 axis[2];
/** origin[a] = corner[0].dot(axis[a]); */
double minProjLength[2]; // 原点 0点在两个轴上的投影
double maxProjLength[2]; // 2点在两个轴上的投影
/** Returns true if other overlaps one dimension of this. */
bool overlaps1Way(const OBB2D& other) const {
for (int a = 0; a < 2; ++a) {
double t = other.corner[0].dot(axis[a]);
// Find the extent of box 2 on axis a
double tMin = t;
double tMax = t;
for (int c = 1; c < 4; ++c) {
t = other.corner[c].dot(axis[a]);
if (t < tMin) {
tMin = t;
} else if (t > tMax) {
tMax = t;
}
}
// We have to subtract off the origin
// See if [tMin, tMax] intersects [minProjLength, maxProjLength]
if (tMin > maxProjLength[a] || tMax < minProjLength[a]) {
// There was no intersection along this dimension;
// the boxes cannot possibly overlap.
return false;
}
}
// There was no dimension along which there is no intersection.
// Therefore the boxes overlap.
return true;
}
/** Updates the axes after the corners move. Assumes the
corners actually form a rectangle. */
void computeAxes() {
axis[0] = corner[1] - corner[0];
axis[1] = corner[3] - corner[0];
// Make the length of each axis 1/edge length so we know any
// dot product must be less than 1 to fall within the edge.
for (int a = 0; a < 2; ++a) {
axis[a] /= axis[a].squaredLength();
minProjLength[a] = corner[0].dot(axis[a]);
maxProjLength[a] = corner[2].dot(axis[a]);
}
}
public:
OBB2D(const Vector2& center, const double w, const double h, double angle)
{
Vector2 X( cos(angle), sin(angle));
Vector2 Y(-sin(angle), cos(angle));
X *= w / 2;
Y *= h / 2;
corner[0] = center - X - Y;
corner[1] = center + X - Y;
corner[2] = center + X + Y;
corner[3] = center - X + Y;
computeAxes();
}
void updateAngle(const Vector2& center, const double w, const double h, double angle) {
Vector2 X( cos(angle), sin(angle));
Vector2 Y(-sin(angle), cos(angle));
X *= w / 2;
Y *= h / 2;
corner[0] = center - X - Y;
corner[1] = center + X - Y;
corner[2] = center + X + Y;
corner[3] = center - X + Y;
computeAxes();
}
/** For testing purposes. */
void moveTo(const Vector2& center) {
Vector2 centroid = (corner[0] + corner[1] + corner[2] + corner[3]) / 4;
Vector2 translation = center - centroid;
for (int c = 0; c < 4; ++c) {
corner[c] += translation;
}
computeAxes();
}
/** Returns true if the intersection of the boxes is non-empty. */
bool overlaps(const OBB2D& other) const {
return overlaps1Way(other) && other.overlaps1Way(*this);
}
void render() const {
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP);
for (int c = 0; c < 5; ++c) {
glVertex2fv(corner[c & 3]);
}
glEnd();
}
};
相交时候用绿色绘制线框, 不相交时候用红色绘制线框。
glut的测试框架:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <gl/glut.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "2dobb.h"
const int g_window_size = 512;
int g_window_width = g_window_size;
int g_window_height = g_window_size;
const char* g_app_string = "OBB2DDemo";
OBB2D* g_rotateObbPtr;
OBB2D* g_moveObbPtr;
float g_obbAngle = 10;
Vector2 g_moveObbCenter(50, 50);
GLenum checkForError(char *loc);
void Init(void)
{
g_rotateObbPtr = new OBB2D( Vector2(100, 100), 50,100, g_obbAngle );
g_moveObbPtr = new OBB2D( g_moveObbCenter, 50,100, 0 );
glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE);
}
void Render(void)
{
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glClearDepth(0.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
if (g_rotateObbPtr->overlaps(*g_moveObbPtr))
{
glColor3f(0, 1, 0);
} else
{
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
}
g_rotateObbPtr->render();
g_moveObbPtr->render();
glutSwapBuffers();
checkForError("swap");
}
void Reshape(int width, int height)
{
g_window_width = width; g_window_height = height;
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glOrtho(0.0f, (GLfloat) g_window_width, 0.0f,
(GLfloat) g_window_height, -1.0f, 1.0f);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
glViewport(0, 0, g_window_width, g_window_height);
}
void keyboard(unsigned char key, int x, int y) {
int state = -1;
switch (key)
{
case '1':
g_obbAngle += 0.1;
g_rotateObbPtr->updateAngle(Vector2(100, 100), 50, 100, g_obbAngle);
break;
case 'w': // move up
state = 0;
break;
case 's':
state = 1;
break;
case 'a':
state = 3;
break;
case 'd':
state = 2;
break;
case 'q':
delete g_rotateObbPtr;
delete g_moveObbPtr;
exit(0);
}
if (state >= 0) {
Vector2::data_type dx = 10 * (state < 2 ? 0 : (state==3 ? -1 : 1) );
Vector2::data_type dy = 10 * (state < 2 ? (state==0 ? 1 : -1) : 0 );
g_moveObbCenter += Vector2(dx, dy);
g_moveObbPtr->moveTo(g_moveObbCenter);
}
glutPostRedisplay();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGB|GLUT_DOUBLE|GLUT_DEPTH);
glutInitWindowSize(g_window_width, g_window_height);
glutCreateWindow(g_app_string);
// set up world space to screen mapping
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glOrtho(0.0f, (GLfloat)g_window_size, 0.0f, (GLfloat)g_window_size, -1.0f, 1.0f);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
glViewport(0, 0, g_window_size, g_window_size);
glutDisplayFunc(Render);
glutReshapeFunc(Reshape);
glutKeyboardFunc(keyboard);
Init();
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
GLenum checkForError(char *loc)
{
GLenum errCode;
const GLubyte *errString;
if ((errCode = glGetError()) != GL_NO_ERROR)
{
errString = gluErrorString(errCode);
printf("OpenGL error: %s",errString);
if (loc != NULL)
printf("(%s)",loc);
printf("\n");
}
return errCode;
}
![[置顶] 二维中的OBB相交测试_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/90fa269e063f43f2bac22624bd5af051.jpg)
![[置顶] 二维中的OBB相交测试_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/2ecb004ded704658a336b8bf660c40c8.jpg)
![[置顶] 二维中的OBB相交测试_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/79046705934b48fabf4cdb6a288d6810.jpg)
![[置顶] 二维中的OBB相交测试_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/a27f7f5947f845d68fad53c0b449ff12.jpg)
![[置顶] 二维中的OBB相交测试_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/cdac40a88dc14444b4229fdb6d7ec3a6.png)
![[置顶] 二维中的OBB相交测试_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/e8b8cce488f24ad4b55c07dbe871e142.png)