Android ActionBar+ViewPager 实现左右滑动Tab
这里用到了Support Library 中的support-v4 包,具体请参看官方文档。
工程目录结构如下:
首先看主界面Activity的布局文件 activity_main.xml
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- tools:context=".MainActivity" >
- <android.support.v4.view.ViewPager
- android:id="@+id/pager"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent" />
- </RelativeLayout>
主界面 MainActivity.java
- package com.example.tab;
- import android.app.ActionBar;
- import android.app.ActionBar.Tab;
- import android.app.ActionBar.TabListener;
- import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
- import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
- import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
- import android.support.v4.app.FragmentPagerAdapter;
- import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager;
- import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener;
- import android.view.Menu;
- import com.example.android_tabtest.R;
- import com.example.tab.fragment.CommonUIFragment;
- import com.example.tab.fragment.LaunchUIFragment;
- public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements TabListener {
- private ViewPager mViewPager;
- public static final int MAX_TAB_SIZE = 4;
- public static final String ARGUMENTS_NAME = "args";
- private TabFragmentPagerAdapter mAdapter;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- findViewById();
- initView();
- }
- private void findViewById() {
- mViewPager = (ViewPager) this.findViewById(R.id.pager);
- }
- private void initView() {
- final ActionBar mActionBar = getActionBar();
- mActionBar.setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(false);
- mActionBar.setNavigationMode(ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS);
- mAdapter = new TabFragmentPagerAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager());
- mViewPager.setAdapter(mAdapter);
- mViewPager.setOnPageChangeListener(new OnPageChangeListener() {
- @Override
- public void onPageSelected(int arg0) {
- mActionBar.setSelectedNavigationItem(arg0);
- }
- @Override
- public void onPageScrolled(int arg0, float arg1, int arg2) {
- }
- @Override
- public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int arg0) {
- }
- });
- //初始化 ActionBar
- for(int i=0;i<MAX_TAB_SIZE;i++){
- Tab tab = mActionBar.newTab();
- tab.setText(mAdapter.getPageTitle(i)).setTabListener(this);
- mActionBar.addTab(tab);
- }
- }
- public static class TabFragmentPagerAdapter extends FragmentPagerAdapter{
- public TabFragmentPagerAdapter(FragmentManager fm) {
- super(fm);
- }
- @Override
- public Fragment getItem(int arg0) {
- Fragment ft = null;
- switch (arg0) {
- case 0:
- ft = new LaunchUIFragment();
- break;
- default:
- ft = new CommonUIFragment();
- Bundle args = new Bundle();
- args.putString(ARGUMENTS_NAME, "TAB"+(arg0+1));
- ft.setArguments(args);
- break;
- }
- return ft;
- }
- @Override
- public int getCount() {
- return MAX_TAB_SIZE;
- }
- @Override
- public CharSequence getPageTitle(int position) {
- return "TAB " + (position + 1);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
- // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
- getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
- return true;
- }
- @Override
- public void onTabSelected(Tab tab, FragmentTransaction ft) {
- mViewPager.setCurrentItem(tab.getPosition());
- }
- @Override
- public void onTabUnselected(Tab tab, FragmentTransaction ft) {
- }
- @Override
- public void onTabReselected(Tab tab, FragmentTransaction ft) {
- }
- }
LaunchUIFragment.java
- package com.example.tab.fragment;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
- import android.view.LayoutInflater;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.ViewGroup;
- import com.example.android_tabtest.R;
- public class LaunchUIFragment extends Fragment {
- @Override
- public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
- Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- View rootView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_selection_launch, container, false);
- return rootView;
- }
- @Override
- public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
- }
- }
LaunchUIFragment 的布局文件 fragment_selection_launch.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical" >
- <Button android:id="@+id/bt_external"
- android:layout_width="300dp"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
- android:layout_marginBottom="16dp"
- android:text="@string/main_qq"/>
- <Button android:id="@+id/bt_internal"
- android:layout_width="300dp"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_marginBottom="16dp"
- android:text="@string/main_wx"/>
- </LinearLayout>
CommonUIFragment.java
- package com.example.tab.fragment;
- import com.example.android_tabtest.R;
- import com.example.tab.MainActivity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
- import android.view.LayoutInflater;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.ViewGroup;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- public class CommonUIFragment extends Fragment {
- @Override
- public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
- Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- View rootView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_selection_common, container, false);
- TextView tv_tabName = (TextView) rootView.findViewById(R.id.tv_tabName);
- Bundle bundle = getArguments();
- tv_tabName.setText(bundle.getString(MainActivity.ARGUMENTS_NAME, ""));
- return rootView;
- }
- @Override
- public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
- }
- }
CommonUIFragment 的布局文件 fragment_selection_common.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical" >
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/tv_tabName"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="30dp"
- android:gravity="center"
- android:textSize="20sp"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
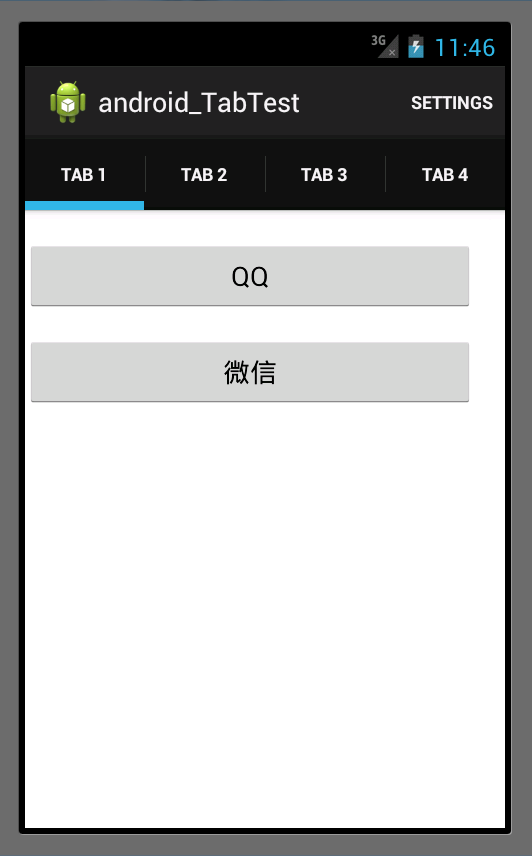
模拟器环境下运行效果图如下:
二、FragmentPagerAdapter和FragmentStatePagerAdapter的区别
官方API文档上的说明
FragmentPagerAdapter
Implementation of PagerAdapter that represents each page as a Fragment that is persistently kept in the fragment manager as long as the user can return to the page.
This version of the pager is best for use when there are a handful of typically more static fragments to be paged through, such as a set of tabs. The fragment of each page the user visits will be kept in memory, though its view hierarchy may be destroyed when not visible. This can result in using a significant amount of memory since fragment instances can hold on to an arbitrary amount of state. For larger sets of pages, consider FragmentStatePagerAdapter.
FragmentStatePagerAdapter
Implementation of PagerAdapter that uses a Fragment to manage each page. This class also handles saving and restoring of fragment's state.
This version of the pager is more useful when there area large number of pages, working more like a list view. When pages are not visible to the user, their entire fragment may be destroyed, only keeping the saved state of that fragment. This allows the pager to hold on to much less memory associated with each visited page as compared to FragmentPagerAdapter at the cost of potentially more overhead when switching between pages.
当我们的应用 有很多个页面(Fragment)的时候,推荐使用FragmentStatePagerAdapter。