poj2318 poj2398
http://poj.org/problem?id=2318
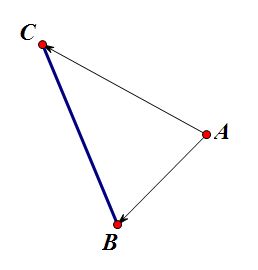
题意不难理解,如图,我的代码是以线段作为最基本单位。其实一开始时写的代码是有一个四边形的概念的,如果点在四边形内,点和左边界的点乘积再乘以点和右边界的点乘积是负的,如图:
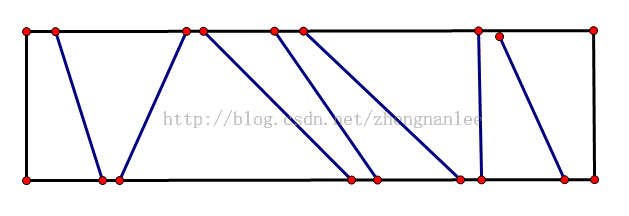
但是这样太慢,而且,原题目给出的是排好序的格子序列,如图:
所以可以二分查找,故有如下代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
struct Line
{
Point a, b;
} line[5005];
int cnt[5005];
int Multi(Point p1, Point p2, Point p0)
{
return (p1.x - p0.x) * (p2.y - p0.y) - (p2.x - p0.x) * (p1.y - p0.y);
}
void BinarySearch(Point a, int n)
{
int l, r, mid;
l = 0; r = n - 1;
while (l < r)
{
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (Multi(a, line[mid].a, line[mid].b) > 0)
{
l = mid + 1;
}
else
{
r = mid;
}
}
if (Multi(a, line[l].a, line[l].b) < 0)
{
cnt[l]++;
}
else
{
cnt[l + 1]++;
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m, x1, y1, x2, y2;
int i, t1, t2;
Point a;
while (cin >> n && n)
{
cin >> m >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> t1 >> t2;
line[i].a.x = t1;
line[i].a.y = y1;
line[i].b.x = t2;
line[i].b.y = y2;
}
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof (cnt));
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> a.x >> a.y;
BinarySearch(a, n);
}
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
printf("%d: %d\n", i, cnt[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
http://poj.org/problem?id=2398
这个是打乱顺序的,输出的时候加个统计功能就好。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Point
{
long long int x, y;
};
struct Line
{
Point a, b;
} line[5005];
long long int cnt[1005], cnt1[1010];
int Multi(Point p1, Point p2, Point p0)
{
return (p1.x - p0.x) * (p2.y - p0.y) - (p2.x - p0.x) * (p1.y - p0.y);
}
bool comp (Line a, Line b)
{
return a.a.x < b.a.x;
}
void BinarySearch(Point a, int n)
{
int l, r, mid;
l = 0; r = n - 1;
while (l < r)
{
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (Multi(a, line[mid].a, line[mid].b) > 0)
{
l = mid + 1;
}
else
{
r = mid;
}
}
if (Multi(a, line[l].a, line[l].b) < 0)
{
cnt[l]++;
}
else
{
cnt[l + 1]++;
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m, x1, y1, x2, y2;
int i, t1, t2;
Point a;
while (cin >> n && n)
{
cin >> m >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> t1 >> t2;
line[i].a.x = t1;
line[i].a.y = y1;
line[i].b.x = t2;
line[i].b.y = y2;
}
sort(line, line + n, comp);
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof (cnt));
memset(cnt1, 0, sizeof(cnt1));
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> a.x >> a.y;
BinarySearch(a, n);
}
cout << "Box" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
if (cnt[i])
{
cnt1[cnt[i]]++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if (cnt1[i])
{
printf("%d: %I64d\n", i, cnt1[i]);
}
}
}
}