ArcGIS Runtime for Android开发教程V2.0(6)基础篇---空间要素可视化
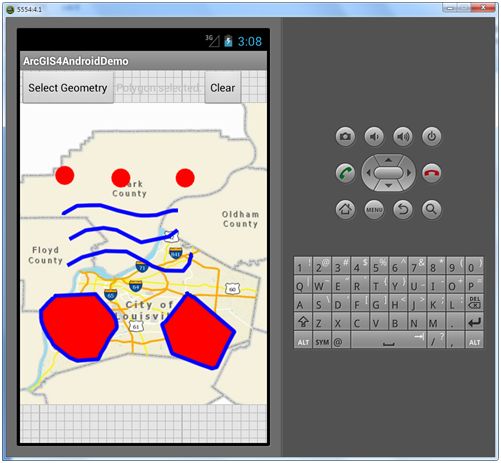
此节主要介绍要素的可视化,但我们不管以什么方式获取数据,将其正确的展现到地图中才更具意义,在ArcGIS Runtime for Android中空间要素一般我们都将添加到GraphicsLayer图层中进行展示,对于空间要素无非就那么几种:点、线、面和文字类型等等,本节将主要介绍Graphic、Geomtry和Symbole,展示效果如图:
1 Graphic
Graphic是承载空间几何要素的载体,Graphic对象可以添加到GraphicsLayer图层中进行展示,Graphic主要有四部分组成:Geomtry、symbol、Map<String,Object>和InfoTemplate。所以通过Graphic对象可以获取这四方面的数据,但当我查看Graphic的API文档时会惊讶的发现,通过这个对象我们可以获取相应的属性信息,而没有相应的方法来修改自身的属性。要想修改Graphic的属性,也不是没有办法,只不过,想通过它自身来修改是不可能了,我们可以通过其他方式来修改,使用GraphicsLayer的updateGraphic()方法可以间接的修改Graphic对象的属性,用法如下:
public boolean onSingleTap(MotionEvent e) {
if (type.length() > 1 && type.equalsIgnoreCase("POINT")) {
//创建Graphic对象,添加几何结构,样式。
Graphic graphic = new Graphic(mapView.toMapPoint(new Point(e.getX(), e
.getY())),new SimpleMarkerSymbol(Color.RED,25,STYLE.CIRCLE));
graphicsLayer.addGraphic(graphic); //添加到图层中
return true;
}
return false;
}
1.1 Geometry
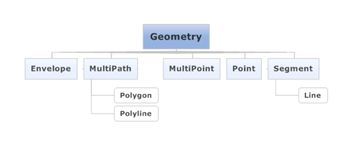
Geometry表示一个空间要素对象,它定义了一个空间位置和几何形体关系。它是所有空间对象的基类,直接子类有Envelope, MultiPath, MultiPoint, Point, Segment。Geometry的继承关系图如下:
1.2 Point
Point针对于空间要素的点对象,point即可代表二维的点也可以是三维点对象,我们可以通过它自身的方法获取x或y坐标。用法如下:
Point point = new Point();//创建点对象 Point.setX(114);//设置x坐标 Point.setY(32);//设置y坐标 Graphic gp = new Graphic(point, new SimpleMarkerSymbol(Color.RED,25,STYLE.CIRCLE)); graphicsLayer.addGraphic(gp);//添加到图层中显示
Point常用接口介绍:
| 序号 |
接口 |
说明 |
| 1 |
copyTo(Geometry dst) |
复制自身并将其附给另一个几何对象 |
| 2 |
setXY(double x,double y) |
设置点对象的x和y的坐标 |
| 3 |
equals(Object _other) |
判断两个点是否相同,当类型,属性,坐标相同时返回true |
| 4 |
getType() |
返回几何对象的类型 |
| 5 |
getX()或setX(double x) |
获取或设置x坐标值 |
| 6 |
getY()或setY(double y) |
获取或设置y坐标值 |
1.3 MultiPoint
MultiPoint表示多点对象,MultiPoint通常存储一系列的基础点,这些点按照一定的顺序存储并且每个点都可以获取它的索引位置。我们可以通过每个点的索引位置对MultiPoint对象进行正、删或改操作,用法如下:
Point point1 = new Point(114,32);//创建点对象 Point point2 = new Point(112,28);//创建点对象 MultiPoint multipoint = new MultiPoint(); multipoint.add(point1);//添加点 multipoint.add(point2);//添加点 multipoint.removePoint(1);//移除第二点
MultiPoint常用接口介绍:
| 序号 |
接口 |
说明 |
| 1 |
add(double x, double y)或add(Point point) |
添加一个点到多点对象里 |
| 2 |
insertPoint(int beforePointIndex,Point pt) |
在某个位置之前插入一个点对象 |
| 3 |
removePoint(int pointIndex) |
移除某个位置上的点 |
| 4 |
setPoint(int index, Point pointSrc) |
替换某个位置上的点 |
| 5 |
queryEnvelope(Envelope env) |
计算多点覆盖的矩形范围,env参数为计算后的结果 |
| 6 |
getType() |
返回几何对象的类型 |
1.4 MultiPath
MultiPath它是polygons 和 polylines的基类,MultiPath与MultiPoint很类似,只不过MultiPoint存储的点的数据集,而MultiPath存储的是一条条轨迹线,MultiPath为我们提供了丰富操作接口。我们可以通过这些接口来操作MultiPath对象里的任何轨迹上点。用法如下:
Point startPoint = new Point(114,28); MultiPath path = new MultiPath(); path.startPath(startPoint);//设置路径的初始位置 path.lineto(new Point(113,32));//给路径添加点
MultiPath常用接口介绍:
| 序号 |
接口 |
说明 |
| 1 |
add(MultiPath src,boolean bReversePaths) |
将src对象中的所有paths添加到自身中去,bReversePaths为true时将src中的paths反向再添加 |
| 2 |
addPath(MultiPath src, int srcPathIndex, boolean bForward) |
将src中srcPathIndex位置的path取出添加到自身中去,bForward为false时path中的点将被反向 |
| 3 |
addSegment(Segment segment,boolean bStartNewPath) |
将segment添加到自身中,bStartNewPath为true时重新创建一个path并将segment添加。 |
| 4 |
insertPath(int pathIndex, MultiPath src, int srcPathIndex, boolean bForward) |
与addPath功能很类似,多了一个添加的位置参数 |
| 5 |
insertPoint(int pathIndex, int beforePointIndex,Point pt) |
在path的beforePointIndex节点之前添加一点 |
| 6 |
getPathCount() |
统计本身paths的数量 |
| 7 |
startPath(double x,double y)或startPath(Point point) |
创建一个path并设置其起点坐标 |
| 8 |
lineTo(double x, double y)或lineTo(Point endPoint) |
在最后一个点上添加一个线的片段 |
1.5 Envelope
Envelope代表一个矩形要素,我们可以通过Envelope对象获取矩形窗口的中心点、矩形的上下四个点、宽和高等等。用法如下:
Envelope env = new Envelope(112,28,113,32);//创建矩形对象 map.setExtent(env);//设置地图显示范围 Point point= env.getCenter();//获取矩形框的中心点
Envelope常用接口介绍:
| 序号 |
接口 |
说明 |
| 1 |
setCoords(double xmin,double ymin, double xmax,double ymax) |
设置Envelope对象的最小x,最小y,最大x,最大y值 |
| 2 |
getCenterX()或getCenterY() |
获取Envelope对象的中心点的x,y值 |
| 3 |
centerAt(Point c, double w,double h) |
设置Envelope对象的中心点和宽高 |
| 4 |
getLowerLeft()、getUpperRight()、getLowerRight()、getUpperLeft() |
返回Envelope的对象的四个点的坐标点 |
| 5 |
contains(Point p) |
返回true表示p点在这个Envelope对象之内 |
| 6 |
getXMin()、getYMin()、getXMax()、getYMax()、setXMin(double x)、setXMax(double x)、setYMin(double y)和setYMax(double y) |
设置或获取Envelope对象的最大或最小x/y值 |
1.6 Polygon
Polygon是MultiPath子类,Polygon表示的是多边形或多多边形,Polygon里的所有path都是闭合的环,Polygon对象我们在日后的开发中经常会涉及到该对象,如标绘多边形或做空间查询时,Polygon对象中至少存在三个点并且不能同时在一条直线上。具体用法如下:
Polygon poly = new Polygon();//创建多边形对象 poly.startPath(new Point(0,0));//添加初始点 poly.lineto(new Point(10,0)); poly.lineto(new Point(10,10)); poly.lineto(new Point(0,0));//多边形是闭合的因此最后我们还要添加初始点的位置
Polygon常用接口介绍:
| 序号 |
接口 |
说明 |
| 1 |
calculateRingArea2D(int ringIndex) |
计算ringIndex对应的2D面积 |
| 2 |
getType() |
返回本身的对象的类型 |
| 3 |
queryEnvelope(Envelope env) |
计算line线段所占据的矩形范围,env参数为计算后的结果 |
1.7 Polyline
Polyline也是MultiPath子类,Polyline表示一条或多条线路径,Polyline跟Polygon用法基本相同,只不过Polyline的最后一个点不必跟初始点坐标相同。
Polyline常用接口介绍:
| 序号 |
接口 |
说明 |
| 1 |
addSegment(Segment segment, boolean bStartNewPath) |
为Polyline对象添加一节线段,当bStartNewPath为true时,创建一个新的path并将segment添加到上面去。 |
| 2 |
getType() |
返回本身的对象的类型 |
| 3 |
equals(Object other) |
判断对象是否相等,如果几何类型、属性、坐标都相同返回true |
1.8 Line
Line与Polyline存在一定的关系,可以说Line是Polyline的组成部分,Line表示两点之间生成的线段。用法如下:
Line line = new Line() line.setStart(new Point(113,32));//起始点 line.setEnd(new Point(114,28));//终止点 Polyline poly = new Polyline(); poly.addSegment(line,true);//添加线段到Polyline对象中
Line常用接口介绍:
| 序号 |
接口 |
说明 |
| 1 |
calculateLength2D() |
计算line对象的2D长度 |
| 2 |
getType() |
返回本身的对象的类型 |
| 3 |
equals(Object other) |
判断对象是否相等,如果几何类型、属性、坐标都相同返回true |