二叉树常见运算问题
http://blog.csdn.net/randyjiawenjie/article/details/6772145
看看思路,下面的小bug还比较多
二叉树的常见问题有如下几个,如果解决好了,就跟链表一样轻松:唯一不一样的是,二叉树是非线性结构。常见的问题如下:
二叉树的问题
1.二叉树三种周游(traversal)方式:
- 二叉树的问题
- 1.二叉树三种周游(traversal)方式:
- 2.怎样从顶部开始逐层打印二叉树结点数据
- 3.如何判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
- 4.设计一个算法,找出二叉树上任意两个节点的最近共同父结点,复杂度如果是O(n2)则不得
- 分。
- 5.如何不用递归实现二叉树的前序/后序/中序遍历?
- 6.在二叉树中找出和为某一值的所有路径
- 7.怎样编写一个程序,把一个有序整数数组放到二叉树中?
- 8.判断整数序列是不是二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果
- 9.求二叉树的镜像
- 10.一棵排序二叉树(即二叉搜索树BST),令 f=(最大值+最小值)/2,设计一个算法,找出距
- 离f值最近、大于f值的结点。复杂度如果是O(n2)则不得分。
- 11.把二叉搜索树转变成排序的双向链表
- 12.打印二叉树中的所有路径(与题目5很相似)
3.如何判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
4.设计一个算法,找出二叉树上任意两个节点的最近共同父结点,复杂度如果是O(n2)则不得分。
5.如何不用递归实现二叉树的前序/后序/中序遍历?
6.在二叉树中找出和为某一值的所有路径(注意是到叶子节点)
7.怎样编写一个程序,把一个有序整数数组放到二叉树中?
8.判断整数序列是不是二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果
9.求二叉树的镜像
10.一棵排序二叉树(即二叉搜索树BST),令 f=(最大值+最小值)/2,设计一个算法,找出距离f值最近、大于f值的结点。复杂度如果是O(n2)则不得分。
11.把二叉搜索树转变成排序的双向链表
12.打印二叉树中的所有路径(与题目6很相似)
解决思路:
1.二叉树三种周游(traversal)方式:任何一本数据结构的书都有描述,略过;
2.怎样从顶部开始逐层打印二叉树结点数据?
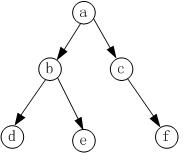
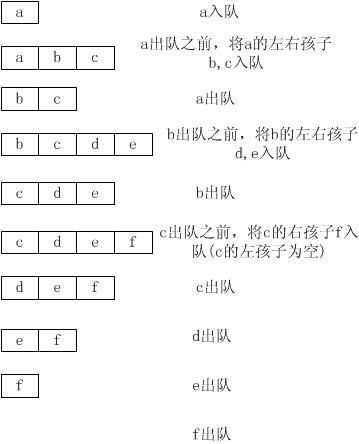
设置一个队列,然后只要队列不为空,将对首元素的左右孩子加入队列(如果左右孩子不为空),然后将队列的首元素出对即可,如下图所示:
二叉树如下图所示:
那么,整个过程如下:
自然,就输出了a,b,c,d,e,f
3.如何判断一个二叉树是否是平衡的?
太简单了,利用递归就可以了:判断根节点的左右子树深度之差是否小于等于1(这里需要用到求深度的方法),如果是,根节点就是平衡的;然后,在判断根节点的左孩子和右孩子是否是平衡的。如此继续下去,直到遇见叶子节点。一旦不是,立刻返回false;
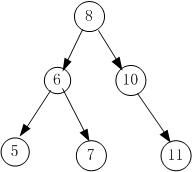
计一个算法,找出二叉树上任意两个节点的最近共同父结点,复杂度如果是O(n2)则不得分
首先找到这两个点key1和key2,并且记录下找到这两个点的路径Path1和Path2。然后,找到第一个点k满足,key1<k<key2就可以了。
如图:
假设key1 = 5,key2 = 7,那么显然,Path1{8,6,5}, Path2{8,6,7}。满足第一个key1<k<key2的k为6。故k = 6。
至于怎么求出Path1和Path2,可以看问题12。
5.如何不用递归实现二叉树的前序/后序/中序遍历?(网易面试就问到了,悲剧了,当时一下子卡住了)
看看书,基本任何一本数据结构的书都有,主要利用栈。
6.在二叉树中找出和为某一值的所有路径?
还是先解决12题目,访问二叉树到叶子节点的任意路径。这个问题解决了,自然求和看是否满足条件就可以了。
7.怎样编写一个程序,把一个有序整数数组放到二叉树中?
递归,还是利用递归:
设有int array[begin,end],首先将array[(begin + end)/2]加入二叉树,然后递归去做array[begin,(begin + end)/2 - 1]和array[(begin + end)/2 + 1, end]。注意写好函数的形式就可以了。一切都很自然。
8.判断整数序列是不是二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果?
看看吧,后续遍历是这样做的:左右根,所以访问的最有一个节点实际上就是整棵二叉树的根节点root:然后,找到第一个大于该节点值的根节点b,b就是root右子树最左边的节点(大于根节点的最小节点)。那么b前面的就是root的左子树。既然是二叉搜索树的遍历结果,那么在b和root之间的遍历结果,都应该大于b。去拿这个作为判断的条件。
9.求二叉树的镜像?
还是利用递归:只要节点不为空,交换左右子树的指针,然后在分别求左子树的镜像,再求右子树的镜像,直到节点为NULL。
10.一棵排序二叉树(即二叉搜索树BST),令 f=(最大值+最小值)/2,设计一个算法,找出距离f值最近、大于f值的结点。复杂度如果是O(n2)则不得分。
首先,在BST中,最小值就是最左边的节点,最大值就是最右边的节点。在分别求出min和max后,求出f。然后利用查找,找出一个大于f的节点就可以了。
复杂度为logN。
11.把二叉搜索树转变成排序的双向链表
12..打印二叉树中的所有路径
路径的定义就是从根节点到叶子节点的点的集合。
还是利用递归:用一个list来保存经过的节点,如果已经是叶子节点了,那么打印list的所有内容;如果不是,那么将节点加入list,然后继续递归调用该函数,只不过,入口的参数变成了该节点的左子树和右子树。
程序如下:
- 解答1:自己看书了
- 解答2:
- //问题2:怎样从顶部开始逐层打印二叉树结点数据
- void PrintAtLevel(BiTNode* root){
- vector<BiTNode*> vector;
- vector.push_back(root);
- while(!vector.empty()){
- BiTNode* tmp = vector.front();
- if(tmp->lchild != NULL)
- vector.push_back(tmp->lchild);
- if (tmp->rchild != NULL)
- vector.push_back(tmp->rchild);
- cout << tmp->data << endl;
- vector.pop_back();
- }
- }
- //问题3:如何判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
- int isBalencedTree(treeNode* root){
- if (root == NULL)
- return 0;
- int depth1 = getDepth(root->lchild);
- int depth2 = getDepth(root->rchild);
- if (depth1 == depth2 || depth1 == depth2 + 1 || depth1 == depth2 - 1)
- return 1;
- else
- return 0;
- int flag1 = isBalencedTree(root->lchild);
- int flag2 = isBalencedTree(root->rchild);
- if (flag1 && flag2)
- return 1;
- else
- return 0;
- }
- //问题4:设计一个算法,找出二叉树上任意两个节点的最近共同父结点,复杂度如果是O(n2)
- 则不得分。
- int getPublicAncestors(treeNode* root,int key1,int key2){
- treeNode* ptr = root;
- int path1[1000];
- int pathLen1 = 0;
- while (ptr != NULL){
- if (key1 == ptr->data){
- path1[pathLen1] = ptr->data;
- pathLen1 ++;
- printArray(path1,pathLen1);
- break;
- }
- else
- if (ptr->data > key1){
- path1[pathLen1] = ptr->data;
- pathLen1 ++;
- ptr = ptr->lchild;
- }
- else
- if (ptr->data < key1){
- path1[pathLen1] = ptr->data;
- pathLen1 ++;
- ptr = ptr->rchild;
- }
- }
- ptr = root;
- int path2[1000];
- int pathLen2 = 0;
- while (ptr != NULL){
- if (key2 == ptr->data){
- path2[pathLen2] = ptr->data;
- pathLen2 ++;
- printArray(path2,pathLen2);
- break;
- }
- else
- if (ptr->data > key2){
- path2[pathLen2] = ptr->data;
- pathLen2 ++;
- ptr = ptr->lchild;
- }
- else
- if (ptr->data < key2){
- path2[pathLen2] = ptr->data;
- pathLen2 ++;
- ptr = ptr->rchild;
- }
- }
- int i = pathLen1 - 1;
- //key1和key2有序,
- if (key2 < key1){
- key2 = key2^key1;
- key1 = key2^key1;
- key2 = key2^key1;
- }
- for (; i > 0; i --){
- if (key1 < path1[i] && path1[i]< key2){
- int result = path1[i];
- return result;
- }
- }
- }
- //问题6:在二叉树中找出和为某一值的所有路径
- void FindPath(treeNode* root, int path[],int pathLen,int expectedSum, int
- currentSum){
- if (root == NULL)
- return;
- currentSum += root->data;
- path[pathLen] = root->data;
- pathLen ++;
- if (currentSum == expectedSum && root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild ==
- NULL){
- printArray(path,pathLen);
- }
- if (root->lchild != NULL){
- FindPath(root->lchild,path,pathLen,expectedSum,currentSum);
- }
- if (root->rchild != NULL){
- FindPath(root-
- >rchild,path,pathLen,expectedSum,currentSum);
- }
- currentSum -= root->data;
- }
- //问题7:怎样编写一个程序,把一个有序整数数组放到二叉树中?
- void createTreeFromArray(int a[], int begin, int end, treeNode** root){
- if (begin > end)
- return;
- else{
- *root = (treeNode*) malloc(sizeof(treeNode));
- int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
- (*root)->data = a[mid];
- (*root)->rchild = NULL;
- (*root)->lchild = NULL;
- createTreeFromArray(a, begin ,mid - 1, &(*root)->lchild);
- createTreeFromArray(a, mid + 1 ,end, &(*root)->rchild);
- }
- }
- //问题8:判断整数序列是不是二叉搜索树的后//序遍历结果
- int isPostTraverse(int a[], int begin ,int end){
- if(begin >= end)
- return 1;
- else{
- int root = a[end];
- int lroot;
- int i;
- int location = begin;
- for (i = begin; i < end ; i ++){
- if(a[i] > root){
- location = i;
- lroot = a[i];
- break;
- }
- }
- for (i = location + 1; i < end; i++){
- if (a[i] < lroot){
- return 0;
- }
- }
- int flag1 = isPostTraverse(a,begin,location -1);
- int flag2 = isPostTraverse(a,location,end - 1);
- if (flag1 && flag2)
- return 1;
- else
- return 0;
- }
- }
- //问题9:求二叉树的镜像
- void changeMirror(treeNode** root){
- if ( *root == NULL)
- return;
- else{
- treeNode* temp = (*root)->lchild;
- (*root)->lchild = (*root)->rchild;
- (*root)->rchild = temp;
- changeMirror(&(*root)->lchild);
- changeMirror(&(*root)->rchild);
- }
- }
- //问题10:10.一棵排序二叉树(即二叉搜索树BST),令 f=(最大值+最小值)/2,设计一个算
- //法,找出距离f值最近、大于f值的结点。复杂度如果是O(n2)则不得分。
- int findNearMid(treeNode** root){
- treeNode* ptr = *root;
- int min, max;
- while (ptr != NULL){
- min = ptr->data;
- ptr = ptr->lchild;
- }
- printf("the min is %d\n",min);
- ptr = *root;
- while (ptr != NULL){
- max = ptr->data;
- ptr = ptr->rchild;
- }
- printf("the max is %d\n",max);
- int half = (min + max) >> 1;
- printf("half is %d\n",half);
- ptr = *root;
- while (1){
- if (ptr->data < half){
- ptr = ptr->rchild;
- }
- else
- if (ptr->data > half){
- int result = ptr->data;
- return result;
- }
- else
- {
- return (ptr->rchild)->data;
- }
- }
- }
- //问题12:打印二叉树中的所有路径(与题目5很相似)
- void printPathsRecur(treeNode* node, int path[], int pathLen) {
- if (node == NULL)
- return;
- // append this node to the path array
- path[pathLen] = node->data;
- pathLen++;
- // it's a leaf, so print the path that led to here
- if (node->lchild == NULL && node->rchild == NULL) {
- printArray(path, pathLen);
- } else {
- // otherwise try both subtrees
- printPathsRecur(node->lchild, path, pathLen);
- printPathsRecur(node->rchild, path, pathLen);
- }
- }
- void printPaths(treeNode* node) {
- int path[1000];
- printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
- }
- //用到的辅助函数:
- /**
- * 求二叉树的深度
- */
- int getDepth(tNode root) {
- if (root == NULL)
- return 0;
- else
- return getDepth(root->lchild) > getLeaf(root->rchild) ? 1 +
- getDepth(
- root->lchild) : 1 + getDepth(root->rchild);
- // {
- // int depthLchild = 1 + getDepth(root->lchild);
- // int depthRchild = 1 + getDepth(root->rchild);
- // return depthLchild > depthRchild ? depthLchild:
- depthRchild;
- // }
- }
- /**
- * 打印数组
- */
- void printArray(int ints[], int len) {
- int i;
- for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- printf("%d ", ints[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }